
Known distal UVJ stone. Has new rt flank pain. Mild hydro but what else? #POCUS #IMPOCUS #FOAMed #FOAMus #MedEd #MedTwitter @ACEP_EUS @SeeWithSound @PhilipsPOCUS @IMPOCUSFocus @medpedshosp @NephroP @jminardi21 @HeyDrNik @TomJelic @cianmcdermott @MH_EMultrasound @thepocusatlas
Area of increased echogenicity of parenchyma seen in upper pole. @Manoj_Wickram @tomkehrl @MH_EMultrasound @MetroHealth_EM @Casscln @ria_dancel @cm_lopresti @DRsonosRD 



Diagnosis: acute focal nephritis. Also called focal lobar nephronia by rads. This is on spectrum somewhere between acute pyelonephritis and renal abscess. CT shown. Contrast image (not shown) demonstrated area of poorly perfused parenchyma without a cortical rim sign. 
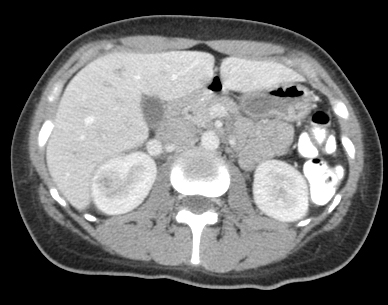
Since had know obstructing stone, the trace perinephric fluid could be a urinoma vs secondary to infection. 

Primary role of u/s in potential renal infection is to evaluate for obstruction (known in this pt) or higher grade infection such as renal abscess or perinephric abscess. In most cases of uncomplicated pyelo the ultrasound will be normal.
Other findings include urothelial thickening. Reliable finding in correct clinical context. However, can be seen with stones, stents, and cancer. Here is urothelial thickening in another patient with higher grade pyelonephritis. 

Video clip of patient with higher grade pyelonephritis with urothelial thickening.
Pyonephrosis can also be seen in renal infections. If echoes seen within the collecting system differential would be blood vs. pus vs. mass. Clinical correlation important. Pyonephrosis in patient with distal obstructing stone. 

Pyonephrosis seen layered in dilated collecting system on TRV image in patient with proximal stone which is also seen.
Renal abscess: Circular area with internal echoes and hyperechoic rim since in lower pole of left kidney.
Doppler image of renal abscess. No internal flow. Since abscesses appear as complex cystic masses could be confused with tumors. You should not see Doppler flow within a renal abscess (same as with soft tissue or other abscesses). Further imaging needed if diagnosis in doubt. 

Another patient with renal abscess.
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis-chronic process. Proteus mirabilis and E.coli common organisms. Commonly associated with staghorn calculi as seen in this patient.
Emphysematous pyelonephritis is a serious infection due to gas forming organisms where air will be identified within the parenchyma (see video) as compared to emphysematous pyelitis where air is only seen in collecting system.
Air within bladder on sag clip. This could be the result of an emphysematous cystitis or pyelitis but could also be iatrogenic due to recent Foley catheter placement or other instrumentation. Also note in this patient a high grade infection, the presence of layered echoes.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





