An in-depth review of intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric hip fractures.
If you're interested in orthopedics you won't want to miss this one!
🦴⚒️🧵👇
If you're interested in orthopedics you won't want to miss this one!
🦴⚒️🧵👇

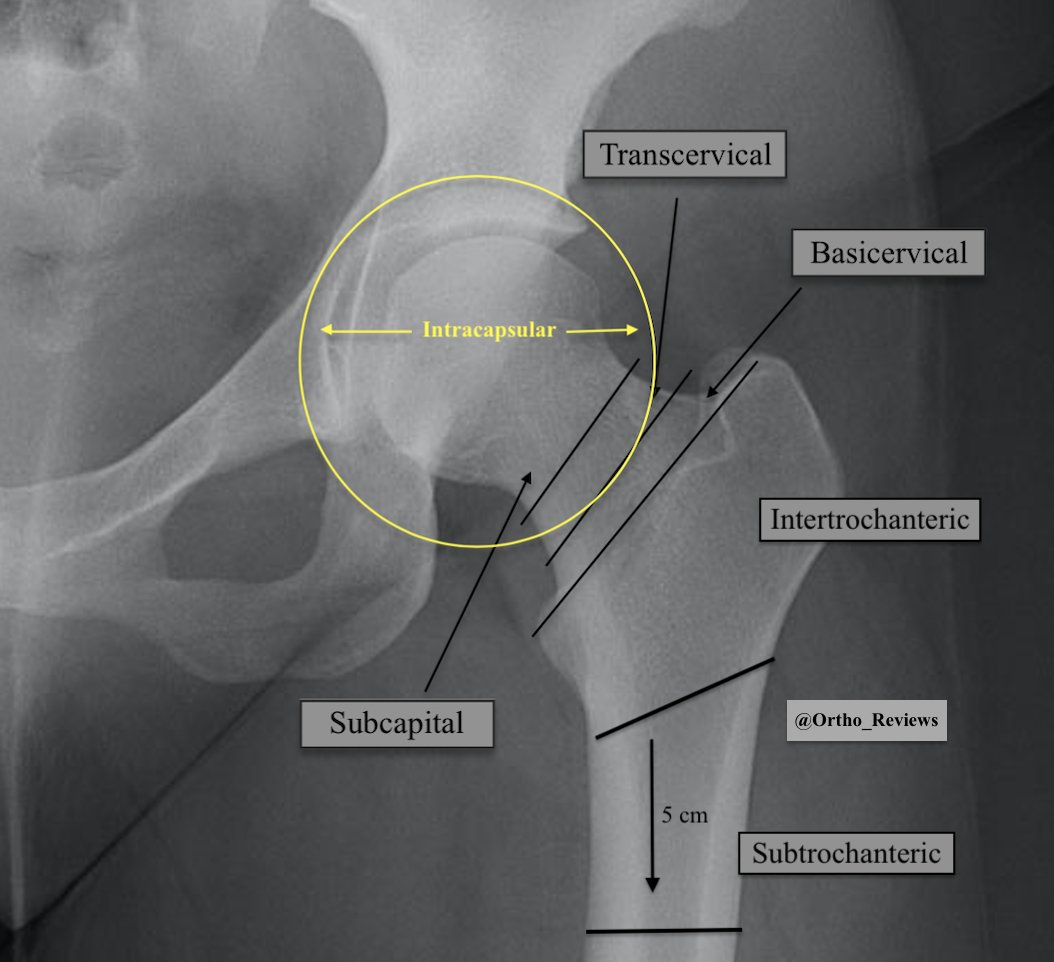
Basicervical femoral neck, intertrochanteric (IT), and subtrochanteric (ST) hip fractures are different from femoral neck fractures in that they are extracapsular.
Extracapsular fractures, unlike intracapsular femoral neck fx, have a low likelihood of blood supply disruption/AVN
Extracapsular fractures, unlike intracapsular femoral neck fx, have a low likelihood of blood supply disruption/AVN
Anatomy:
The calcar femorale is an extension of cortical bone from the proximal shaft to the posteromedial femoral neck. It aids in weight distribution from the hip to the proximal femoral shaft.
The subtrochanteric region extends 5 cm below the lesser trochanter.
The calcar femorale is an extension of cortical bone from the proximal shaft to the posteromedial femoral neck. It aids in weight distribution from the hip to the proximal femoral shaft.
The subtrochanteric region extends 5 cm below the lesser trochanter.

Deforming forces on IT and ST Fractures:
GT: proximally & laterally (hip abductors)
LT: proximally & medially (iliopsoas)
Distal Fragment: proximally & medially (adductors/hip flexors)
GT: proximally & laterally (hip abductors)
LT: proximally & medially (iliopsoas)
Distal Fragment: proximally & medially (adductors/hip flexors)

Which of the following medications is associated with atypical subtrochanteric hip fractures?
Atypical features: cortical thickening, transverse nature, and/or medial fracture spike.
Atypical features: cortical thickening, transverse nature, and/or medial fracture spike.
Atypical ST fractures are associated with prolonged bisphosphonate use (alendronate).
Features of atypical ST fractures:
✯ Transverse/short oblique pattern
✯ Diaphyseal cortical thickening
✯ Medial fracture spike
Features of atypical ST fractures:
✯ Transverse/short oblique pattern
✯ Diaphyseal cortical thickening
✯ Medial fracture spike

It is important to determine whether an intertrochanteric fracture is stable or unstable as this helps guide treatment.
Unstable fracture patterns:
Posteromedial comminution (calcar disruption)
Reverse obliquity fracture
Large posteromedial fragment
Subtrochanteric Extension
Unstable fracture patterns:
Posteromedial comminution (calcar disruption)
Reverse obliquity fracture
Large posteromedial fragment
Subtrochanteric Extension

Treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures depends on the stability of the fracture.
Stable intertrochanteric and basicervical fractures are commonly treated with sliding hip screws (left) or short cephalomedullary nails (right).
Stable intertrochanteric and basicervical fractures are commonly treated with sliding hip screws (left) or short cephalomedullary nails (right).

To reduce the risk of hardware failure and screw cut out the tip-to-apex distance may be utilized.
Of note: the tip-to-apex distance was initially utilized for sliding hip screws but is commonly adopted for cephalomedullary nails.
Of note: the tip-to-apex distance was initially utilized for sliding hip screws but is commonly adopted for cephalomedullary nails.

The tip-to-apex distance is the distance from the tip of the lag screw to the apex of the femoral head.
It is measured on both AP and Lateral views and the sum of the two distances should be < 25 mm.
If the combined distances are > 45 mm there's as high as a 60% failure rate.
It is measured on both AP and Lateral views and the sum of the two distances should be < 25 mm.
If the combined distances are > 45 mm there's as high as a 60% failure rate.

In general, unstable intertrochanteric fractures and subtrochanteric fractures are both treated with long cephalomedullary nails. 

Complications:
Hardware failure/screw cut-out
Loss of reduction
Shortening/malrotation of the leg
Hardware failure/screw cut-out
Loss of reduction
Shortening/malrotation of the leg
If you enjoyed this review please, like or retweet to help the page grow and give us a follow!
Author: @CSMorford
#HipFractures #Intertrochanteric #Subtrochanteric #Trauma #Ortho #Orthopedics #OrthoTwitter #Trauma #MedEd #MedicalEducation #MedTwitter #Tweetorials #Radiology
Author: @CSMorford
#HipFractures #Intertrochanteric #Subtrochanteric #Trauma #Ortho #Orthopedics #OrthoTwitter #Trauma #MedEd #MedicalEducation #MedTwitter #Tweetorials #Radiology
We're also excited to announce we've created a website for easy access to our past and future reviews!
If you enjoy our reviews, check it out at myorthoreviews.com!
If you enjoy our reviews, check it out at myorthoreviews.com!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh