An in-depth review of Distal Radius Fractures.
If you're interested in orthopedics, you'll definitely want to check this review out.
1/15
If you're interested in orthopedics, you'll definitely want to check this review out.
1/15

Distal radius (DR) fractures have a bimodal age distribution. “accounting for around 25% of fractures in the pediatric population and up to 18% of all fractures in the elderly age group.” (2)
2/
2/
Which of the following does not articulate with the radius?
The distal radius articulates with the distal ulna, scaphoid, and lunate. The capitate is in the second carpal row and therefore does not articulate with the radius.
4/
4/

What is the most commonly injured nerve in distal radius fractures?
Answer: Median Nerve.
Median nerve neuropathy may also occur during immobilization. It can be prevented by avoiding immobilization in excessive wrist flexion and ulnar deviation.
Median nerve neuropathy may also occur during immobilization. It can be prevented by avoiding immobilization in excessive wrist flexion and ulnar deviation.
Normal distal radius measurements:
Radial Inclination: 23°
Radial Height (shortening): 12 mm
Volar tilt: 11°
6/
Radial Inclination: 23°
Radial Height (shortening): 12 mm
Volar tilt: 11°
6/

LaFontaines Predictors of Instability.
Patients with 3 or more of the following have a high chance of loss of reduction:
Initial radial shortening > 5 mm (✯)
Dorsal angulation > 20 °
Dorsal Comminution > 50%
Associated Ulna fx
Severe Osteoporosis
✯ Most Important
Patients with 3 or more of the following have a high chance of loss of reduction:
Initial radial shortening > 5 mm (✯)
Dorsal angulation > 20 °
Dorsal Comminution > 50%
Associated Ulna fx
Severe Osteoporosis
✯ Most Important
The Frykmann classification system.
Even numbers are the previous fracture type with an associated ulnar styloid fracture.
1: Extra-articular
3: Intraarticular involving radiocarpal joint
5: IA involving the DRUJ
7: IA involving both the radiocarpal joint and DRUJ
8/
Even numbers are the previous fracture type with an associated ulnar styloid fracture.
1: Extra-articular
3: Intraarticular involving radiocarpal joint
5: IA involving the DRUJ
7: IA involving both the radiocarpal joint and DRUJ
8/

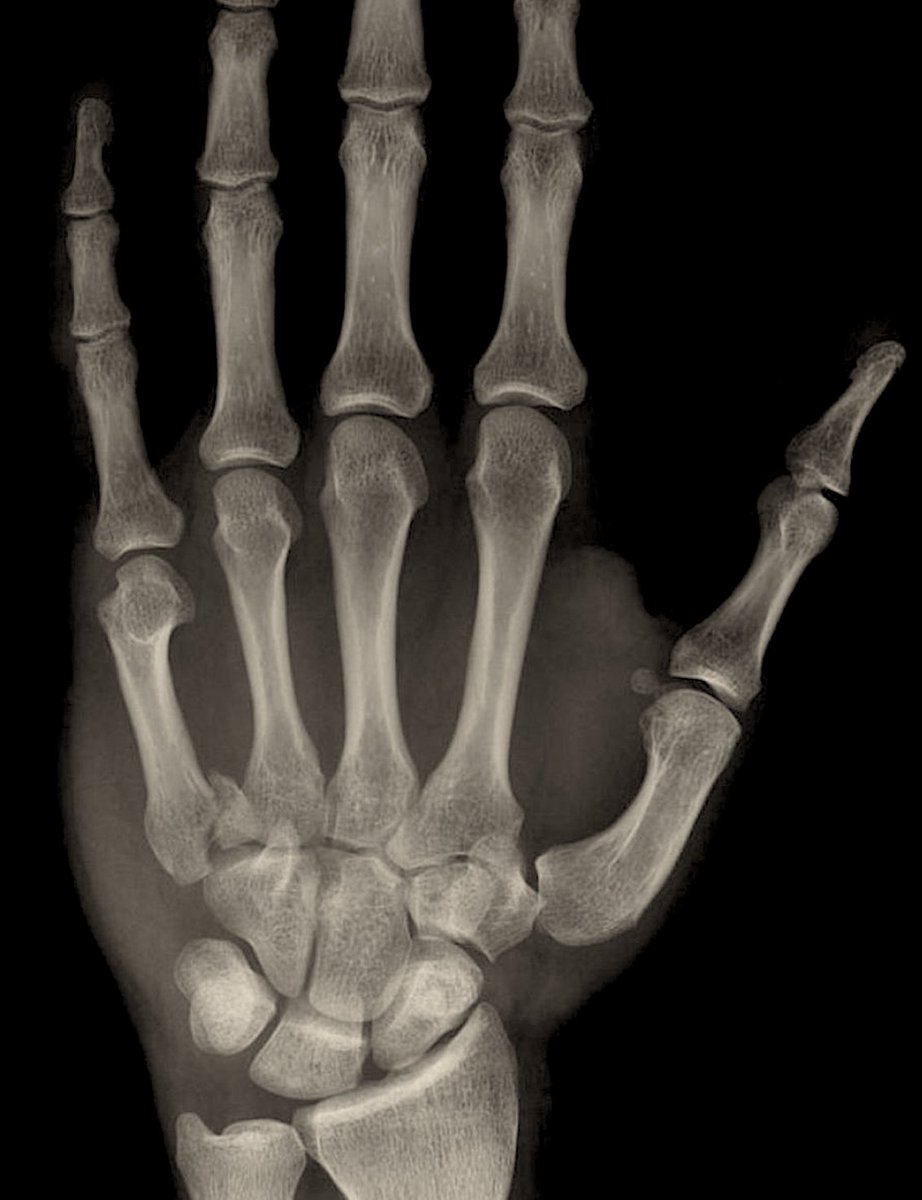
Which type of fracture is shown below?
a) Smith's Fracture
b) Colle's Fracture
c) Barton's Fracture
d) Chauffer's Fracture
a) Smith's Fracture
b) Colle's Fracture
c) Barton's Fracture
d) Chauffer's Fracture

The radiograph is demonstrating a Colle's Fracture, it is extra-articular and dorsally displaced. A Smith's fracture is EA and volarly displaced.
A Chauferr's fx is a radial styolid fx.
A Barton's fx is fracture-dislocation of either the volar or dorsal lip of the radius.
10/
A Chauferr's fx is a radial styolid fx.
A Barton's fx is fracture-dislocation of either the volar or dorsal lip of the radius.
10/

Treatment methods:
Non-operative treatment
ORIF with Volar or Dorsal Plating
Closed reduction with percutaneous pinning
Operative Indications:
> 5 mm shortening
> 5° dorsal angulation
> 2 mm articular step off
11/
Non-operative treatment
ORIF with Volar or Dorsal Plating
Closed reduction with percutaneous pinning
Operative Indications:
> 5 mm shortening
> 5° dorsal angulation
> 2 mm articular step off
11/
Volar plating is preferred over dorsal plating. The volar approach to the distal radius is through a Volar Henry or Modified Volar Henry approach.
VH: an interval is made between the brachioradialis and radial artery
MVH: an interval is made between the FCR and radial artery
VH: an interval is made between the brachioradialis and radial artery
MVH: an interval is made between the FCR and radial artery

Complications:
Median nerve neuropathy
Radiocarpal Arthritis
EPL and FPL rupture
Ulnar nerve neuropathy (DRUJ injury)
13/
Median nerve neuropathy
Radiocarpal Arthritis
EPL and FPL rupture
Ulnar nerve neuropathy (DRUJ injury)
13/
Spontaneous extensor pollicis longus rupture may occur following DR fracture. Which type of fx is it more common with?
Answer: Non-displaced fractures. The reasoning for this has been a topic for debate, some say it may be due to limited room for hematoma expansion in non-displaced fractures.
Note: FPL tendon rupture can occur following volar plating if the plate is placed too distal.
15/
Note: FPL tendon rupture can occur following volar plating if the plate is placed too distal.
15/

References:
1: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53691…
2: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
3: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
1: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53691…
2: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
3: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
If you enjoyed this review please like or retweet to help the page grow and give us a follow.
Author: @CSMorford
#OrthoTwitter #MedED #DistalRadius #Fractures #MedTwitter #Trauma #Orthopedics
@MedTweetorials @RosenelliEM @DrEbraheim_UTMC @TweetsOrtho
Author: @CSMorford
#OrthoTwitter #MedED #DistalRadius #Fractures #MedTwitter #Trauma #Orthopedics
@MedTweetorials @RosenelliEM @DrEbraheim_UTMC @TweetsOrtho
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh