Bifidobacteria-mediated immune system imprinting early in life biorxiv.org/content/10.110… 

1) Risk of asthma/allergies/autoimmunity etc associated with perturbed immune-microbe interactions early in life, but mechanisms are elusive 

2) In human newborns/infants we report a series of immune cell activation events, likely triggered by microbial interactions at mucosal surfaces 

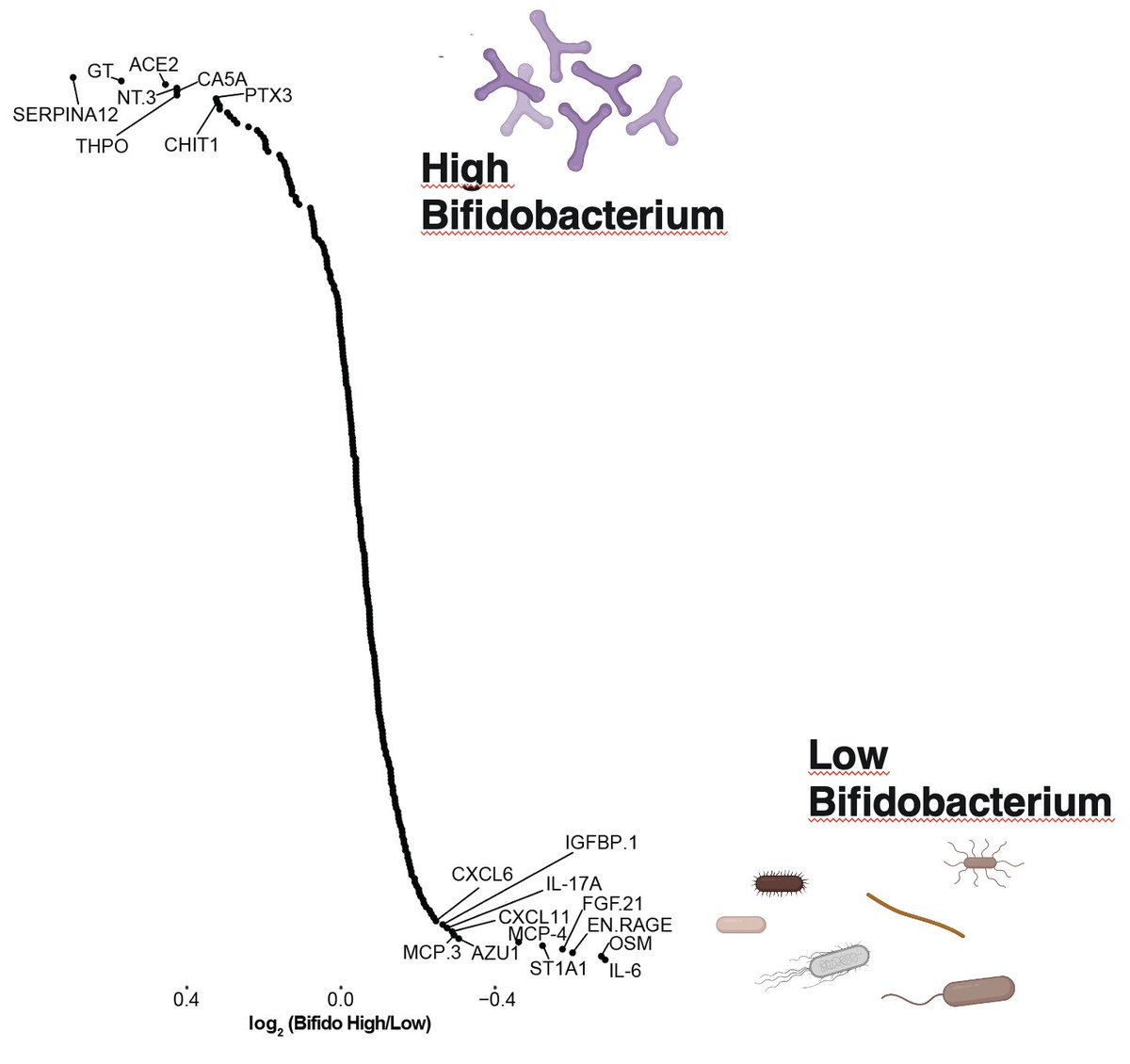
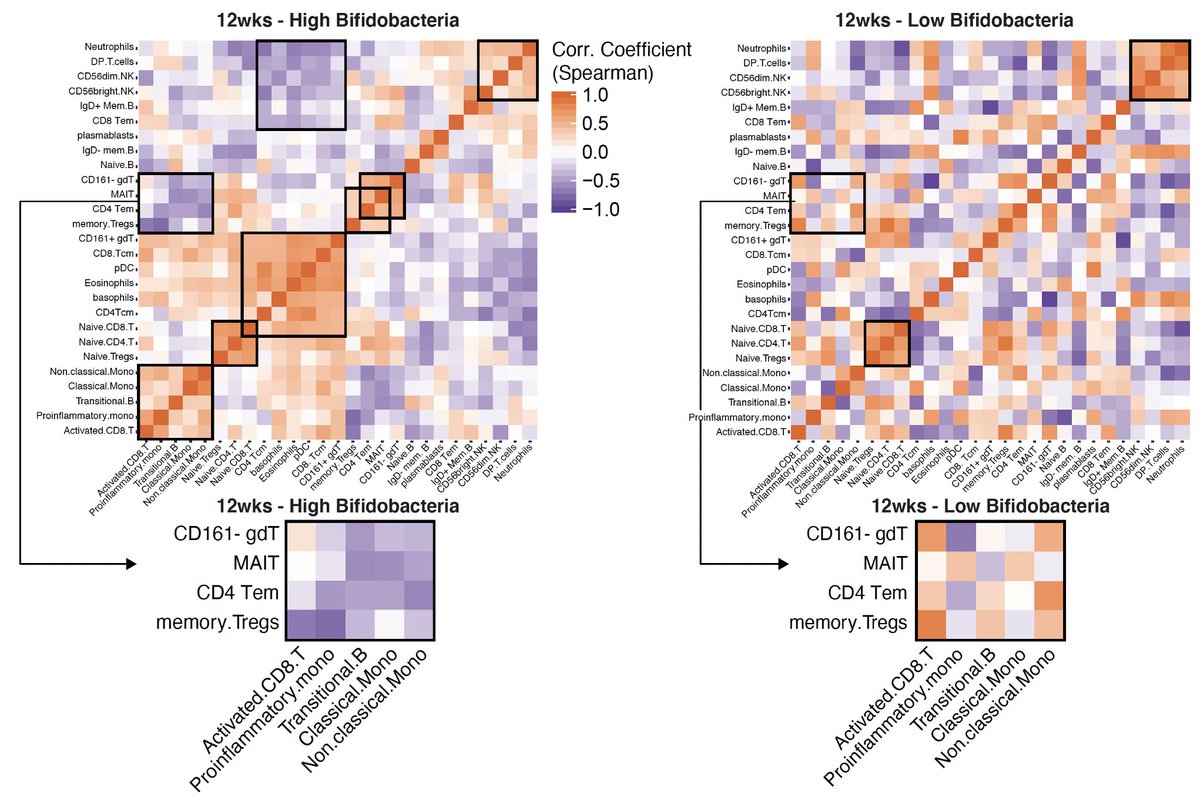
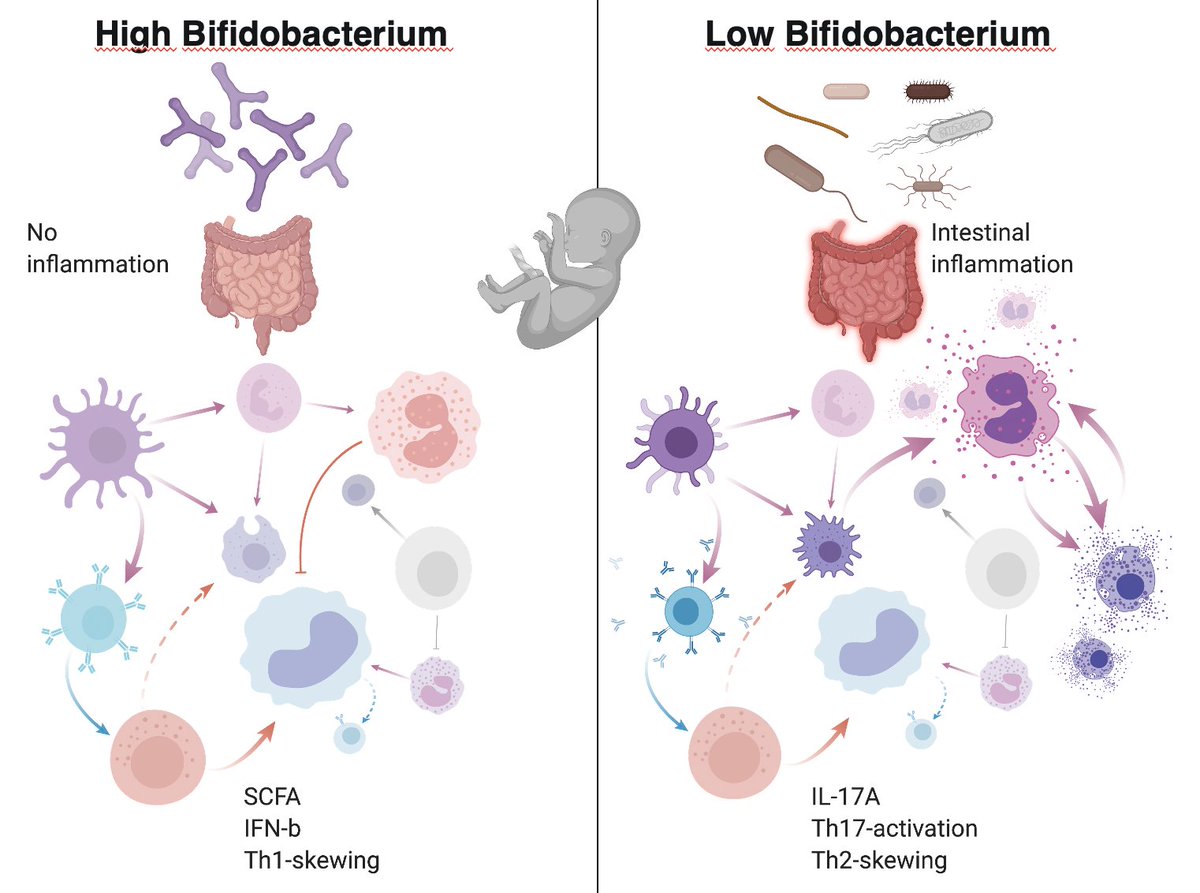
3) Gut Bifidobacteria expand in most, but not all infants, and their absence is associated with elevated markers of intestinal inflammation and a perturbed immune cell regulatory network 

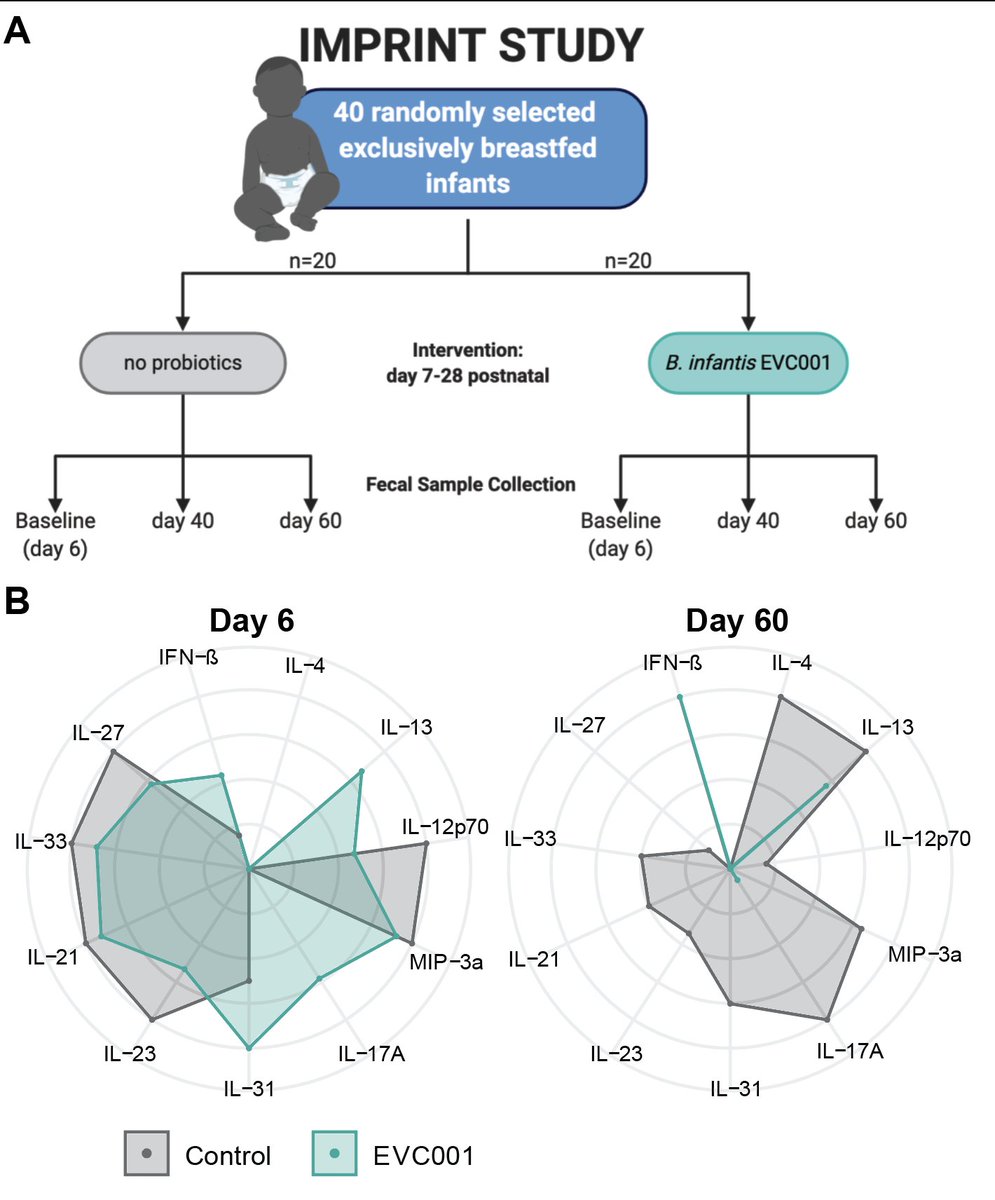
4) Together w @EvolveBio a Bifido. infantis EVC001 supplement was given to breastfed infants that silence intestinal inflammation (IL-17, -4) and induce intestinal IFNb 
5) B. infantis EVC001 metabolites skew T-cell polarization towards Th1, while control microbiome metabolites skew towards Th2 (associated with asthma/allergy etc) 
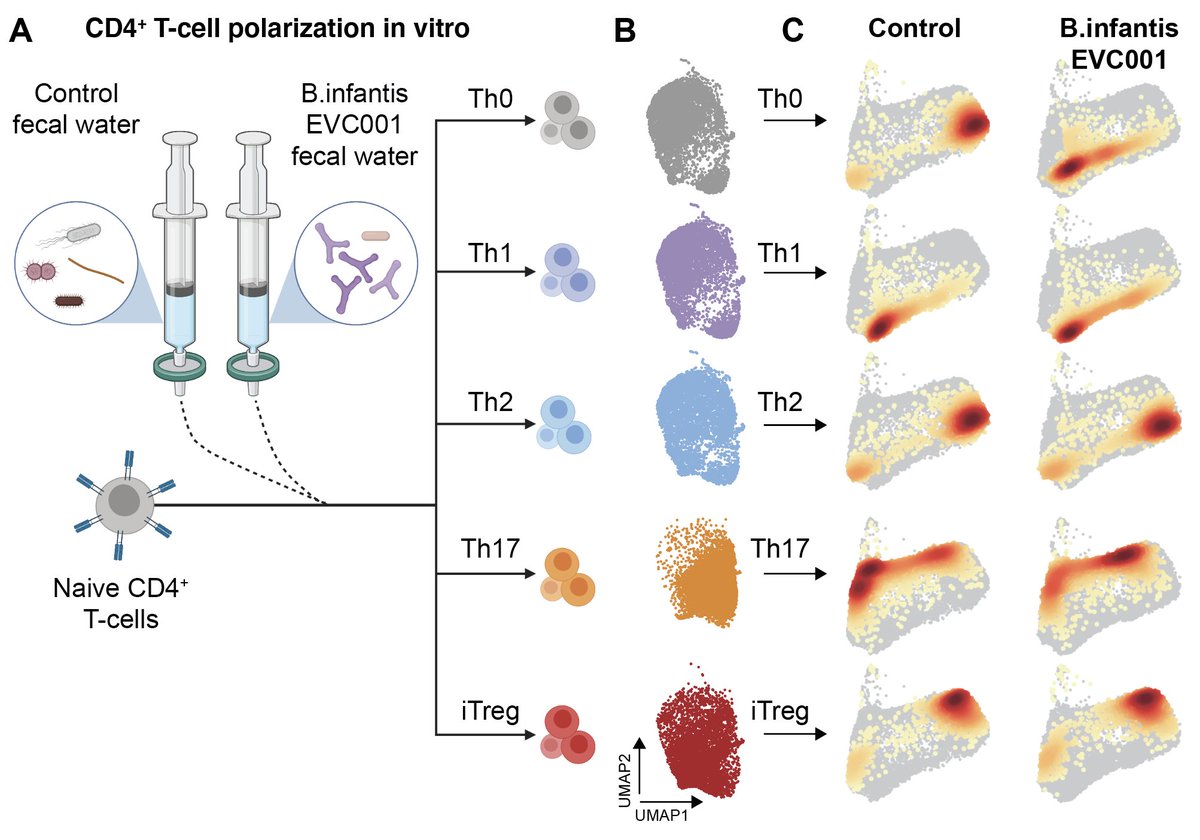
6) Great collaborative work spearheaded by @bethany_henrick @LucieSTRod @LkanthTadepally @pou_christian @EwaHenckel @akbernhard1 Axel Olin, Jun Wang, Jaromir Mikes, Yang Chen, Ziyang Tan @koitaxoumemesa @EvolveBio and many more 
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh