Oh dear.
Non-farm payrolls in September rose by only +194k, after +366k last month.
The recovery has stalled.
We're missing about 8 million jobs, and at this rate, we're not bringing them back any time soon.
Non-farm payrolls in September rose by only +194k, after +366k last month.
The recovery has stalled.
We're missing about 8 million jobs, and at this rate, we're not bringing them back any time soon.
Slightly brighter news in the revisions: Last month's gains were revised from +235k to +366k. The previous month's gains were revised up by an additional +38k. So the prior two months were in total +169k better than we thought.
But this month is about 300k worse than we hoped.
But this month is about 300k worse than we hoped.
The unemployment rate fell from 5.2% to 4.8%, but celebrations on this score would be premature, as it partly reflects the labor force shrinking by about -183k.
Household survey is slightly sunnier than the payrolls survey, showing employment growth of +526k.
Household survey is slightly sunnier than the payrolls survey, showing employment growth of +526k.
Some questions about how the extent to which the disappointing jobs number reflects the pandemic shifting seasonal hiring patterns among teachers.
https://twitter.com/Neil_Irwin/status/1446453695139418126
Also, all that talk of end UI being a big driver. It's a nothingburger. The real issue is -- and remains -- the virus.
https://twitter.com/Neil_Irwin/status/1446454253984395264
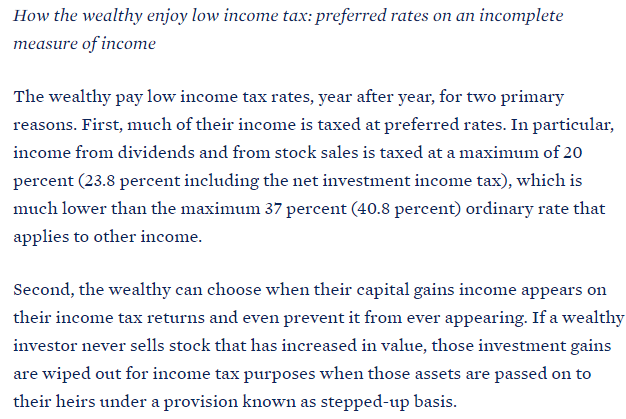
Fed economists this morning will be furiously debating the definition of the term "decent." There's a decent case that this jobs report isn't decent enough to taper. 
We're still missing nearly 9 million jobs. That's a hole about as deep as that in the depths of the recession following the 2008 financial crisis.
https://twitter.com/aaronsojourner/status/1446455361054072837
The real question at this point is whether the economy has been temporarily delayed, or whether it has stalled.
If you want to kickstart the economic recovery, we've all got one simple job to do: Get vaccinated.
Even better, get your family vaccinated, encourage your friends to get vaccinated, and encourage or even mandate your workforce to get vaccinated.
Jabs => Safety => Jobs
Even better, get your family vaccinated, encourage your friends to get vaccinated, and encourage or even mandate your workforce to get vaccinated.
Jabs => Safety => Jobs
Oh hey, if you want to see my pandemic hair, I'll be on @CNN in just a few minutes, talking about the jobs report, fiscal policy, and the road ahead.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh