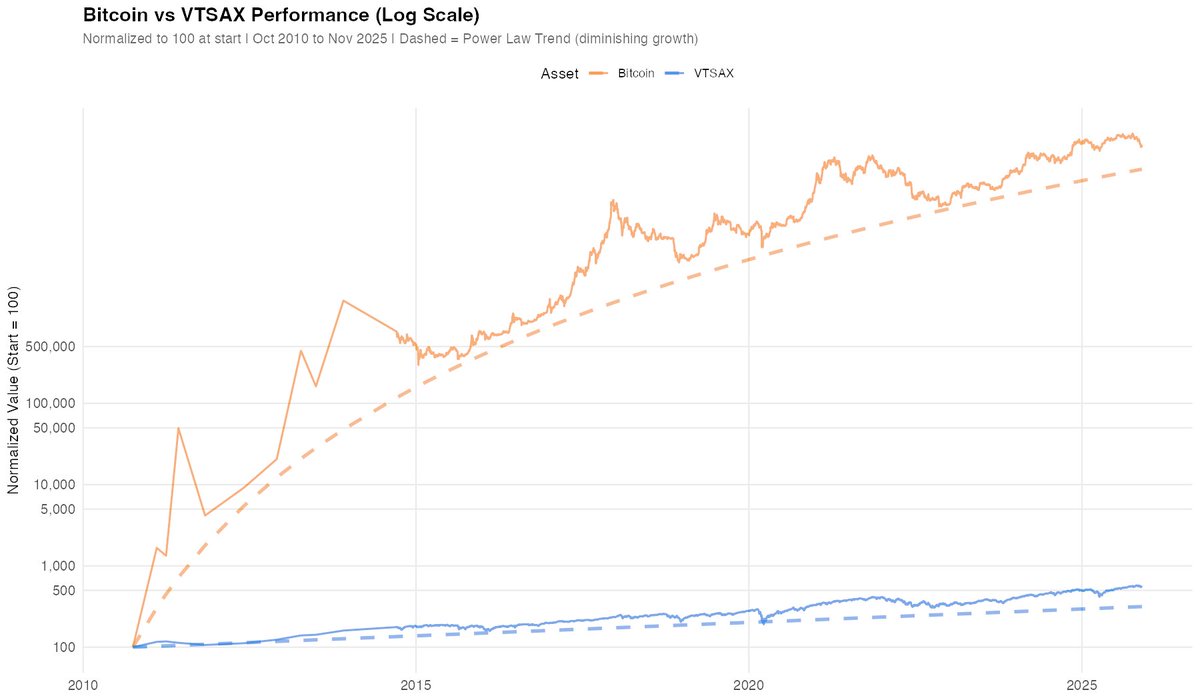
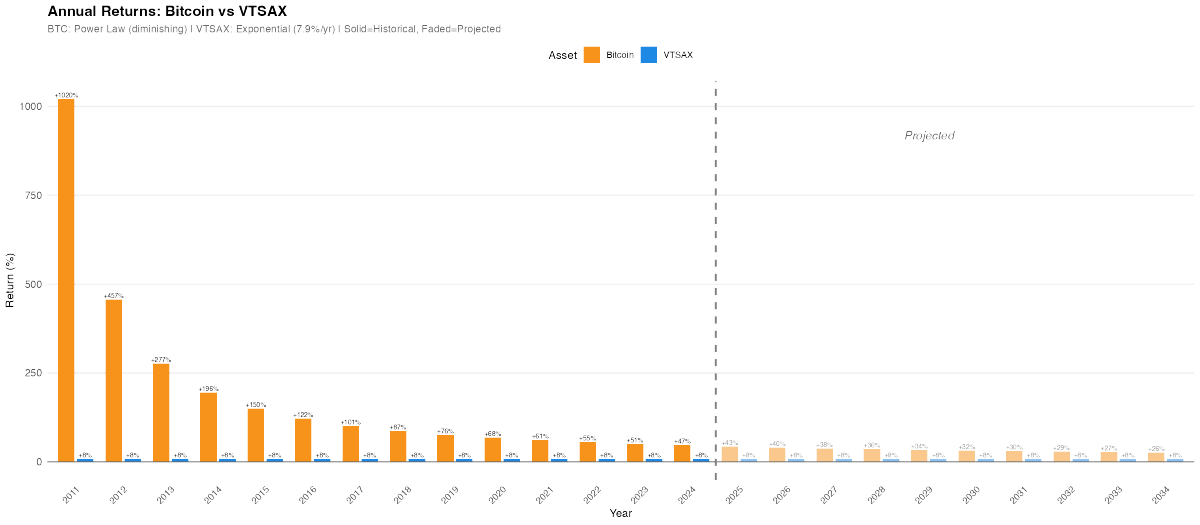
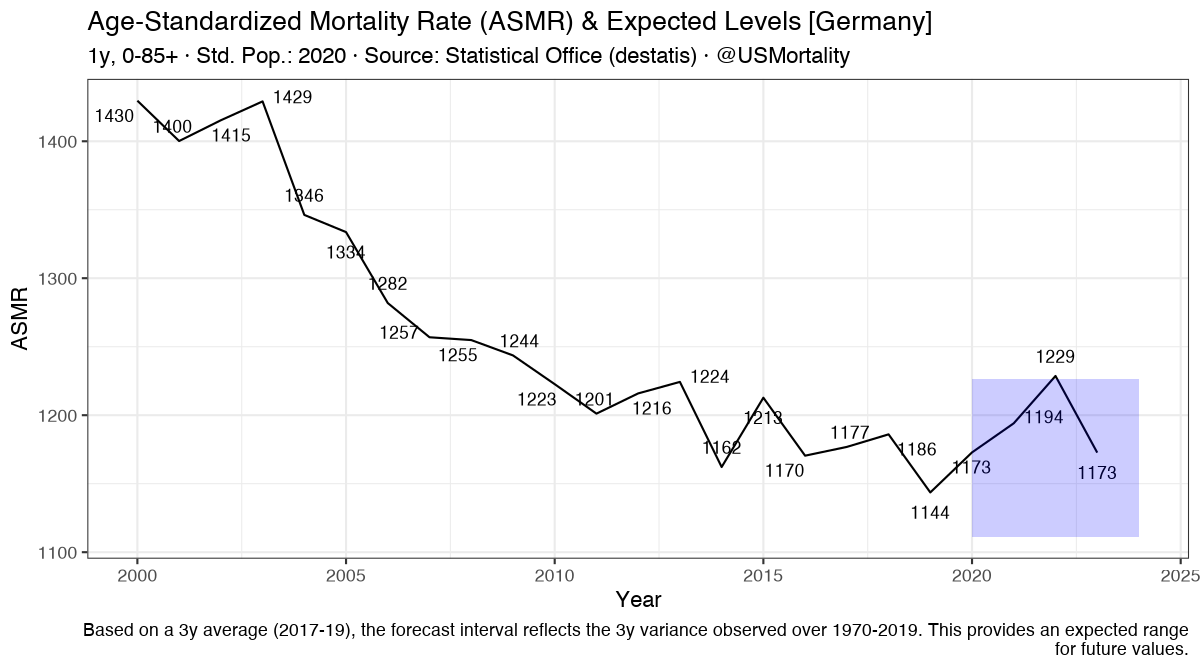
Great presentation by Dr. Scot Youngblood, MD about #Covid19 vaccine facts & mandates!
1/n
#Corona #Coronavirus #Covid
1/n
#Corona #Coronavirus #Covid
4/4
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh