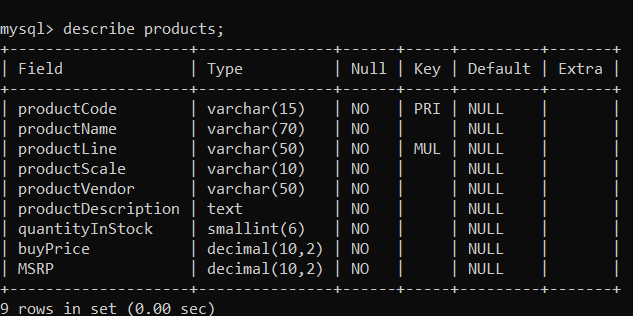
What else can I say about SQL to prove that it is crucial to know how to work around databases?
Having said that, SQL could be the one thing that you could begin your programming journey with. 🤩
A Beginner-friendly version of SQL (UPDATE and DELETE)
🧵👇
Having said that, SQL could be the one thing that you could begin your programming journey with. 🤩
A Beginner-friendly version of SQL (UPDATE and DELETE)
🧵👇
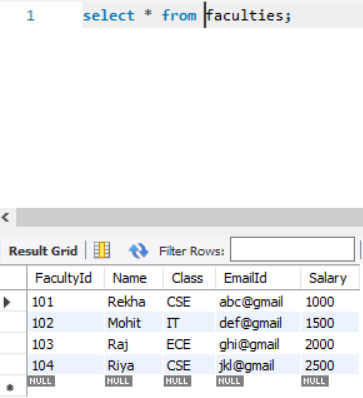
🌟 Let's look at the table first!
The name of the table is -> faculties
We have columns as FacultyId, Name, Class, EmailId and Salary.
The name of the table is -> faculties
We have columns as FacultyId, Name, Class, EmailId and Salary.
☑️ UPDATE
This clause is used to change values in a specified column.
You may or may not provide a condition along with the change you want to make.
👉 Update without condition:-
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = column_value;
This clause is used to change values in a specified column.
You may or may not provide a condition along with the change you want to make.
👉 Update without condition:-
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = column_value;
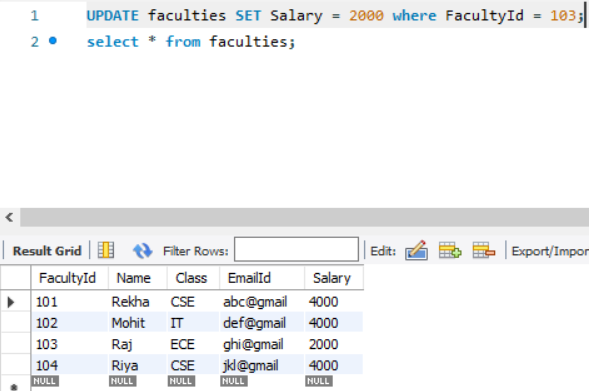
Query: Change the salaries of the faculties to 4000.
SQL Query: UPDATE faculties SET Salary = 4000;
O/P: All the values in the Salary Column would change to 4000.
SQL Query: UPDATE faculties SET Salary = 4000;
O/P: All the values in the Salary Column would change to 4000.

👉 Update with a condition:-
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = column_value where CONDITION;
Query: Change the value of Salary to 2000 where the FacultyId is 103.
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = column_value where CONDITION;
Query: Change the value of Salary to 2000 where the FacultyId is 103.
☑️ DELETE
The DELETE clause would help you remove the row(s) from the table.
You have to specify a condition to delete a specific row.
*Important Note*: If you do not specify a condition within the DELETE clause, all rows would be deleted.
The DELETE clause would help you remove the row(s) from the table.
You have to specify a condition to delete a specific row.
*Important Note*: If you do not specify a condition within the DELETE clause, all rows would be deleted.
👉 Delete with the condition:-
DELETE from table_name where CONDITION;
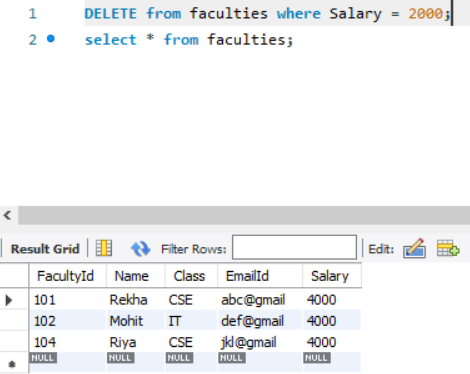
Query: Delete the values from the Faculties table where the salary is 2000.
SQL Query: DELETE from faculties where Salary = 2000;
O/P: The row where the Salary is 2000 is deleted from the table.
DELETE from table_name where CONDITION;
Query: Delete the values from the Faculties table where the salary is 2000.
SQL Query: DELETE from faculties where Salary = 2000;
O/P: The row where the Salary is 2000 is deleted from the table.
👉 Delete all rows:-
TRUNCATE table_name;
With TRUNCATE, the table will exist in the database, but all the rows in that table will be deleted.
👉 To Delete a table from the database:-
DROP table table_name;
👉 To Delete a database:-
DROP database database_name;
TRUNCATE table_name;
With TRUNCATE, the table will exist in the database, but all the rows in that table will be deleted.
👉 To Delete a table from the database:-
DROP table table_name;
👉 To Delete a database:-
DROP database database_name;
FYI, I wanted to put this thread yesterday, but somehow I was unable to access my Twitter Web. Even now, I had to login via Incognito Mode.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh