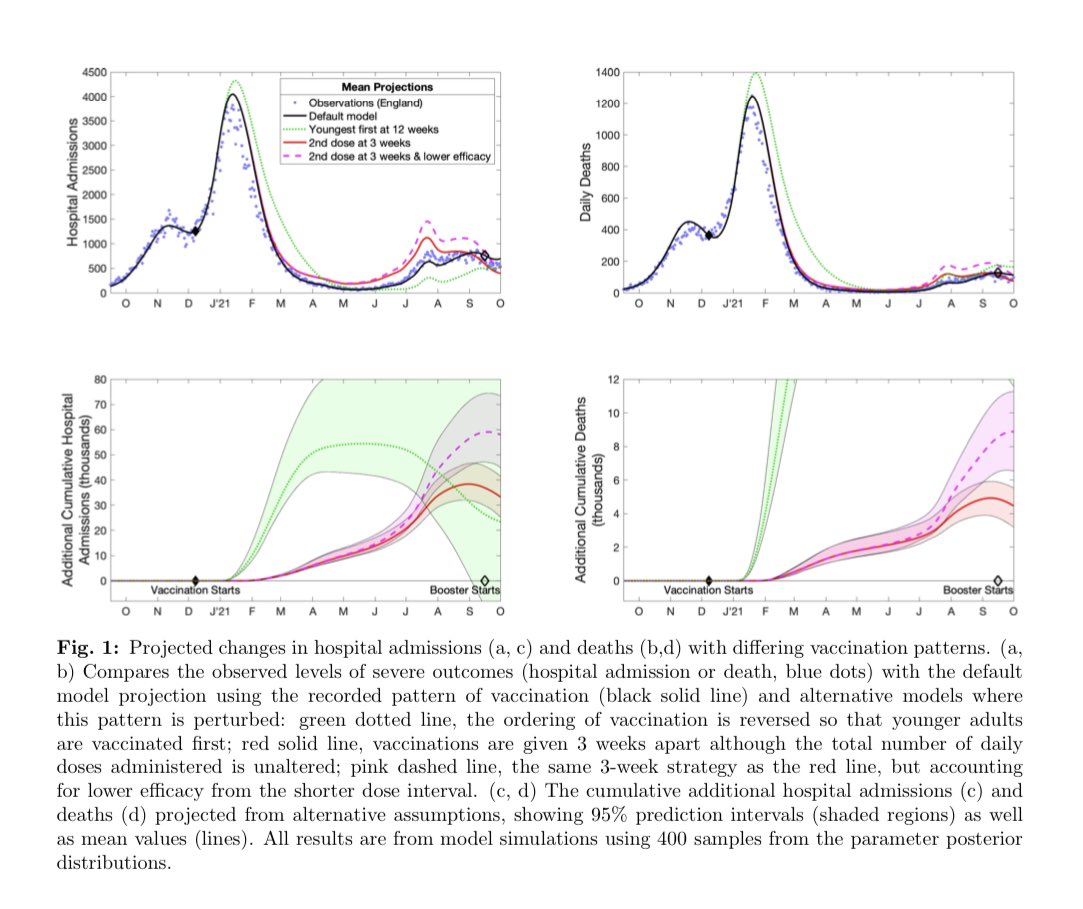
Little is known about the protection following prior infection with different #SARS2 variants, #COVID19 vaccination, and a combination of the two (hybrid immunity) in #adolescents. 1/
A new study from #England estimated protection following previous infection and vaccination against symptomatic PCR-confirmed delta & omicron (BA.1 or BA.2) variants in 11-17-year-olds using a test-negative case-control design. 2/
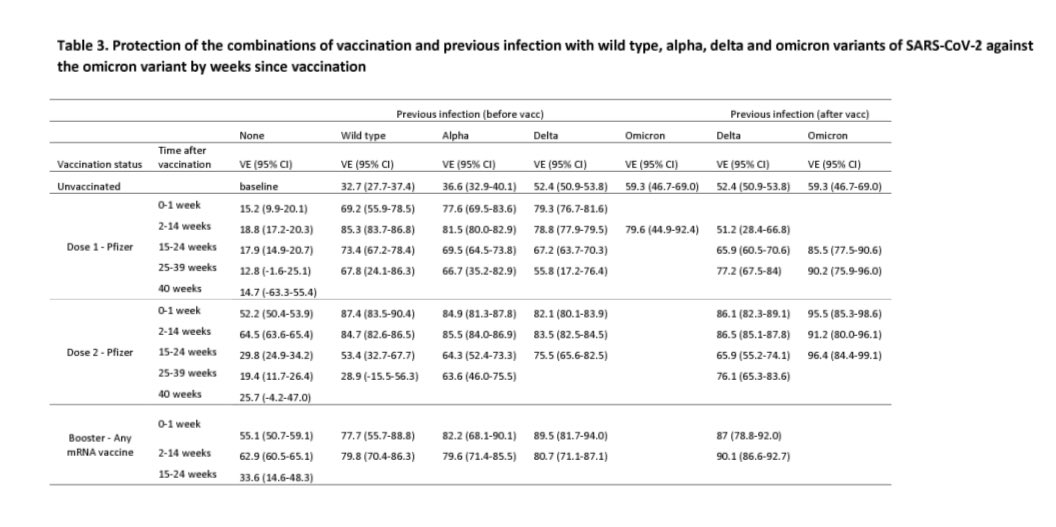
In unvaccinated adolescents, prior infection with WT, Alpha or Delta provided greater protection against subsequent Delta infection than subsequent Omicron; prior omicron infection provided the highest protection against omicron reinfection 3/ 

In infection-naive adolescents, #vaccination provided lower protection against symptomatic omicron infection than delta, peaking at 64.5% 2-14 days after dose two and 62.9% 2-14 weeks after dose three, with rapidly waning protection after each dose. 4/ 

Previously infected & vaccinated adolescents had the highest protection, irrespective of primary infecting SARS2 strain.
The highest protection ag Omicron was observed in vaccinated adolescents w/ prior omicron infection, reaching 96.4% at 15-24 weeks post dose two. 5/


The highest protection ag Omicron was observed in vaccinated adolescents w/ prior omicron infection, reaching 96.4% at 15-24 weeks post dose two. 5/


Key findings:
1-All variants provide some protection against symptomatic reinfection & vaccination adds to protection.
2-Vaccination provides low-to-moderate protection against symptomatic omicron infection, with waning protection after each dose.
6/
1-All variants provide some protection against symptomatic reinfection & vaccination adds to protection.
2-Vaccination provides low-to-moderate protection against symptomatic omicron infection, with waning protection after each dose.
6/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh