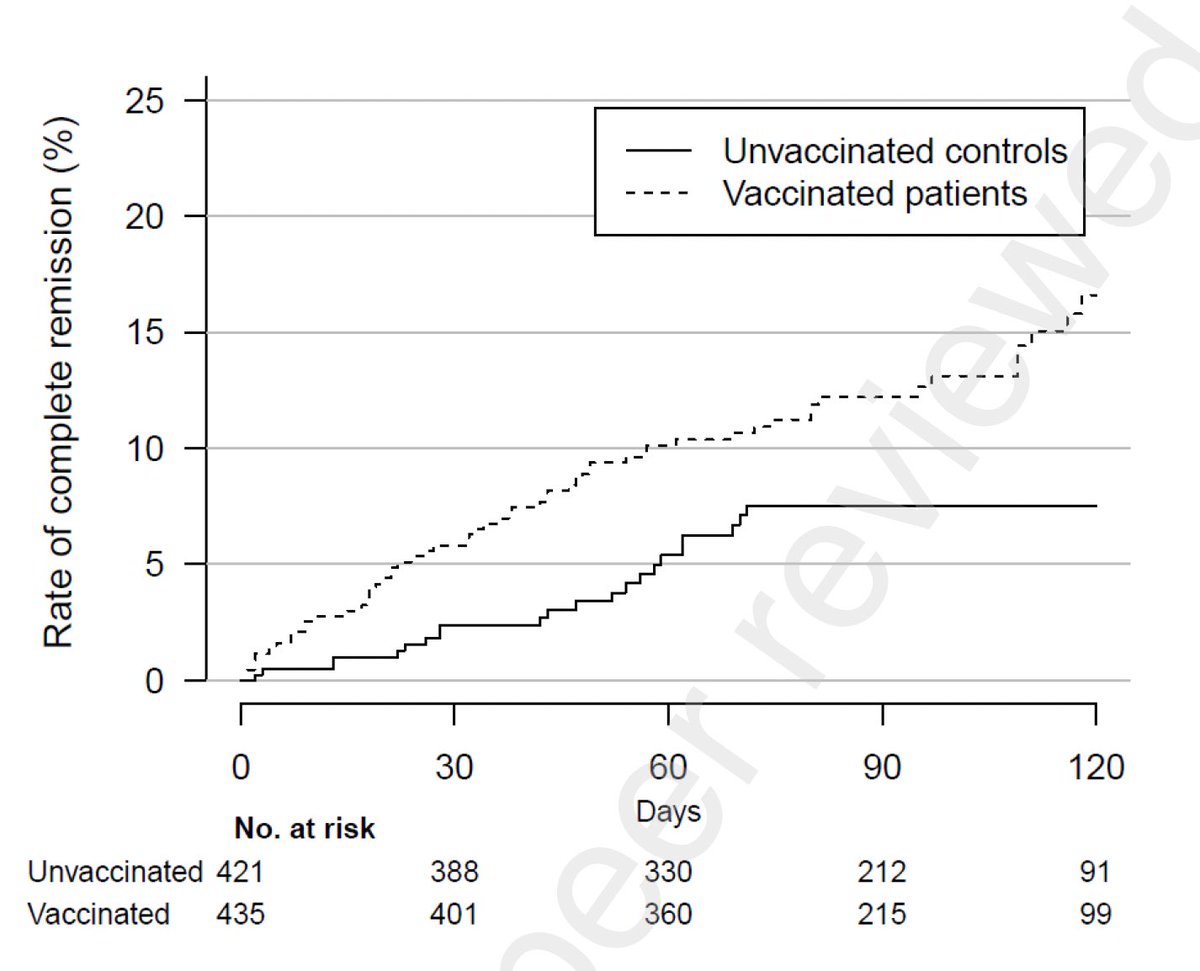
Our study on immune profiling of a solid organ transplant recipient with SARS-CoV-2 reinfection is now published.
Congrats to lead authors @sneakyvirus1 @AndersonBrito_ Paul Trubin @peowenlu and senior authors Marwan Azar & @BenIsraelow 👏🏼 👏🏼 (1/)
academic.oup.com/jid/advance-ar…
Congrats to lead authors @sneakyvirus1 @AndersonBrito_ Paul Trubin @peowenlu and senior authors Marwan Azar & @BenIsraelow 👏🏼 👏🏼 (1/)
academic.oup.com/jid/advance-ar…
For description of this study, please see my thread from when we first posted the paper in @medrxivpreprint in March 👇🏽 One of the deepest immune profiling that captures reinfection in a longitudinal manner. (2/)
https://twitter.com/VirusesImmunity/status/1375555960337543171?s=20
In a nutshell, this transplant patient had, prior to reinfection;
• Huge levels of circulating innate and adaptive cytokines (chronic inflammation)
• Very few naive lymphocytes & dominant exhausted T cells
• Elicited poor and transient neutralizing Ab responses
(3/)
• Huge levels of circulating innate and adaptive cytokines (chronic inflammation)
• Very few naive lymphocytes & dominant exhausted T cells
• Elicited poor and transient neutralizing Ab responses
(3/)
We are delighted to have this study published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases @IDSAInfo!
Kudos to @BenIsraelow @YaleIDFellows for bringing this over the finish line 💪🏼
And thank you @Primary_Immune for encouraging me to post this thread 🙏🏼
(end)
Kudos to @BenIsraelow @YaleIDFellows for bringing this over the finish line 💪🏼
And thank you @Primary_Immune for encouraging me to post this thread 🙏🏼
(end)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh