HISTORIC THANKSGIVING AND THE ARMY
HAPPY THANKSGIVING FROM THE U.S. ARMY CENTER OF MILITARY HISTORY!
Thanksgiving wasn’t always the fourth Thursday of November.
#Armyhistory #USArmy #Thanksgiving #TRADOC #MilitaryHistory
HAPPY THANKSGIVING FROM THE U.S. ARMY CENTER OF MILITARY HISTORY!
Thanksgiving wasn’t always the fourth Thursday of November.
#Armyhistory #USArmy #Thanksgiving #TRADOC #MilitaryHistory

While the holiday has roots dating back to the Pilgrims and post-harvest celebrations, it wasn’t until the late 17th century that a Thanksgiving-style holiday became customary throughout New England.
The New England colonists were accustomed to regularly celebrating "thanksgivings"—days of prayer thanking God for blessings. During the revolution, the Continental Congress decided to declare several days of thanksgiving to help inspire our troops to victory. 
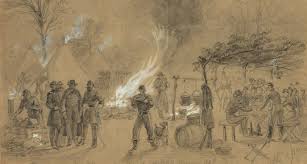
The first such day fell on Nov. 1, 1777, when news of victories against the British reached their ears. Gen. George Washington also called for a day of thanksgiving on Dec. 18, 1777, as a victory celebration for the colonial army’s win during the Battle of Saratoga that October. 

In 1789, Pres Washington was the first president to proclaim a day of national thanksgiving, which happened to be Nov 26, "a blessing to all the people by constantly being a Government of wise, just, and constitutional laws, discreetly and faithfully executed and obeyed..." 

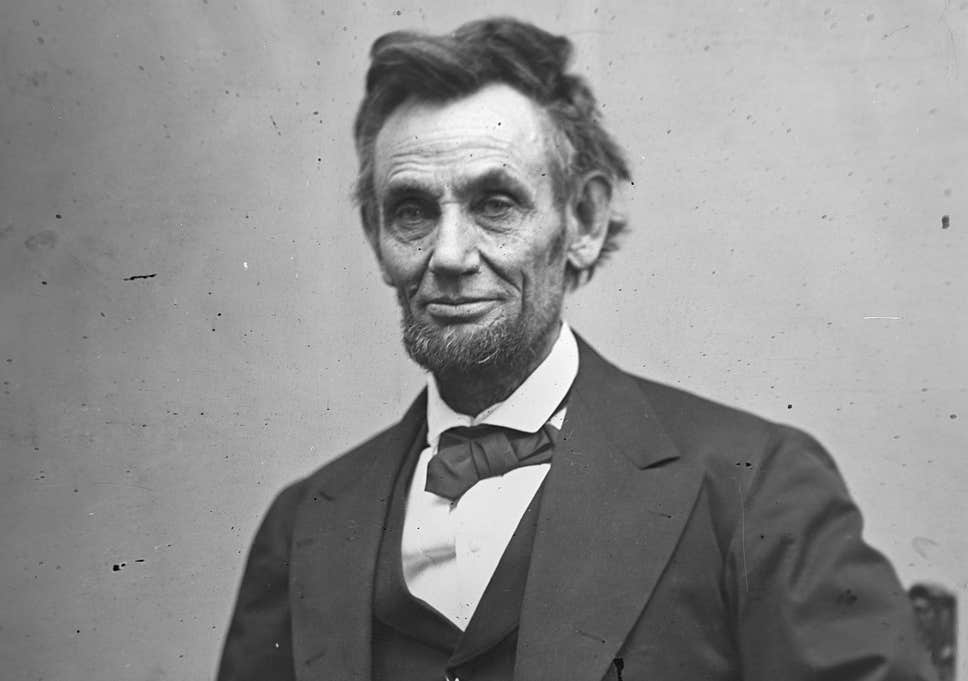
Sarah Josepha Buell Hale, a 74-year-old magazine editor, and the author of “Mary Had a Little Lamb”, wrote a letter to #AbrahamLincoln in 1863, urging him to have the "day of our annual Thanksgiving made a National and fixed Union Festival." 

President Lincoln declared Thanksgiving to fall on the last Thursday of November, and the modern holiday was created. He proclaimed a national day of "Thanksgiving and Praise to our beneficent Father who dwelleth in the Heavens.”
What are your Army Thanksgiving memories?
What are your Army Thanksgiving memories?
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


















