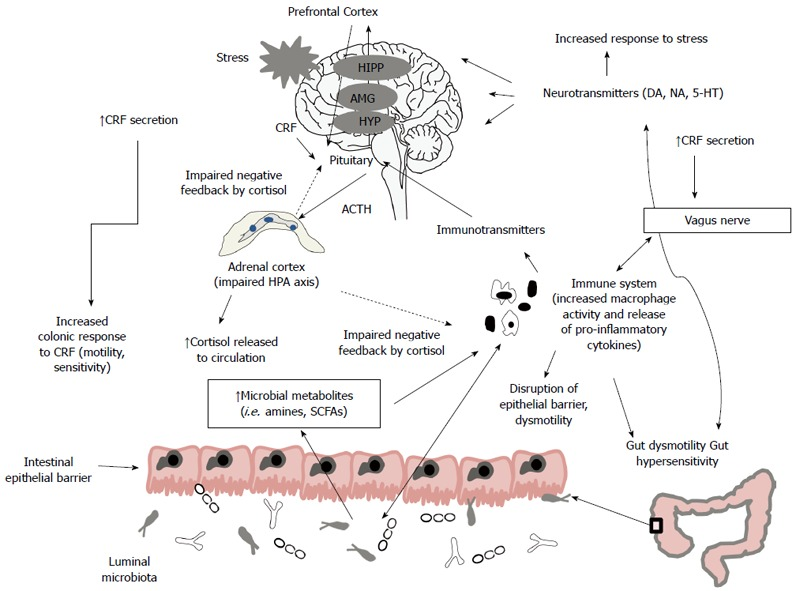
Covid-19: Do many people have pre-existing immunity?
A THREAD compiling 6 major studies on T-Cell reactivity against #SARSCoV2 that provide strong evidence that measuring only antibodies is NOT enough to understand #COVID19 immunity.
bmj.com/content/370/bm…
A THREAD compiling 6 major studies on T-Cell reactivity against #SARSCoV2 that provide strong evidence that measuring only antibodies is NOT enough to understand #COVID19 immunity.
bmj.com/content/370/bm…

1. @Alba_Grifoni and colleagues have reported SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD4+ T cells in ∼40%-60% of unexposed individuals, suggesting cross-reactive T cell recognition between circulating "common cold" coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32473127/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32473127/
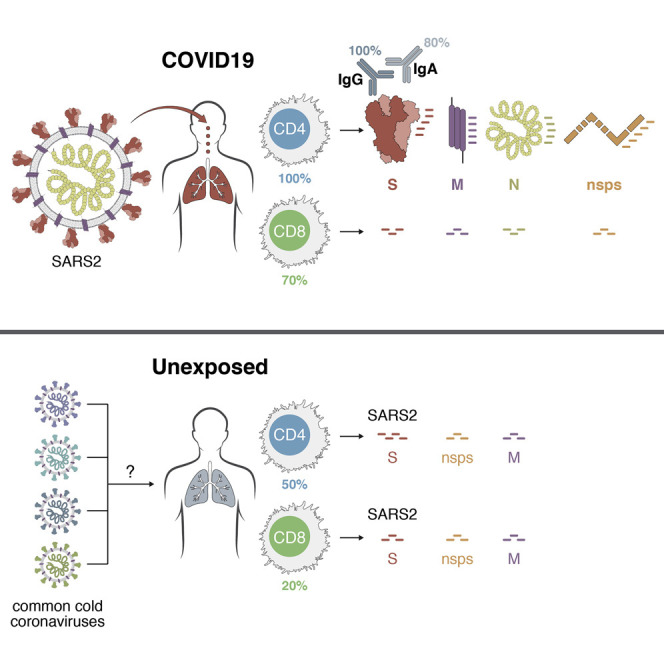
2. Using the FACS-based method, @KevinWNg and colleagues have demonstrated the presence of pre-existing humoral immunity in uninfected and unexposed humans to the new coronavirus.
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…

3. @Dani6020 & colleagues from La Jolla Institute for Immunology detected SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4+ & CD8+ T cells in 100% and 80% of COVID-19 patients, respectively. (1/2)
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

They have also detected low levels of SARS-CoV-2-reactive T-cells in 20% of the healthy controls, not previously exposed to SARS-CoV-2, and indicative of cross-reactivity due to infection with common cold coronaviruses. (2/2)
4. Study in 36 individuals with COVID 19 found CD4 and CD8 T cells that recognized multiple regions of the N protein & long-lasting memory T cells of SARS-CoV, 17 years after the outbreak of SARS in 2003 in 23 patients COVID 19 recovered patients.
nature.com/articles/s4158…

nature.com/articles/s4158…


5. Study in 32 COVID-19 patients found increased proportions of cytotoxic follicular helper (T FH ) cells and cytotoxic T helper cells (CD4-CTLs) responding to SARS-CoV-2 and reduced proportion of SARS-CoV-2 reactive regulatory T cells.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
6. @marcus_buggert and colleagues reported SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells were detectable in antibody-seronegative family members and individuals with a history of asymptomatic or mild COVID-19.
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh