Grateful for the hard work of dedicated public health scientists at @PHE_uk like @kallmemeg and unsung others who work overtime to produce excellent reports on the variant of concern B1.617.2 🇮🇳
🧵analysis of vax effectiveness, and why interpretation of reduced VE limited.
1/
🧵analysis of vax effectiveness, and why interpretation of reduced VE limited.
1/
PHE did a 'test negative case control study' w/ logistic regression as I outlined yday.
From test and vax databases they retrospectively created a control cohort of 99k who tested negative and compared to 6.4k test positive for B117 & 1k for B1.617.2
2/
From test and vax databases they retrospectively created a control cohort of 99k who tested negative and compared to 6.4k test positive for B117 & 1k for B1.617.2
2/
https://twitter.com/DevanSinha/status/1396060081511444495
PHE found a statistically significant dip in symptomatic protection after 1 vax dose.
51% ➡️ 33% against B1.617.2 variant (yellow).
For both Pfizer and Ox/AZ (21 days after 1st dose).
No statistically significant change after 2 vax doses (14 days after 2nd dose).
3/
51% ➡️ 33% against B1.617.2 variant (yellow).
For both Pfizer and Ox/AZ (21 days after 1st dose).
No statistically significant change after 2 vax doses (14 days after 2nd dose).
3/

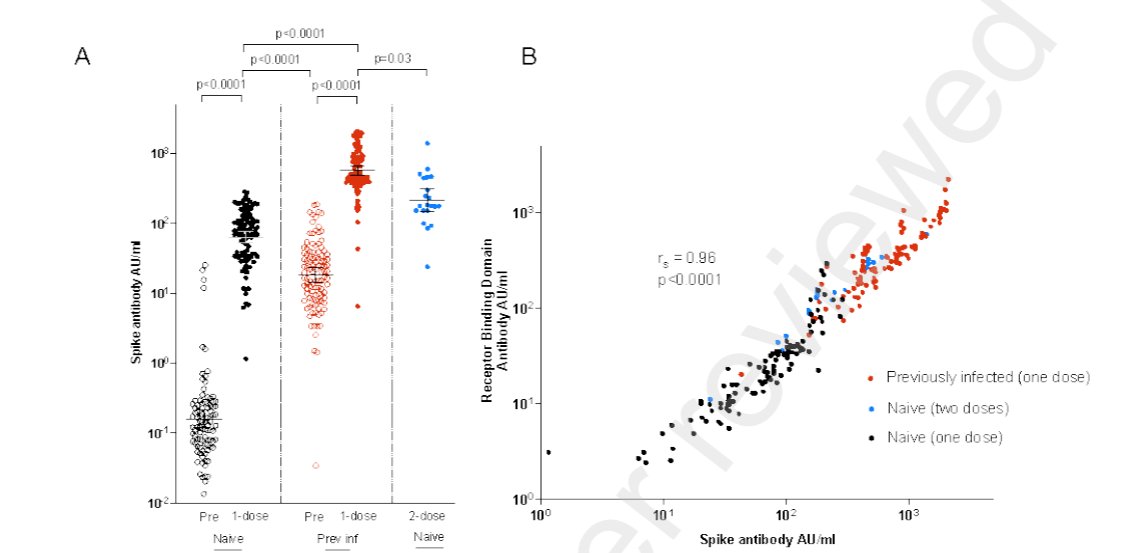
This is expected from first principles: symptomatic protection is highly correlated to antibody (Ab) neutralisation level.
Mutations that reduce neutralisation will have greater efficacy impact in the linear response part of the curve, where Ab lower - like after 1 dose.
4/
Mutations that reduce neutralisation will have greater efficacy impact in the linear response part of the curve, where Ab lower - like after 1 dose.
4/

The mechanism for variants to 'evade' antibody immunity via mutations in spike protein is described here 👇
(T-cells role appears more in priming, regulation and severe disease protection.)
5/
(T-cells role appears more in priming, regulation and severe disease protection.)
5/
https://twitter.com/DevanSinha/status/1393992239475462146
However there are a couple of limitations to the PHE study. We are undoubtedly very lucky they could publish something this important so rapidly and comprehensively! However, no scientific study is perfect and we have to read this study like others with nuance.
6/
6/
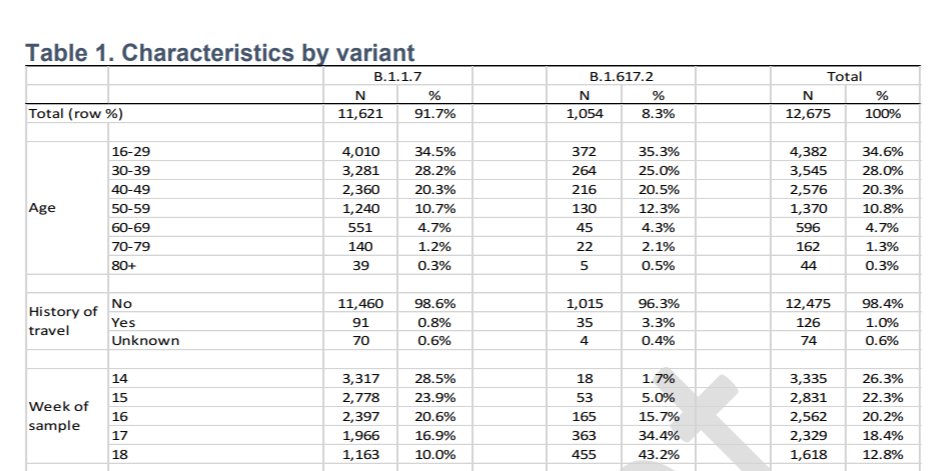
In defining B117 and B1.617.2 PHE used PCR S-gene target positive (B117) and negative ( B1.617.2) as proxies when full sequencing was not available.
PHE justify this as from the sequenced pool 87.5% of S-gene positive were B.1.617.2 and 99.7% S-gene negative were as B117.
7/
PHE justify this as from the sequenced pool 87.5% of S-gene positive were B.1.617.2 and 99.7% S-gene negative were as B117.
7/
1/3 of B.1.617.2 cases were classified on this PCR S-gene basis.
However, variants B1.351 🇿🇦 and P.1 🇧🇷 also have this trait, and both have well studied reduction in Ab neutralisation/Ab immune evasion particularly B1.351.
8/
However, variants B1.351 🇿🇦 and P.1 🇧🇷 also have this trait, and both have well studied reduction in Ab neutralisation/Ab immune evasion particularly B1.351.
8/

Given relatively low event numbers involved after 2 doses in the study, misclassification of 1 or 2 cases will have large effects on statistical power and confidence intervals - let alone change the VE point estimate⬆️.
Excellent CI charts from @steber232!
9/


Excellent CI charts from @steber232!
9/

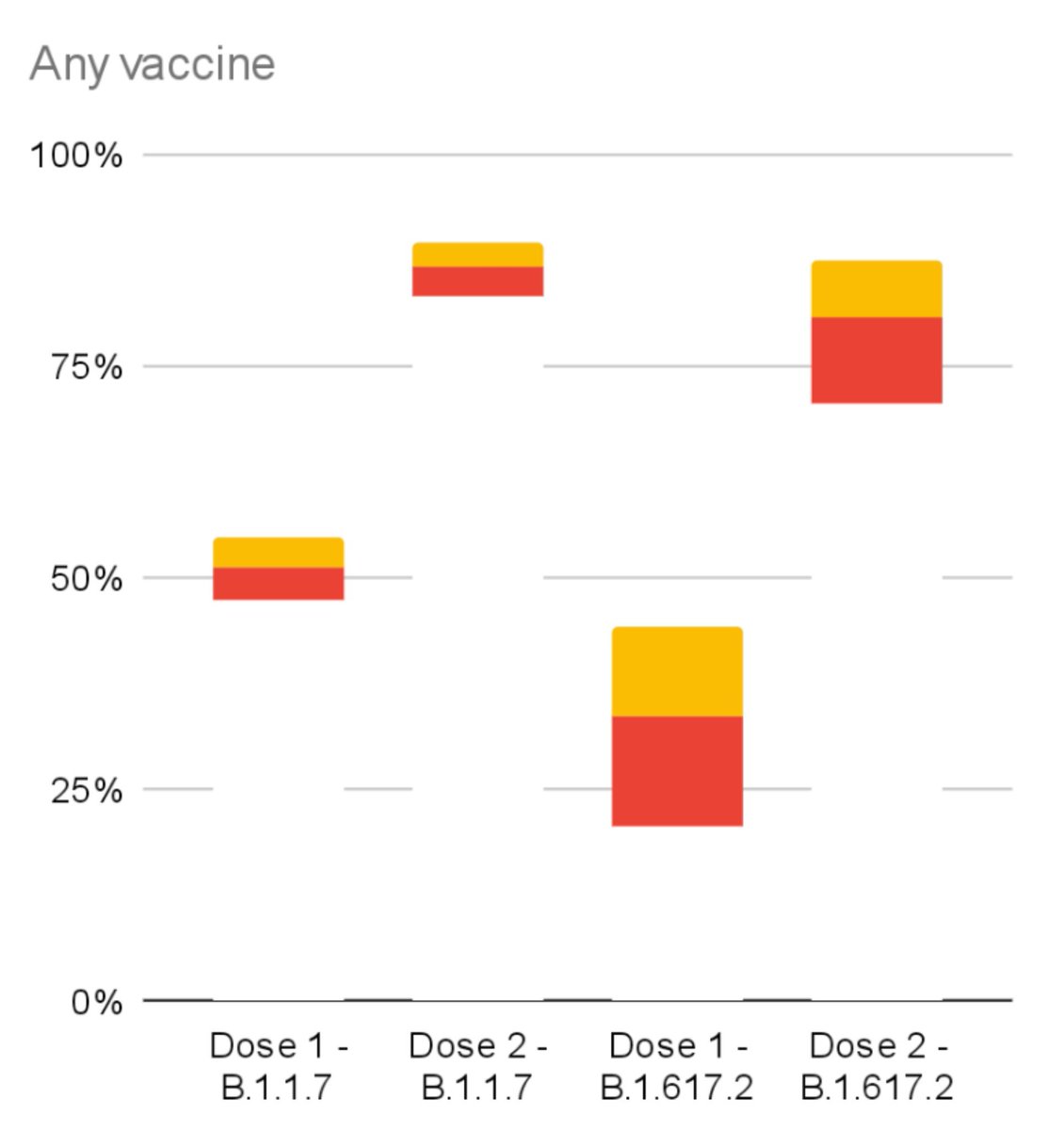

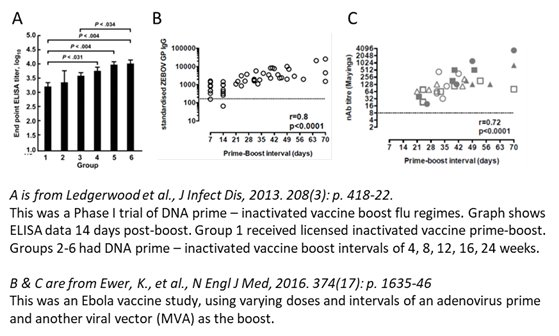
A sensitivity analysis restricting to fully sequenced cases should ideally have been provided in the supplementary. (NB 10-15% misclassification if 1/3 S-G positive for the 1 dose Ox/AZ group will not have changed much).
10/
10/
The bigger discrepancy between this study and previous ones potentially comes from handling/exclusion of previous infected who have a acquired a level of natural immunity.
ONS survey found 65% effectiveness for 1 dose >21 days after ONS excluded prev Ab or PCR positives.
11/
ONS survey found 65% effectiveness for 1 dose >21 days after ONS excluded prev Ab or PCR positives.
11/

PHE only excluded cases w/ prior PCR positive result (not Ab). 7% of England's population have tested PCR positive over pandemic. But Serology surveys and models (w/ waning Ab) place true figure ~4x higher.
Most phase 3 vax trials excluded or separated Ab+ for analysis.
12/
Most phase 3 vax trials excluded or separated Ab+ for analysis.
12/
A substantial fraction of PHE control group will have actually been previously infected and acquired natural immunity. The median ages of variant cases was 30-40 with 1/3 aged 16-29 = groups w/ highest exposure. Despite 'exclusion' 20%+ likely in control previously infected.
13/
13/
This will have significant confounding effect on vax effectiveness (VE) calculation vs control.
Multiple well conducted studies eg SIREN and CHARM (US marines) found prior infxn 80-85% protective against re-infection.
14/
thelancet.com/journals/lanre…
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
Multiple well conducted studies eg SIREN and CHARM (US marines) found prior infxn 80-85% protective against re-infection.
14/
thelancet.com/journals/lanre…
thelancet.com/journals/lance…
This prior immunity in the control group could reduce the observed baseline infxn rate by 16-17%+.
And correspondingly cause underestimation of Vax effectiveness against symptomatic disease in B1.617.2 for 1 dose with VE ~44%. (case control adjustment wd vary)
15/
And correspondingly cause underestimation of Vax effectiveness against symptomatic disease in B1.617.2 for 1 dose with VE ~44%. (case control adjustment wd vary)
15/
Now vaxxed groups wd also benefit from prior infxn immunity - boosting VE higher than otherwise the case. But differential infection rates overall (effectiveness) between baseline 0 infxn/vax and prior infx is greater so will bias toward underestimation of VE.
16/
16/
Taking this into account I'm not certain that confidence intervals for 1 dose vax effectiveness B117 vs B1.617.2 won't overlap ➡️ the difference might not be statistically significant.
Though my prior belief remains if Ab 'escape' 1 dose will be more affected than 2 doses.
17/
Though my prior belief remains if Ab 'escape' 1 dose will be more affected than 2 doses.
17/
PHE study also had 2 dose Ox/AZ symptomatic effectiveness lower than previous analysis: 89% [78,94] 14 days post 2 dose.
But as @kallmemeg noted the weighted distribution of cases in new report had AZ recipients much sooner after doses. 74% AZ in past 28 days v 46% Pfizer.
18/
But as @kallmemeg noted the weighted distribution of cases in new report had AZ recipients much sooner after doses. 74% AZ in past 28 days v 46% Pfizer.
18/

Ox/AZ vax mechanism is comparatively slow release. Non-replicating adenovirus vector can continue to persist and stimulate immune system:
frontiersin.org/articles/10.33…
Especially T-cells:
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
19/
frontiersin.org/articles/10.33…
Especially T-cells:
ashpublications.org/blood/article/…
19/
https://mobile.twitter.com/DevanSinha/status/1363828689914519558
Thus the effectiveness of Ox/AZ may not have fully peaked at the time of assessment . When JnJ- also adenovector based- analysed vax effectiveness against B1.315 in South African trial they used a >28 day cut off for analysis.
20/
20/
Summary:
- 1 dose VE vs B1.617.2 is likely reduced but this is less certain than presented.
- VE will be higher than headline reported results.
- 2 dose minimally affected - may take 10ks matched cases to say if difference at all.
- 1 dose VE vs B1.617.2 is likely reduced but this is less certain than presented.
- VE will be higher than headline reported results.
- 2 dose minimally affected - may take 10ks matched cases to say if difference at all.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh