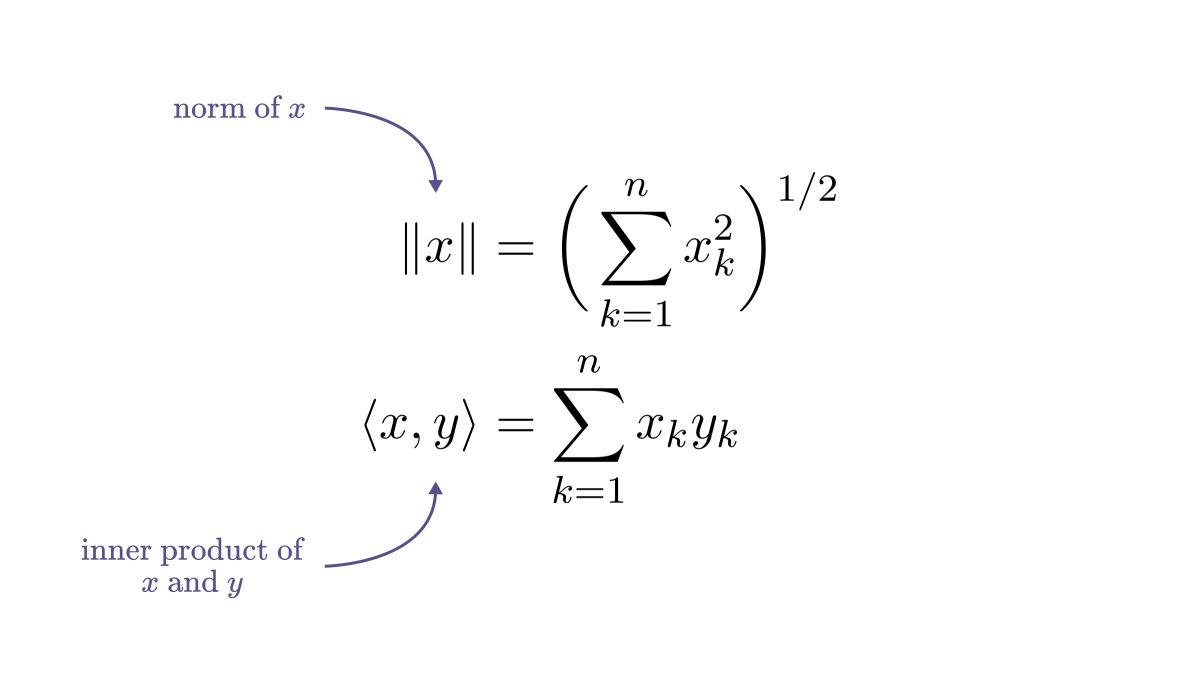
You don't need to go to a university to learn machine learning - you can do it from your living room, for completely free.
Here is an extensive list of curated free courses and tutorials, from beginner to advanced. ↓
(Trust me, you want to bookmark this tweet.)
Here is an extensive list of curated free courses and tutorials, from beginner to advanced. ↓
(Trust me, you want to bookmark this tweet.)
This is how I'll group the courses.
Machine learning
├── Getting started
├── Computer vision
├── NLP
├── Reinforcement learning
└── Applications
Coding
├── Python
├── R
├── Javascript
└── Machine learning frameworks
Let's start!
Machine learning
├── Getting started
├── Computer vision
├── NLP
├── Reinforcement learning
└── Applications
Coding
├── Python
├── R
├── Javascript
└── Machine learning frameworks
Let's start!
Machine learning
└── Getting started
1. Neural networks (by @3blue1brown)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
└── Getting started
1. Neural networks (by @3blue1brown)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
4. MIT RES.LL-005 Mathematics of Big Data and Machine Learning (by Jeremy Kepner and Vijay Gadepally)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
Machine learning
└── Computer vision
1. Stanford cs231n Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition (by @karpathy)
(This is my all-time favorite machine learning course.)
└── Computer vision
1. Stanford cs231n Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition (by @karpathy)
(This is my all-time favorite machine learning course.)
3. Advanced Computer Vision with Python (by Murtaza Hassan and freecodecamp)
Machine learning
└── Natural language processing
1. Stanford CS224N: NLP with Deep Learning (by @chrmanning)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
└── Natural language processing
1. Stanford CS224N: NLP with Deep Learning (by @chrmanning)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
2. Natural Language Processing with TensorFlow 2 - Beginner's Course (by Phil Tabor and freecodecamp)
Machine learning
└── Reinforcement learning
1. Stanford CS234: Reinforcement Learning (by @EmmaBrunskill)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
└── Reinforcement learning
1. Stanford CS234: Reinforcement Learning (by @EmmaBrunskill)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
2. Reinforcement Learning Course - Full Machine Learning Tutorial (by Phil Tabor and freecodecamp)
3. Deep Reinforcement Learning in Python Tutorial - A Course on How to Implement Deep Learning Papers (by Phil Tabor and freecodecamp)
Machine learning
└── Applications
1. MIT 6.S897 Machine Learning for Healthcare (by @david_sontag and Peter Szolovits)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
└── Applications
1. MIT 6.S897 Machine Learning for Healthcare (by @david_sontag and Peter Szolovits)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
2. Applied Deep Learning with PyTorch (by Fawaz Sammani and freecodecamp)
6. Python for Bioinformatics - Drug Discovery Using Machine Learning and Data Analysis (by @thedataprof and freecodecamp)
Coding
└── Python
1. MIT 6.0001 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming in Python (by @anabellphd)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
└── Python
1. MIT 6.0001 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming in Python (by @anabellphd)
youtube.com/playlist?list=…
3. Python for Data Science - Course for Beginners (by freecodecamp and Maxwell Armi)
Coding
└── R
1. R Programming Tutorial - Learn the Basics of Statistical Computing (by @datalabcc and freecodecamp)
└── R
1. R Programming Tutorial - Learn the Basics of Statistical Computing (by @datalabcc and freecodecamp)
Coding
└── JavaScript
(Yes, you can do machine learning in JavaScript.)
1. Learn TensorFlow.js - Deep Learning and Neural Networks with JavaScript (by @deeplizard and freecodecamp)
└── JavaScript
(Yes, you can do machine learning in JavaScript.)
1. Learn TensorFlow.js - Deep Learning and Neural Networks with JavaScript (by @deeplizard and freecodecamp)
2. Neural Networks with JavaScript - Full Course using Brain.js (by @robertlplummer and freecodecamp)
Coding
└── Machine learning frameworks
1. TensorFlow 2.0 Complete Course (by @TechWithTimm and freecodecamp)
└── Machine learning frameworks
1. TensorFlow 2.0 Complete Course (by @TechWithTimm and freecodecamp)
2. Keras with TensorFlow Course - Python Deep Learning and Neural Networks for Beginners (by @deeplizard and freecodecamp)
4. Scikit-learn Crash Course - Machine Learning Library for Python (by @fishnets88 and freecodecamp)
If you are still here, and perhaps finished some courses after coming back to this list, congratulations! You are off to a great start in machine learning.
Now go, and build something awesome!
Now go, and build something awesome!
We are pushing the limits of Twitter, as I cannot add any more tweets to this thread :)
I post threads like this every week, diving deep into concepts in machine learning and mathematics.
If you have enjoyed this, make sure to follow me and stay tuned for more!
I post threads like this every week, diving deep into concepts in machine learning and mathematics.
If you have enjoyed this, make sure to follow me and stay tuned for more!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh