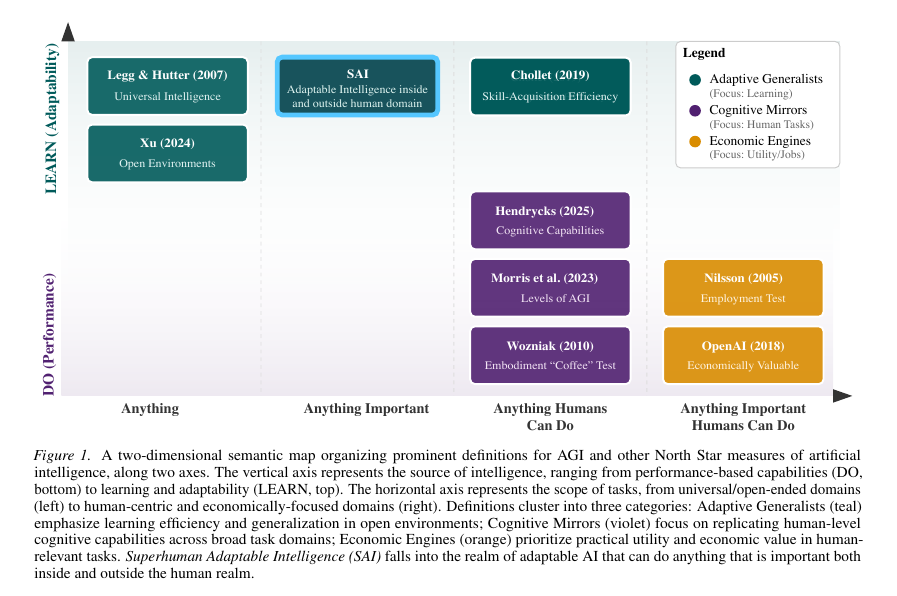
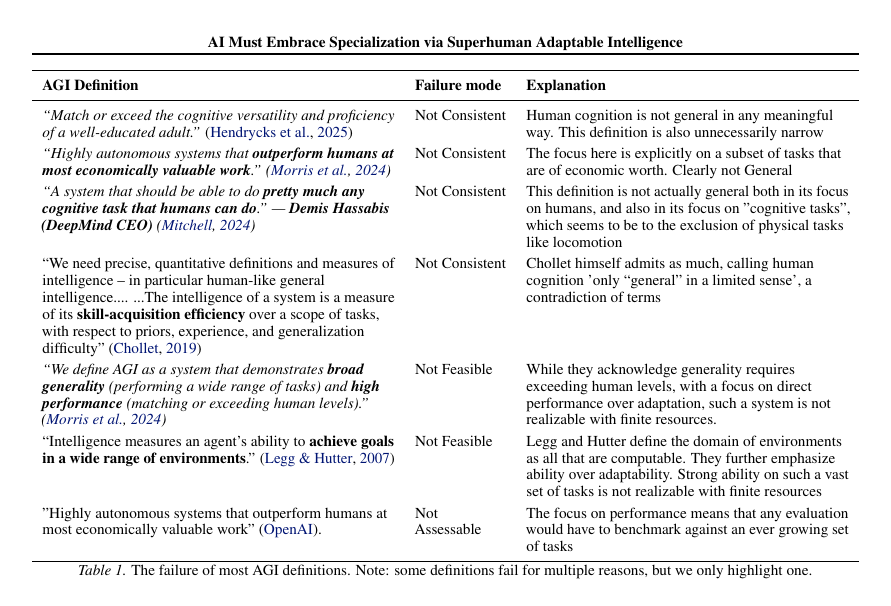
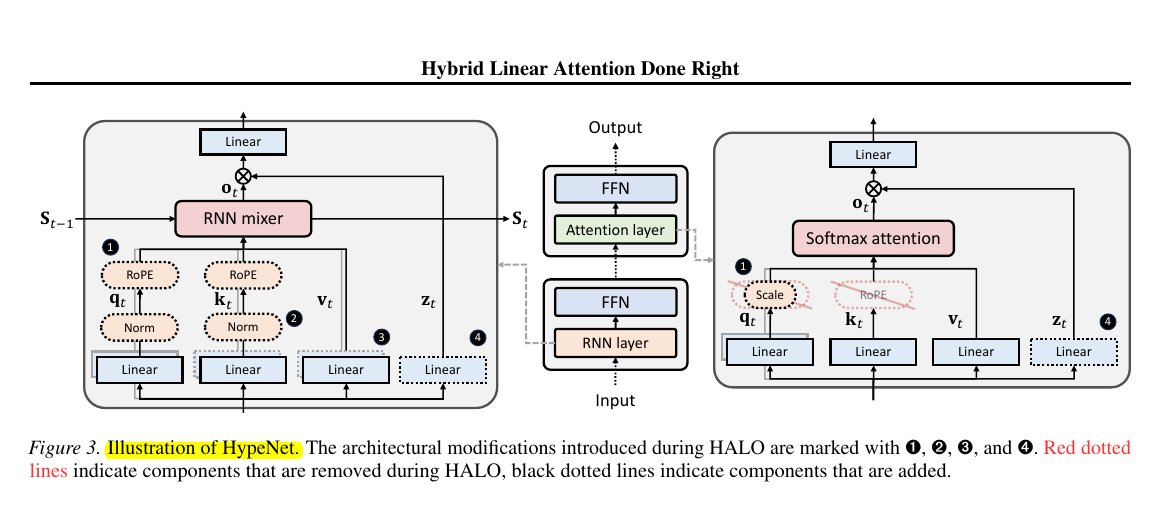
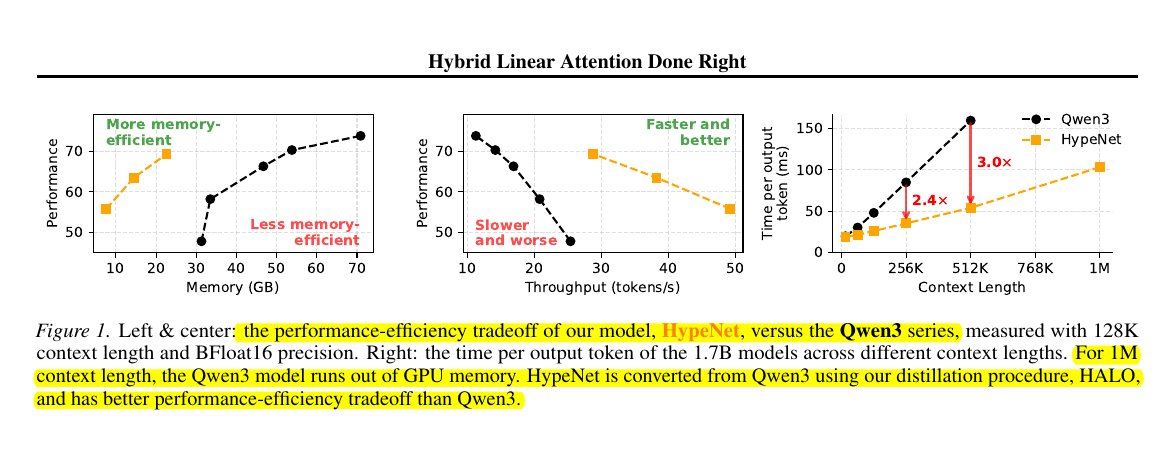
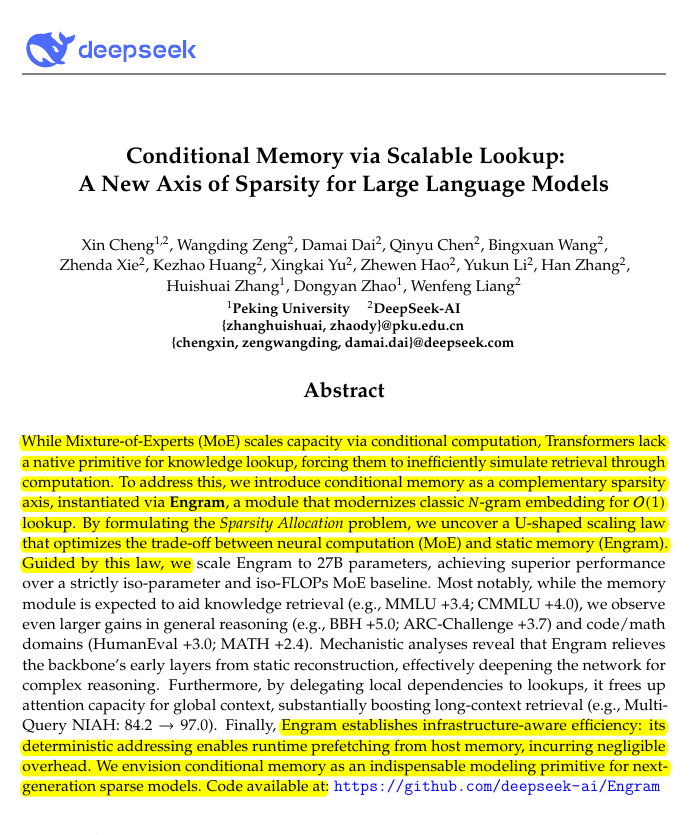
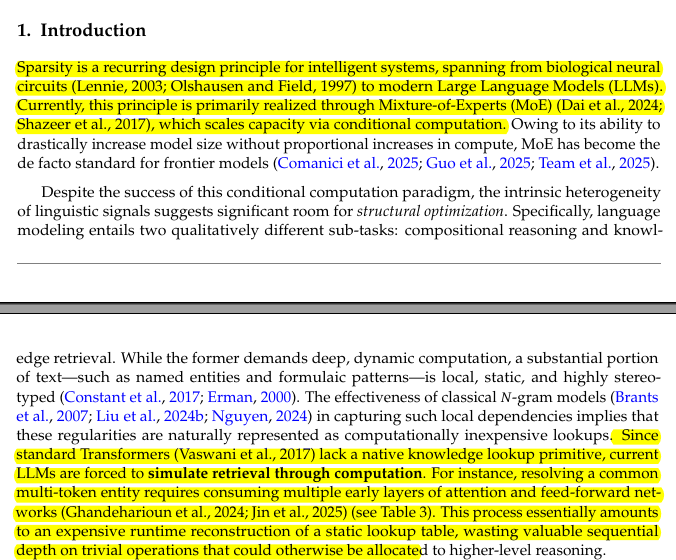
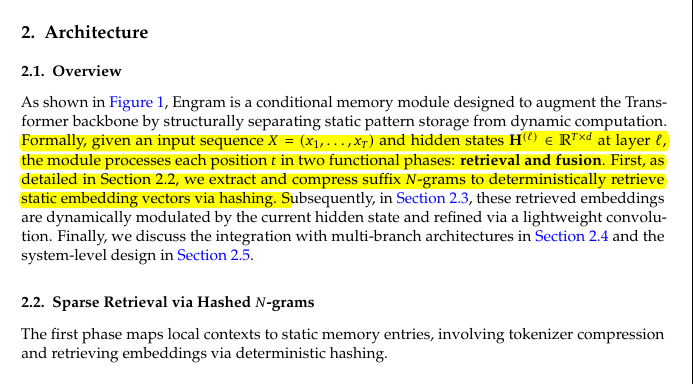
Kullback-Leibler (KL) Divergence - A Thread
It is a measure of how one probability distribution diverges from another expected probability distribution.
#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode #Python #programming #ArtificialIntelligence #Data
It is a measure of how one probability distribution diverges from another expected probability distribution.
#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode #Python #programming #ArtificialIntelligence #Data

#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode #Python #programming #ArtificialIntelligence #Data #DataAnalytics #pythoncode #AI #MachineLearning #NeuralNetworks 

#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode #Python #programming #ArtificialIntelligence #Data #DataAnalytics #pythoncode #AI #MachineLearning #NeuralNetworks 

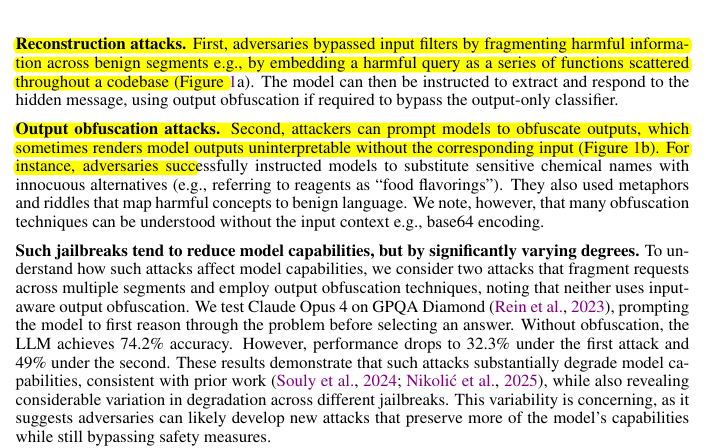
KL Divergence has its origins in information theory. The primary goal of information theory is to quantify how much information is in data. The most important metric in information theory is called Entropy
#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode
#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode
#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode #Python #programming #ArtificialIntelligence #Data #DataAnalytics #pythoncode #AI #MachineLearning #NeuralNetworks 

Mathematical Expression of KL Divergence
#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode #Python #programming #ArtificialIntelligence #Data #DataAnalytics #pythoncode #AI #MachineLearning #NeuralNetworks
#DataScience #Statistics #DeepLearning #ComputerVision #100DaysOfMLCode #Python #programming #ArtificialIntelligence #Data #DataAnalytics #pythoncode #AI #MachineLearning #NeuralNetworks

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh