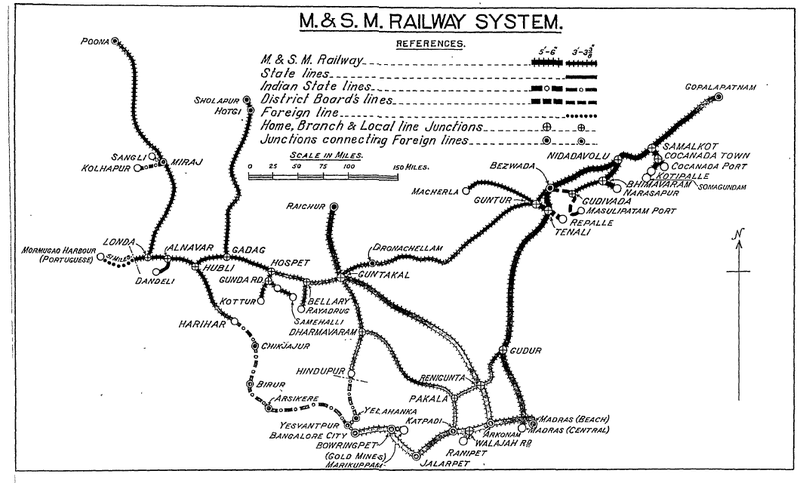
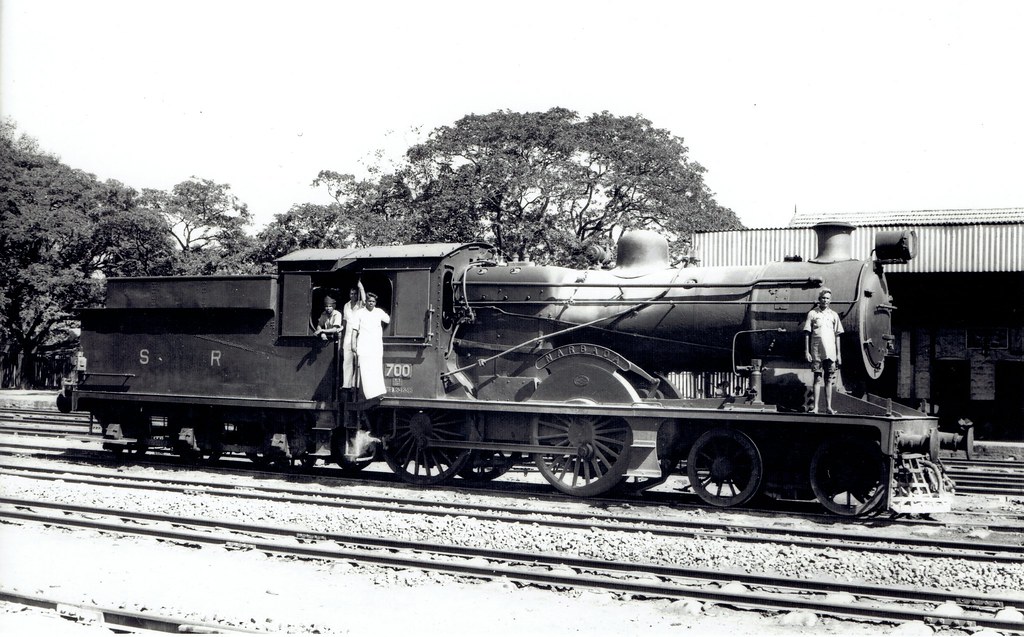
The Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway (MSM) was formed in 1908 from the merger of the Madras Railway Company (MR) which operated a broad gauge (BG) system and the Southern Mahratta Railway(SMR) metre gauge (MG) system. 

In 1943, MSM operated 1518 miles of Broad gauge track and 2087 miles of Metre gauge track across southern India. 
Madras Railway Company (MR) was incorporated in 1845 for the purposes of building a 70 mile line between Madras and the military base at Arcot. In 1859, its mandate was expanded to Beypore, with branches to Bangalore, and via Bellary, to join the line from Bombay. 

Before the first section of the line from Madras to Arcot was opened on 1 July 1856. A viaduct across the Piney River had to be built. 

By 1871, the network would grow to about 862 miles in BG lines. In 1901, it took over the southern portion of the East Coast Railway connecting Madras to Vishakapatnam. 

Madras Central was built in 1873 at Parktown as a second terminus to decongest the Royapuram harbour station. In 1907, Madras Central was made the Madras Railway Company's main station. 



In 1908, the northern portion (ie the north east, north west and Bangalore branches) was merged with the Southern Mahratta Railway(SMR) to form the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway(MSM). The southern section of Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline section,transferred to the SIR. 



The Southern Mahratta Railway (SMR) was founded in 1882 to construct a metre gauge(MG) railway between Hotgi and Gadag (opened to traffic in 1884), one of the "famine lines" set up with a guarantee. 

In 1888, a line was extended from Londa towards the PortugueseGoa where it connected with the Marmagao line at Castle Rock. By 1890, this line extendedeastwards via Guntakal to Bezwada, and northwards to Poona. 



In 1882, SMR took over management and operations for almost 300 miles of MG and NG track from the Mysore State Railway (Mysore Kingdom) 

In 1908, the SMR , with a route mileage of 1687 miles(2715km), merged with sections of the ‘South Indian Railway’ to form the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway - MSM Metre Gauge Division 

In 1922, MSMR established itself at a newly built head quarters on Poonamallee High Road. The building today is the HQ of Southern Railways 

In addition to the lines comprised in the system, the Company, worked the ‘Birur-Shimoga Section’, the ‘Mysore-Nanjangud Section’ and ‘Mysore-Bangalore Section’, all of which were made over to the Mysore Durbar on 1 Oct 1919. 





In 1937 MSMR became a pioneer in running regular railbus service with 110HP Armstrong- Whitworth diesel rail cars to replace steam hauled trains on thin unprofitable routes. 

On April 2, 1931, the first electrically-operated railway service between Madras Beach and Tambaram was launched by South Indian Railway. This was a operation jointly run from 1937 onwards. 



The Government took over direct control of the MSMR on 1 April 1944. On 14 April 1951, the MSMR, the South Indian Railway(SIR) and the Mysore State Railway(MSR) merged together to become Southern Railway, a zone of the nationalized Indian Railways. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh