An in-depth review of ACL injury.
If you're interested in sports medicine, you won't want to miss this one!
🦴⚒️🧵👇
To view our past reviews, check out:
💻 myorthoreviews.com📱
If you're interested in sports medicine, you won't want to miss this one!
🦴⚒️🧵👇
To view our past reviews, check out:
💻 myorthoreviews.com📱
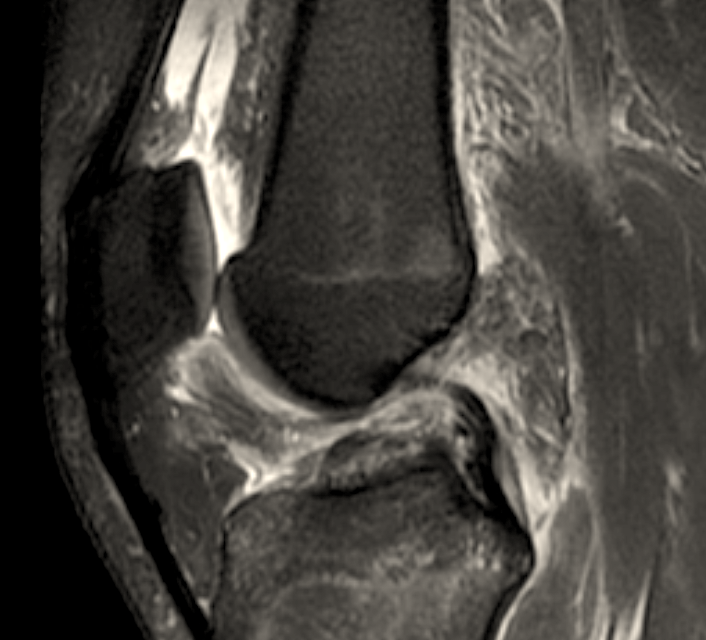
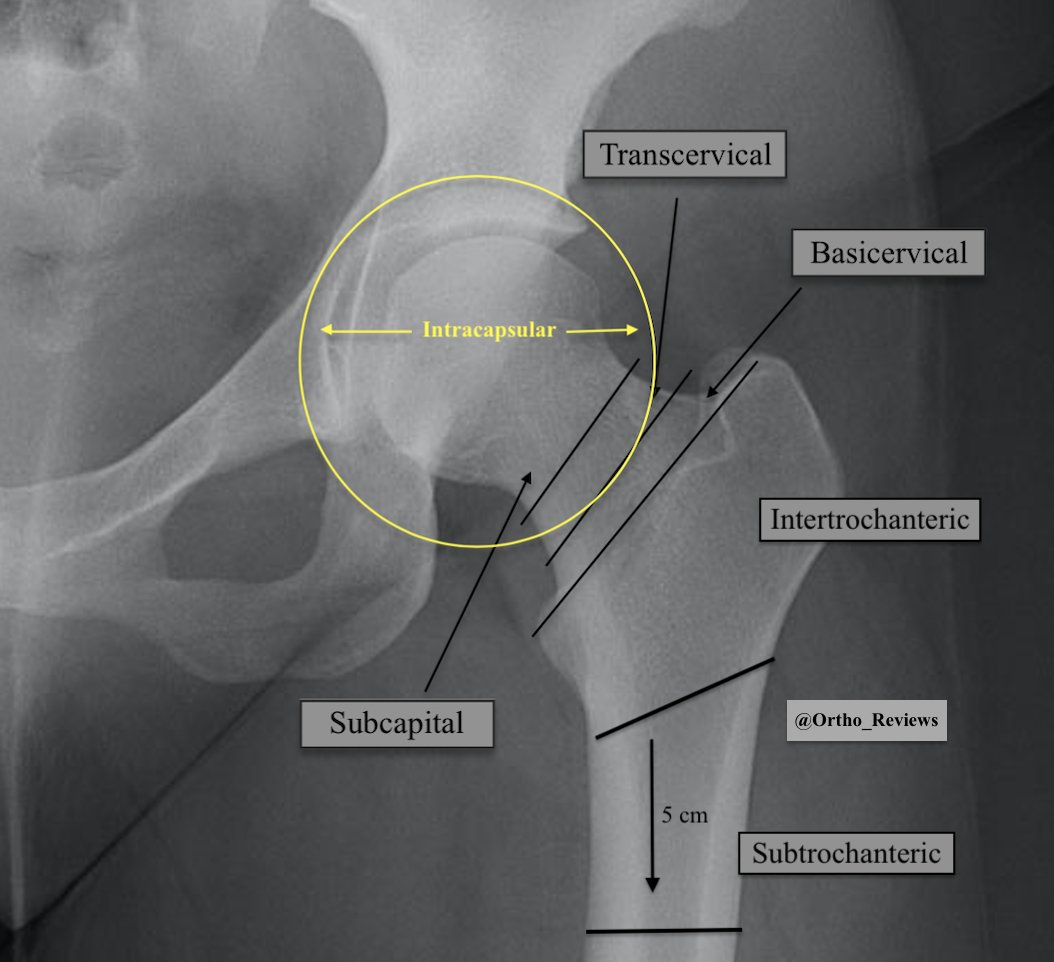
The ACL is the primary restraint to anterior tibial translation and also plays a role in rotary stability
It is composed of two bundles, named based on their tibial insertions:
✯ Anteromedial
✯ Posterolateral
What structure separates the femoral insertions of the two bundles?
It is composed of two bundles, named based on their tibial insertions:
✯ Anteromedial
✯ Posterolateral
What structure separates the femoral insertions of the two bundles?
AM bundle:
✯ Tightest in Flexion
✯ Resists anterior tibial translation
✯ Tested by Lachman's/Anterior Drawer
PL bundle:
✯ Tightest in Extension
✯ Rotatory Restraint
✯ Tested by Pivot Shift
The bifurcate ridge separates the femoral insertions of the AM and PL bundles.
✯ Tightest in Flexion
✯ Resists anterior tibial translation
✯ Tested by Lachman's/Anterior Drawer
PL bundle:
✯ Tightest in Extension
✯ Rotatory Restraint
✯ Tested by Pivot Shift
The bifurcate ridge separates the femoral insertions of the AM and PL bundles.

ACL injuries occur more frequently in female athletes, potential reasons include:
✯ Having a smaller femoral notch
✯ Ligamentous Laxity
✯ Quadriceps dominance
✯ Muscle recruitment patterns when landing/decelerating
✯ Having a smaller femoral notch
✯ Ligamentous Laxity
✯ Quadriceps dominance
✯ Muscle recruitment patterns when landing/decelerating
The majority of ACL injuries, around 70%, are due to non-contact injuries (pivoting/deceleration).
Of note: nearly half of ACL tears are associated with lateral meniscus tears.
Concomitant posterolateral corner injuries lead to an increased risk of graft failure if unaddressed
Of note: nearly half of ACL tears are associated with lateral meniscus tears.
Concomitant posterolateral corner injuries lead to an increased risk of graft failure if unaddressed

Patients will present with knee pain, difficulty weight-bearing, and they may report hearing a "pop".
Up to ¾ of patients will present with a joint effusion from hemarthrosis.
Which of the following tests is most sensitive for identifying an ACL tear?
Up to ¾ of patients will present with a joint effusion from hemarthrosis.
Which of the following tests is most sensitive for identifying an ACL tear?
Provocative Tests:
✯ Anterior Drawer Test
-Assesses ant. tibial translation at 90° flexion with the foot fixed
✯ Lachman Test
-Assesses ant. tibial translation at 30° flexion
✯ Pivot Shift
-Explained below.
Lachman's test has been noted to be the most sensitive.
✯ Anterior Drawer Test
-Assesses ant. tibial translation at 90° flexion with the foot fixed
✯ Lachman Test
-Assesses ant. tibial translation at 30° flexion
✯ Pivot Shift
-Explained below.
Lachman's test has been noted to be the most sensitive.

Knee radiographs may be obtained along with an MRI if ACL injury is suspected.
Additional radiographic signs of ACL injury:
✯ Segond fractures (shown below) are highly associated with ACL tears
✯ Bruising of the lateral femoral condyle and tibial plateau may be seen on MRI
Additional radiographic signs of ACL injury:
✯ Segond fractures (shown below) are highly associated with ACL tears
✯ Bruising of the lateral femoral condyle and tibial plateau may be seen on MRI

Non-operative treatment is generally poorly tolerated, and patients are at an increased risk of chondral damage and meniscal injury.
Most active patients require ACL reconstruction.
ACL repair is a rare practice due to high failure rates.
Most active patients require ACL reconstruction.
ACL repair is a rare practice due to high failure rates.
Grafts may be autograft (from the patient) or allograft (cadaver).
Graft options include bone-patellar tendon-bone (BPTB), quadriceps tendon, and hamstring tendon.
Graft choice should come from a discussion between the patient and surgeon.
Graft options include bone-patellar tendon-bone (BPTB), quadriceps tendon, and hamstring tendon.
Graft choice should come from a discussion between the patient and surgeon.
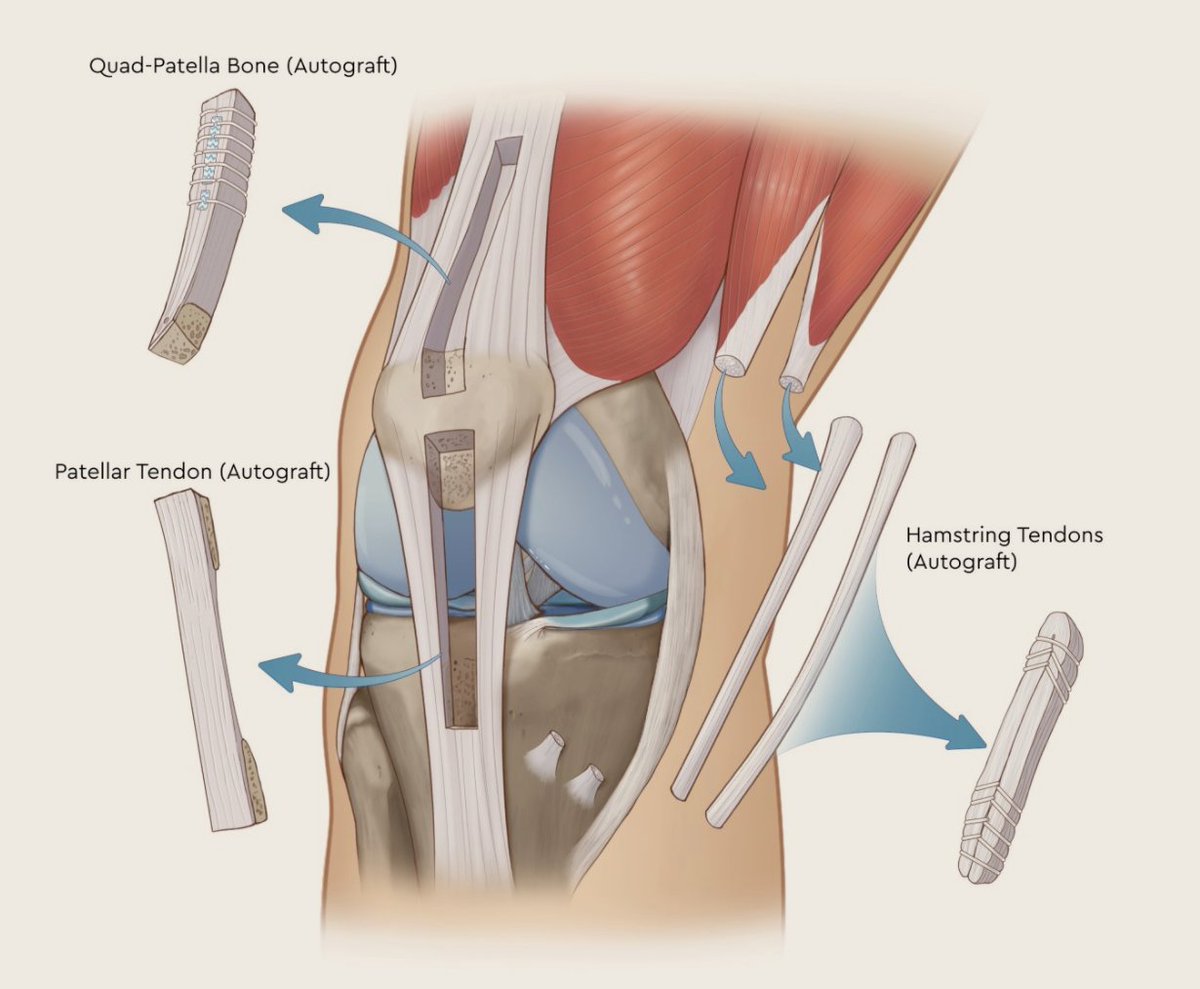
Bone-patellar tendon-bone graft is unique in that it allows the potential for bone-to-bone healing.
Anterior knee pain following BPTB grafting has been reported and there is an increased risk of patellar fracture, particularly during the rehab period.
Anterior knee pain following BPTB grafting has been reported and there is an increased risk of patellar fracture, particularly during the rehab period.
Grafts are commonly single bundle.
Double bundle grafts were introduced with the idea of being biomechanically stronger and were aimed at producing a more anatomic graft, but have not shown clinically significant differences and are at an increased risk of graft impingement.
Double bundle grafts were introduced with the idea of being biomechanically stronger and were aimed at producing a more anatomic graft, but have not shown clinically significant differences and are at an increased risk of graft impingement.
A 2015 study by Wasserstein et al. showed a 2.6x higher rate of graft failure among patients < 25 y.o. treated with allograft vs. autograft.
In general, patients < 25 y.o. should utilize autograft.
In general, patients < 25 y.o. should utilize autograft.
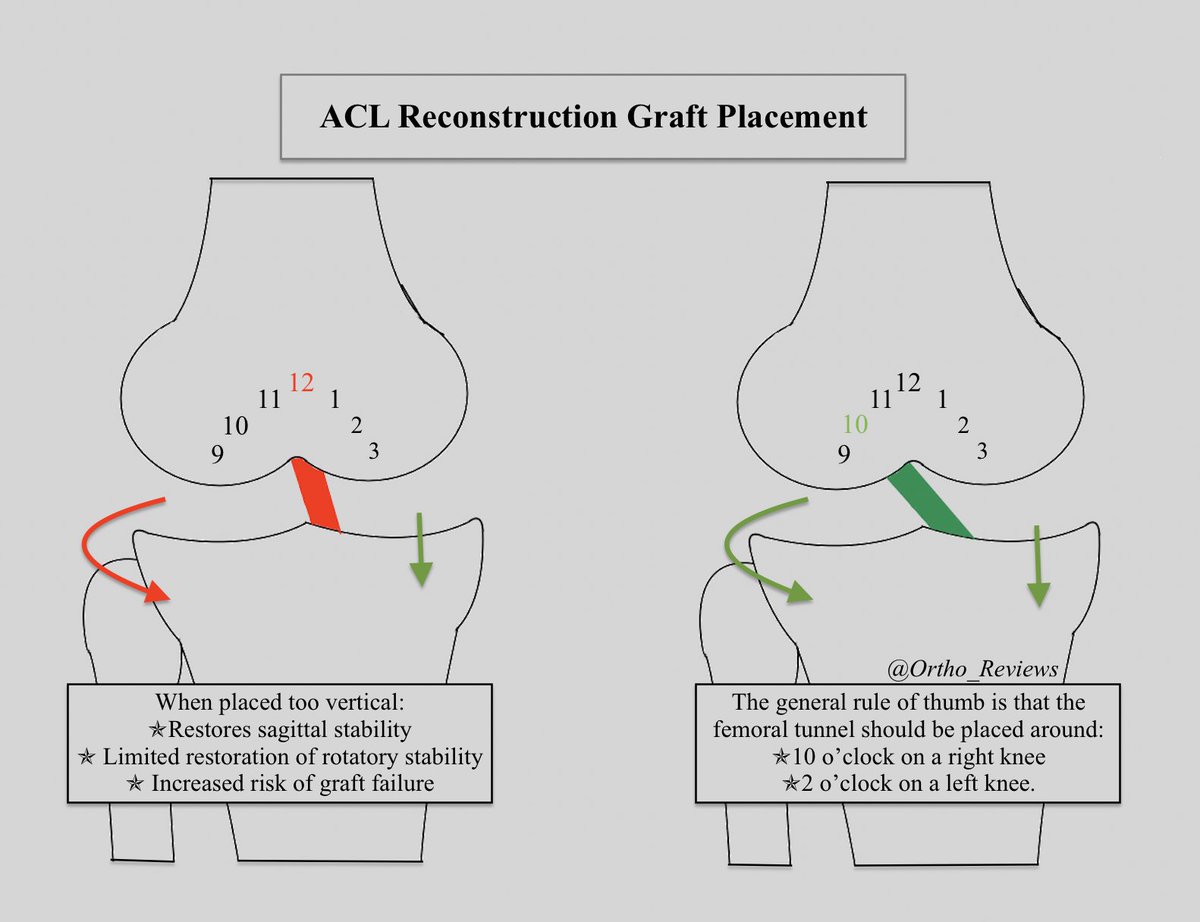
A concern when performing ACL reconstructions is the orientation of the graft.
If the graft is placed too vertical, it will allow for restoration of sagittal stability but has a limited effect on rotatory stability.
It also leads to an increased risk of graft failure.
If the graft is placed too vertical, it will allow for restoration of sagittal stability but has a limited effect on rotatory stability.
It also leads to an increased risk of graft failure.
Following ACL reconstruction, the main goals are to prevent joint effusion, avoid placing stress onto the graft, and achieve full passive knee extension.
Early progression to weight-bearing has been shown to reduce patellofemoral pain and decrease quadriceps inhibition.
Early progression to weight-bearing has been shown to reduce patellofemoral pain and decrease quadriceps inhibition.
References:
1) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28966380
2) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559233
3) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27053841
4) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26131297
5) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28791612
1) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28966380
2) ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559233
3) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27053841
4) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26131297
5) pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28791612
If you enjoyed this review, please retweet to help the page grow and give us a follow!
Author: @CSMorford
#ACL #Meniscus #Knee #SportsMedicine #Sports #Trauma #Ortho #Orthopedics #OrthoTwitter #Bones #Trauma #MedEd #MedicalEducation #MedTwitter #ERAS #Tweetorials #Radiology
Author: @CSMorford
#ACL #Meniscus #Knee #SportsMedicine #Sports #Trauma #Ortho #Orthopedics #OrthoTwitter #Bones #Trauma #MedEd #MedicalEducation #MedTwitter #ERAS #Tweetorials #Radiology
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh