1/They say form follows function! Brain #MRI anatomy is best understood in terms of both form & function
A #tweetorial on how to remember important functional #brain #anatomy
#meded #medtwitter #neurosurgery #neurology #neurorad #FOAMed #FOAMrad #radiology #medstudent #radres
A #tweetorial on how to remember important functional #brain #anatomy
#meded #medtwitter #neurosurgery #neurology #neurorad #FOAMed #FOAMrad #radiology #medstudent #radres

2/Let’s start at the top. At the vertex is the superior frontal gyrus. This is easy to remember, bc it’s at the top—and being at the top is superior. It’s like the superior king at the top of the vertex. 
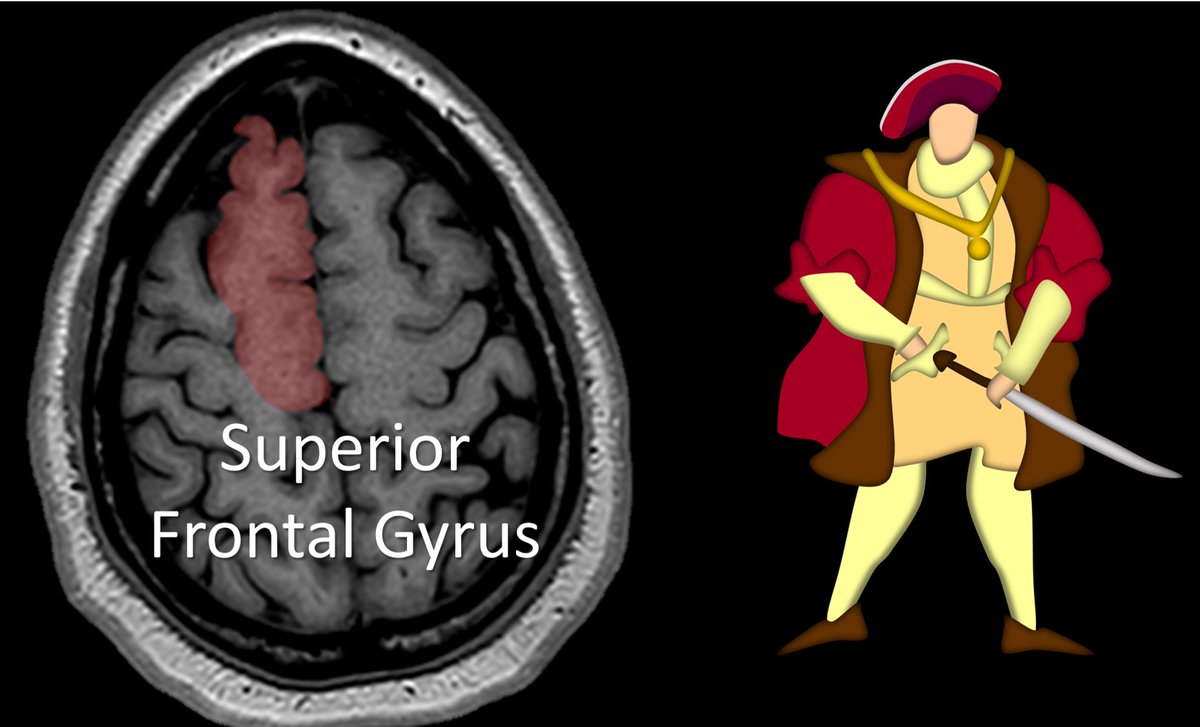
3/It is also easy to recognize on imaging. It looks like a big thumb pointing straight up out of the brain. I always look for that thumbs up when I am looking for the superior frontal gyrus (SFG) 

4/The SFG contains the supplementary motor area or SMA. As the name suggests, SMA contains a motor region—but not as expected, it also contains a verbal area. I remember that the motor portion is behind the language area bc we all walk before we talk, so motor comes before verbal 

5/Next to the superior frontal gyrus is the middle frontal gyrus. It is important for verbal memory. I think it looks like the knuckles of a hand 
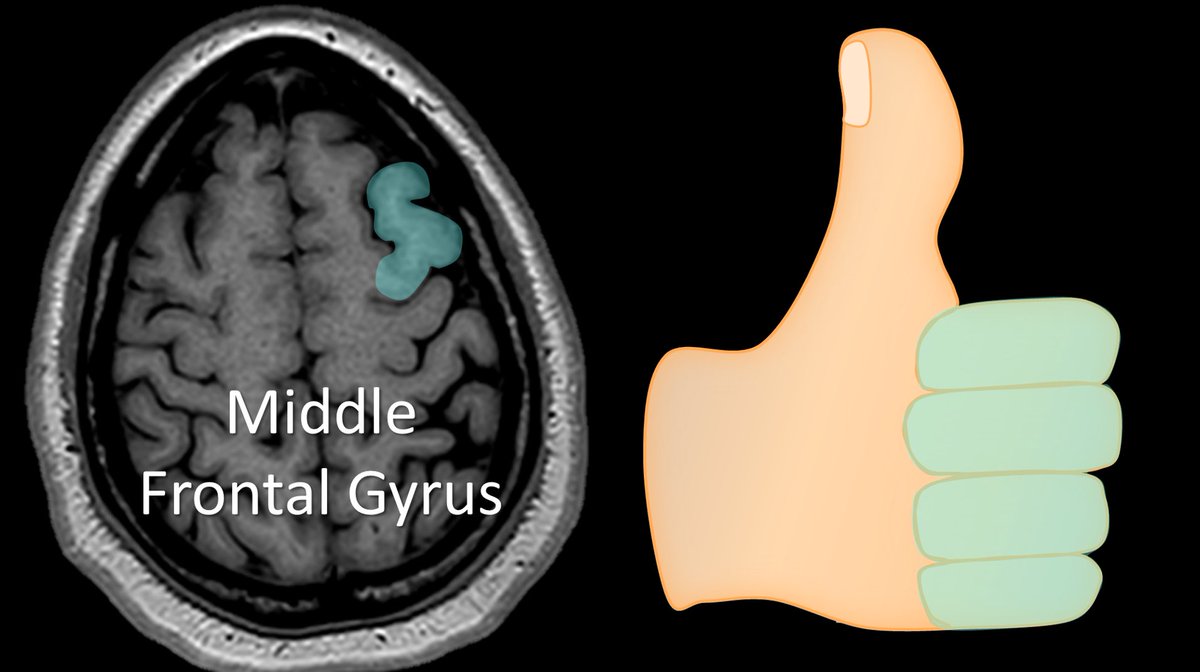
6/So every time I read a brain MRI, I look at the vertex for the hand giving me the thumbs up. The thumb is the superior frontal gyrus, and next to it, the curved knuckles of the middle frontal gyrus 

7/The superior frontal gyrus crashes into the motor strip or pre central gyrus. This is how I like to find the motor cortex. I follow the thumb back until it crashes into a gyrus—and I know that gyrus is the motor strip 
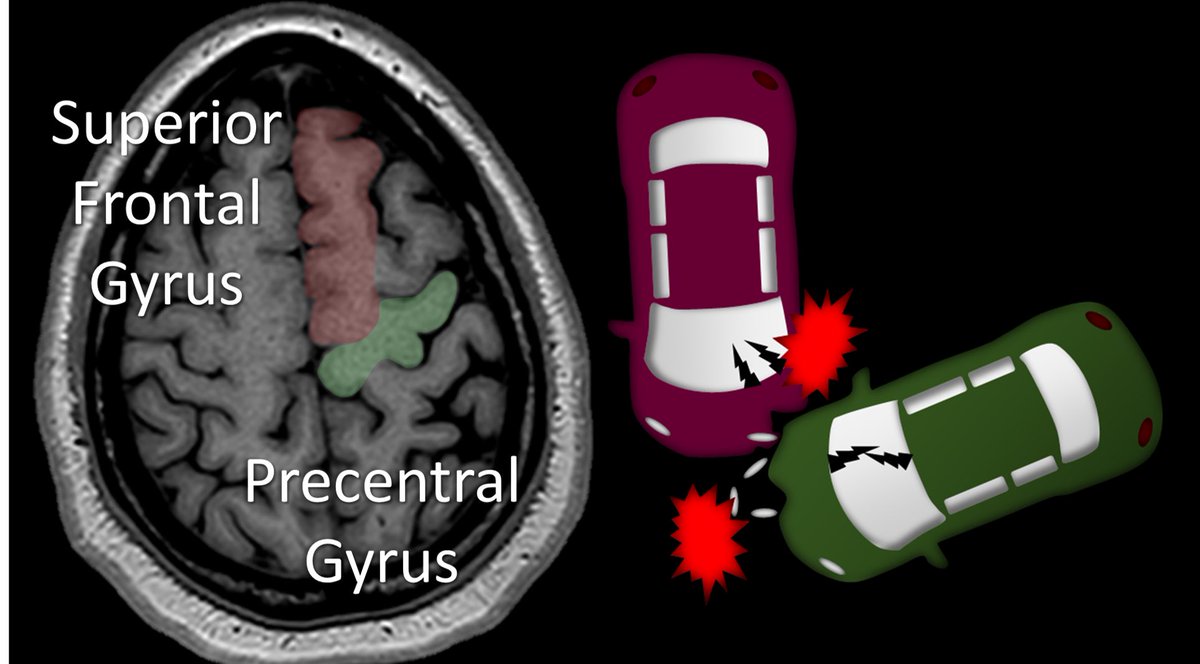
8/The motor area of the superior frontal gyrus is right next to the motor cortex. I remember this bc when two cars crash head on, it’s their motors that crash into each other—so the motor area of the SMA crashes into the main motor strip. 
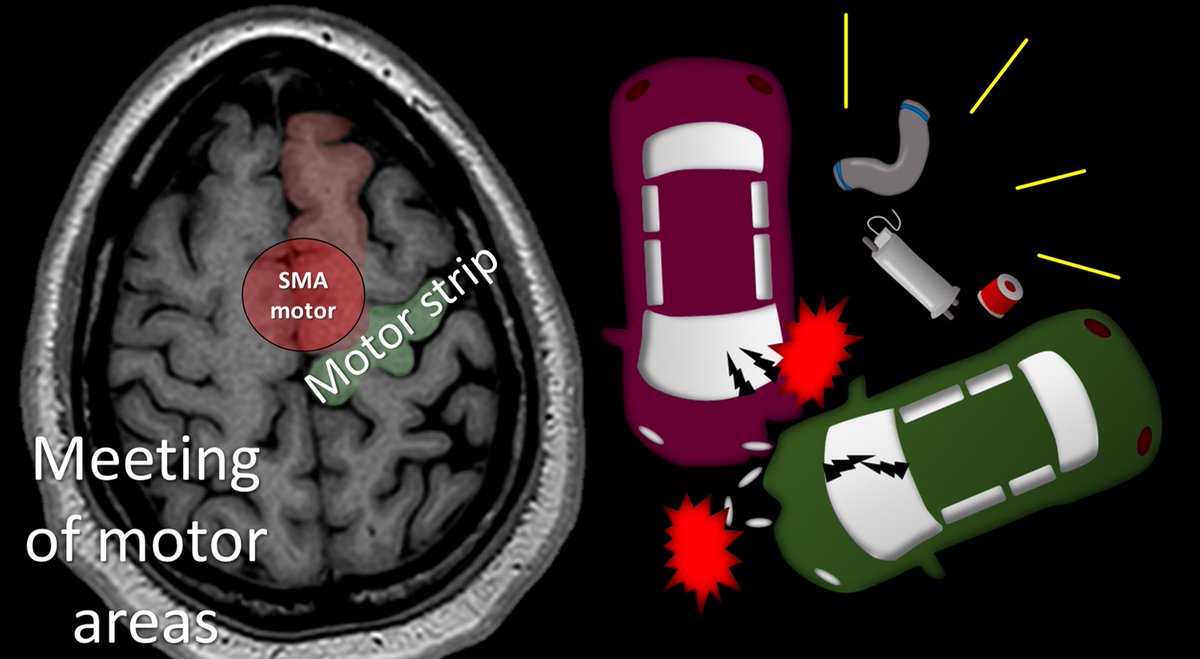
9/You can confirm the motor strip by looking for the hand motor region. This is uniquely shaped like an Omega. You can remember that the hand motor region is shaped like an Omega bc Omega is a fancy watch brand and you wear watches near your hand 
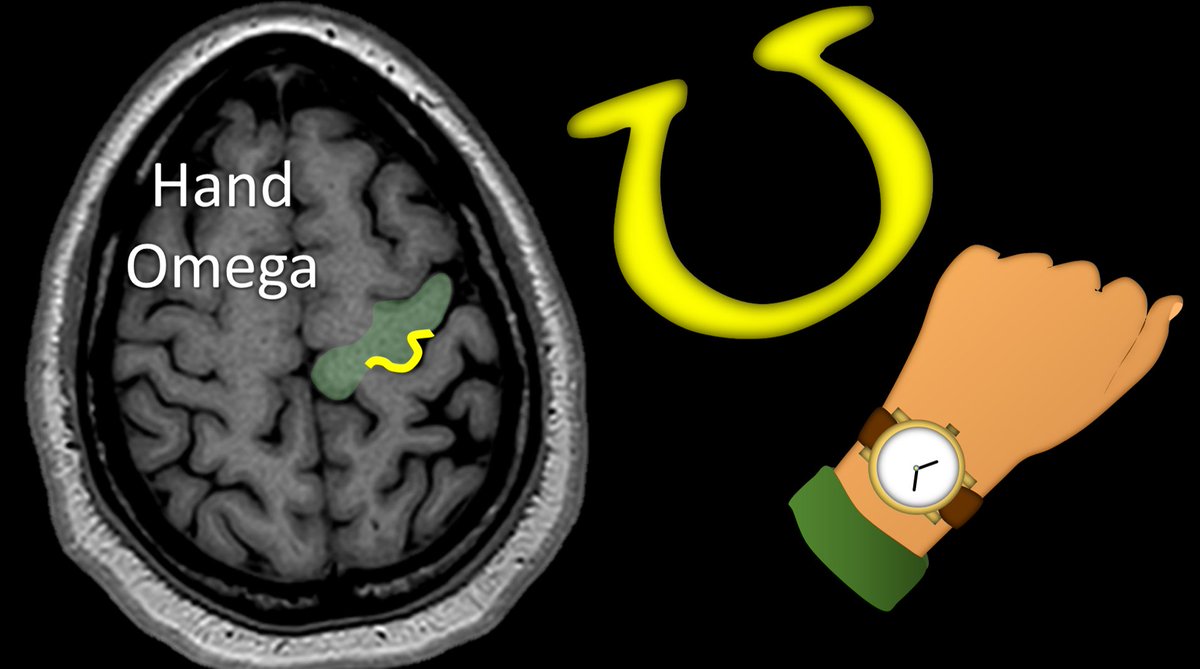
10/Motor strip goes into to the paracentral lobule, which connects the motor strip & main sensory strip. I think it looks like the “C” on Coach brand purses. I remember this bc this is eloquent cortex, some might say elegant—& elegant people own fancy brands like Coach & Omega 
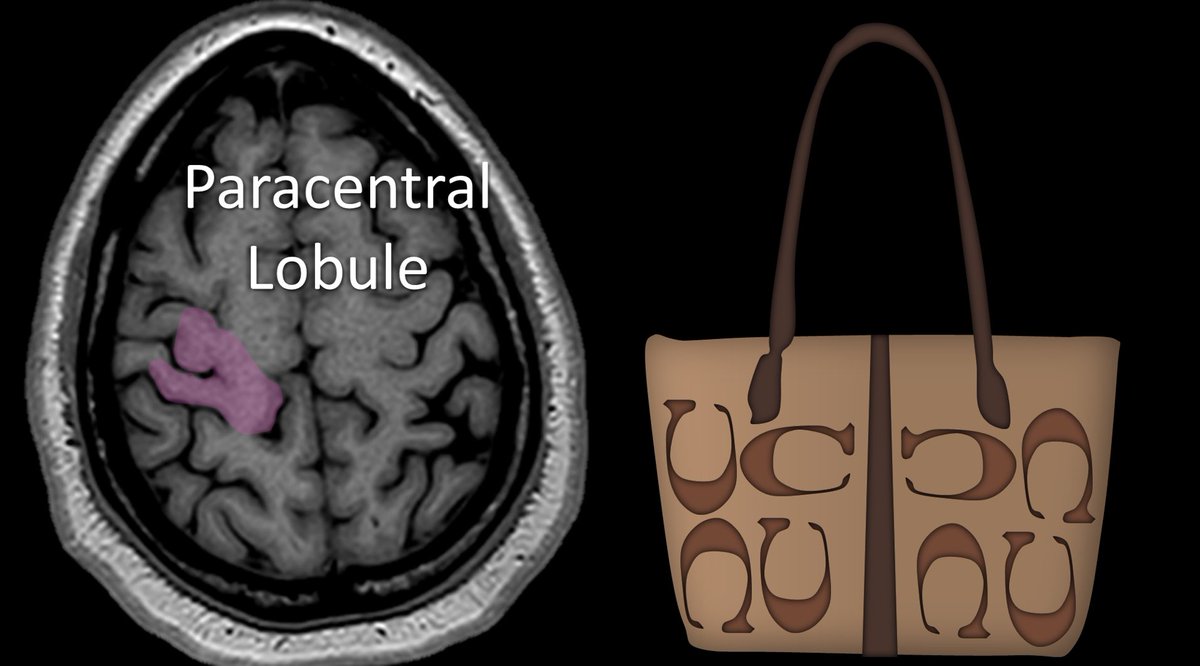
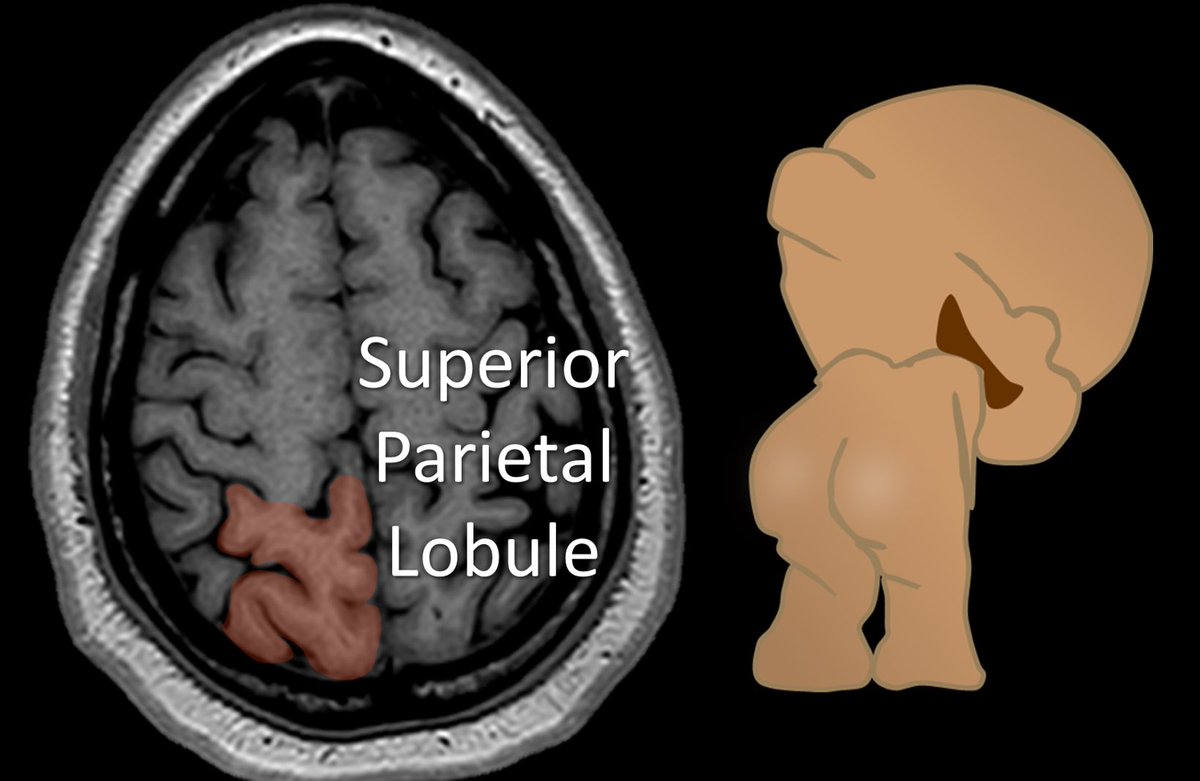
11/Finally, the cortex behind the sensory strip is the superior parietal lobule. It is the butt of the functional regions at the vertex. It is important for spatial orientation and hand function—so it makes sense that it sits right behind the hand motor and sensory cortices 
12/So on every brain MRI I read, I go to the vertex & look for:
1. A thumbs up
2. Luxury brands around the eloquent cortex
3. The functional cortex backside (superior parietal lobule)
Hopefully, you will now be eloquent when it comes to functional brain anatomy! 😜
1. A thumbs up
2. Luxury brands around the eloquent cortex
3. The functional cortex backside (superior parietal lobule)
Hopefully, you will now be eloquent when it comes to functional brain anatomy! 😜

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















