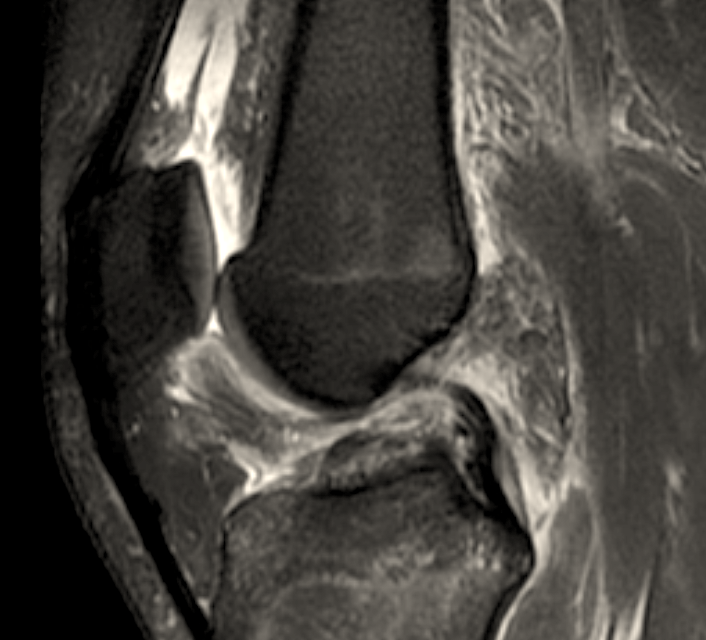
An in-depth review of Tibial Pilon Fractures.
If you’re interested in orthopedics, you’ll definitely want to check this review out.
🦴⚒️🧵👇
To view our past reviews, visit:
💻 myorthoreviews.com📱
If you’re interested in orthopedics, you’ll definitely want to check this review out.
🦴⚒️🧵👇
To view our past reviews, visit:
💻 myorthoreviews.com📱
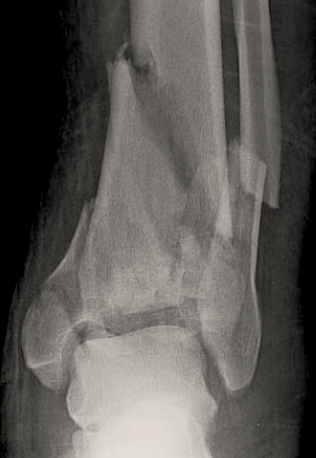
Most tibial pilon fractures result from high-energy axial loading through the talus.
They are also commonly referred to as Tibial Plafond fractures. The tibial plafond is the distal articular surface of the tibia, which gained the name from its French meaning, "ceiling".
They are also commonly referred to as Tibial Plafond fractures. The tibial plafond is the distal articular surface of the tibia, which gained the name from its French meaning, "ceiling".

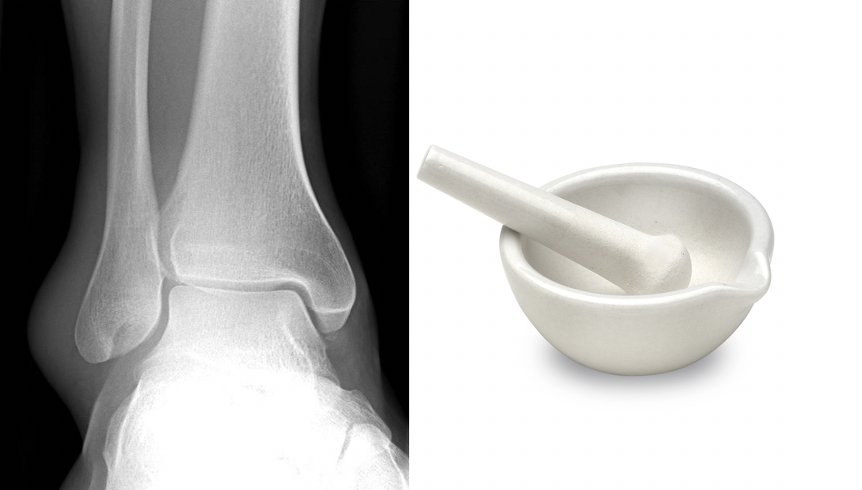
The term tibial pilon was first used by Étienne Destot in 1911 to describe the interaction of the distal tibia and talus during axial loading.
Pilon is the French term for "pestle".
The term was later adopted as a term for vertical impaction fractures of the distal tibia.
Pilon is the French term for "pestle".
The term was later adopted as a term for vertical impaction fractures of the distal tibia.
Due to the high-energy mechanism of most pilon fractures, it is important to perform a thorough trauma eval to rule out concomitant injuries.
Careful skin and soft tissue evaluation are also important with these injuries.
Ankle radiographs and a CT scan should be obtained.
Careful skin and soft tissue evaluation are also important with these injuries.
Ankle radiographs and a CT scan should be obtained.
Up to ¾ of pilon fractures have an associated fibula fracture.
Tibial pilon fractures commonly result in three fragments with each having intact ligamentous attachments.
Which fragment is attached to the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL)?
Tibial pilon fractures commonly result in three fragments with each having intact ligamentous attachments.
Which fragment is attached to the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL)?
The three fragments commonly seen in tibial pilon fractures are the:
✯ Volkmann Fragment (posterolateral)
-attached to the PITFL
✯ Chaput Fragment (anterolateral)
-attached to the AITFL
✯ Medial Malleolar Fragment
-attached to the deltoid ligament
✯ Volkmann Fragment (posterolateral)
-attached to the PITFL
✯ Chaput Fragment (anterolateral)
-attached to the AITFL
✯ Medial Malleolar Fragment
-attached to the deltoid ligament

An easy way to remember which fragments are the Chaput and Volkmann...
In golf, you "putt" forward (anteriorly). Therefore the Chaput fragment is anterolateral.
Then the Volkmann fragment must be the other one, the posterolateral fragment.
In golf, you "putt" forward (anteriorly). Therefore the Chaput fragment is anterolateral.
Then the Volkmann fragment must be the other one, the posterolateral fragment.

The majority of pilon fractures are treated surgically but non-operative management with casting may be an option for severely debilitated patients.
Due to the high-energy nature of pilon fractures, soft-tissue disruption is of significant concern.
Due to the high-energy nature of pilon fractures, soft-tissue disruption is of significant concern.
Staged management with temporary external fixation and definitive ORIF at a later date, commonly 7-14 days later, can allow for soft tissue optimization.
Based on soft-tissue quality acute definitive ORIF can also be performed.
Based on soft-tissue quality acute definitive ORIF can also be performed.

In a 1979 study, Rüedi and Allgöwer proposed four principles for the surgical management of tibial pilon fractures:
1) Restoration of fibular length
2) Restoration of the articular surface
3) Bone grafting of metaphyseal defects
4) Stabilization of the medial column
1) Restoration of fibular length
2) Restoration of the articular surface
3) Bone grafting of metaphyseal defects
4) Stabilization of the medial column
There are many approaches to the distal tibia and the approaches utilized are based on the fracture pattern.
Anterior approaches allow direct visualization of the articular surface.
Restoration of the tibia begins with the articular surface followed by the metaphyseal region.

Anterior approaches allow direct visualization of the articular surface.
Restoration of the tibia begins with the articular surface followed by the metaphyseal region.


Complications:
✯ Post-traumatic arthritis: signifies the importance of anatomic reduction
✯ Infection: increased risk due to soft tissue compromise, studies have shown ↓ risk with staged management
✯ Wound complications (e.g. dehiscence): reduced risk with staged management
✯ Post-traumatic arthritis: signifies the importance of anatomic reduction
✯ Infection: increased risk due to soft tissue compromise, studies have shown ↓ risk with staged management
✯ Wound complications (e.g. dehiscence): reduced risk with staged management
References:
1) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
2) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15006336/
3) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
4) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
1) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
2) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15006336/
3) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
4) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
If you enjoyed this review please like or retweet to help the page grow and give us a follow.
Author: @CSMorford
#Tibia #Pilon #Plafond #Fracture #Ankle #Trauma #OrthoTwitter #MedED #Fractures #MedTwitter #Orthopedics #Tweetorials #Radiology
Author: @CSMorford
#Tibia #Pilon #Plafond #Fracture #Ankle #Trauma #OrthoTwitter #MedED #Fractures #MedTwitter #Orthopedics #Tweetorials #Radiology
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh