1/Having trouble remembering how to differentiate dementias on imaging?
Here’s a #tweetorial to show you how to remember the imaging findings in dementia & never forget!
#medtwitter #meded #neurorad #radres #dementia #alzheimers #neurotwitter #neurology #FOAMed #FOAMrad #PET
Here’s a #tweetorial to show you how to remember the imaging findings in dementia & never forget!
#medtwitter #meded #neurorad #radres #dementia #alzheimers #neurotwitter #neurology #FOAMed #FOAMrad #PET

2/The most common functional imaging used in dementia is FDG PET. And the most common dementia is Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
On PET, AD demonstrates a typical Nike swoosh pattern—with decreased metabolism in the parietal & temporal regions
On PET, AD demonstrates a typical Nike swoosh pattern—with decreased metabolism in the parietal & temporal regions

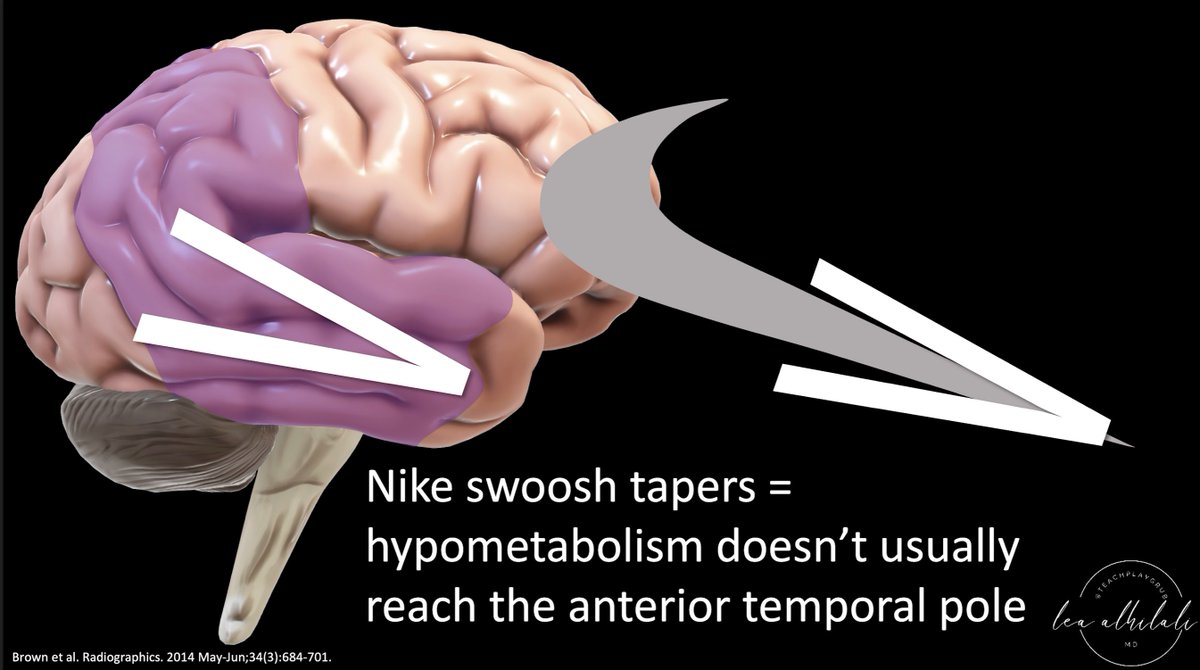
3/The swoosh rapidly tapers anteriorly—& so does hypometabolism in AD in the temporal lobe. It usually spares the anterior temporal poles.
So in AD look for a rapidly tapering Nike swoosh, w/hypometabolism in the parietal/temporal regions—sparing the anterior temporal pole
So in AD look for a rapidly tapering Nike swoosh, w/hypometabolism in the parietal/temporal regions—sparing the anterior temporal pole
4/Medially, in AD, there’s involvement of the precuneus & posterior cingulate. In fact, the earliest AD findings may be in the precuneus
So medially, instead of a Nike swoosh, you see an Adidas logo—w/a wedge in the region of the precuneus widening anteriorly to the cingulate
So medially, instead of a Nike swoosh, you see an Adidas logo—w/a wedge in the region of the precuneus widening anteriorly to the cingulate
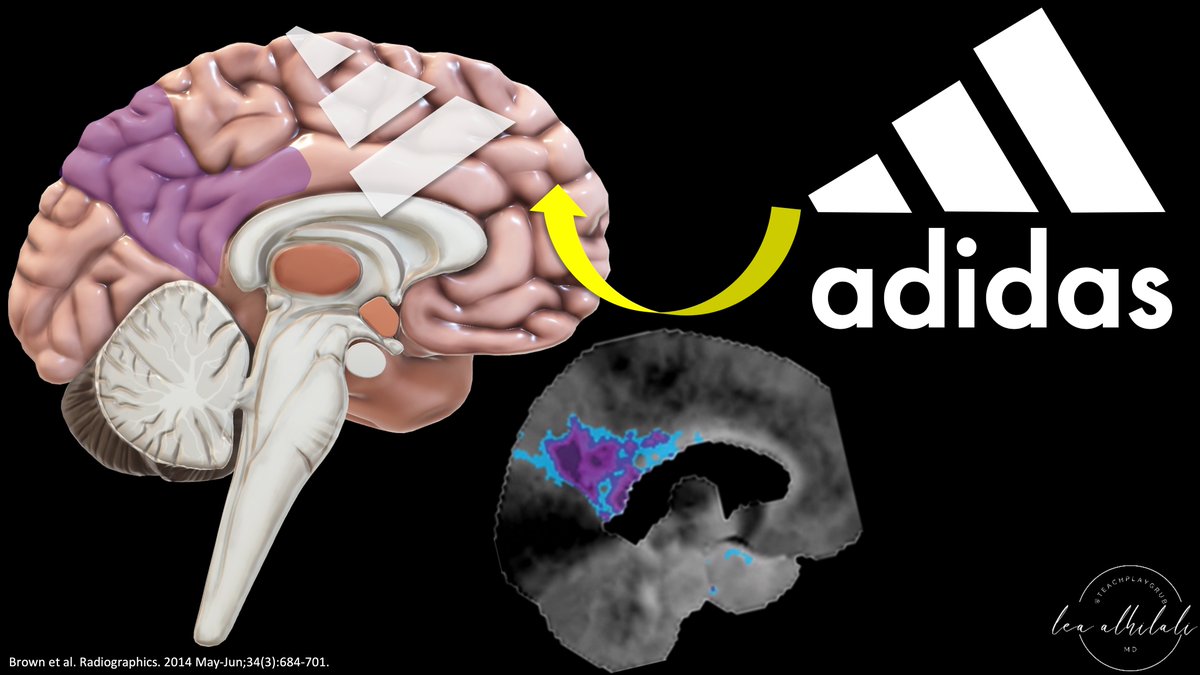
5/So in AD, look for the sneaker signs:
—Adidas logo medially in the region of the precuneus
—Nike swoosh along the parietal & temporal regions, sparing the anterior temporal pole.
So if you see sneaker logos—it’s AD. Just call it!
—Adidas logo medially in the region of the precuneus
—Nike swoosh along the parietal & temporal regions, sparing the anterior temporal pole.
So if you see sneaker logos—it’s AD. Just call it!

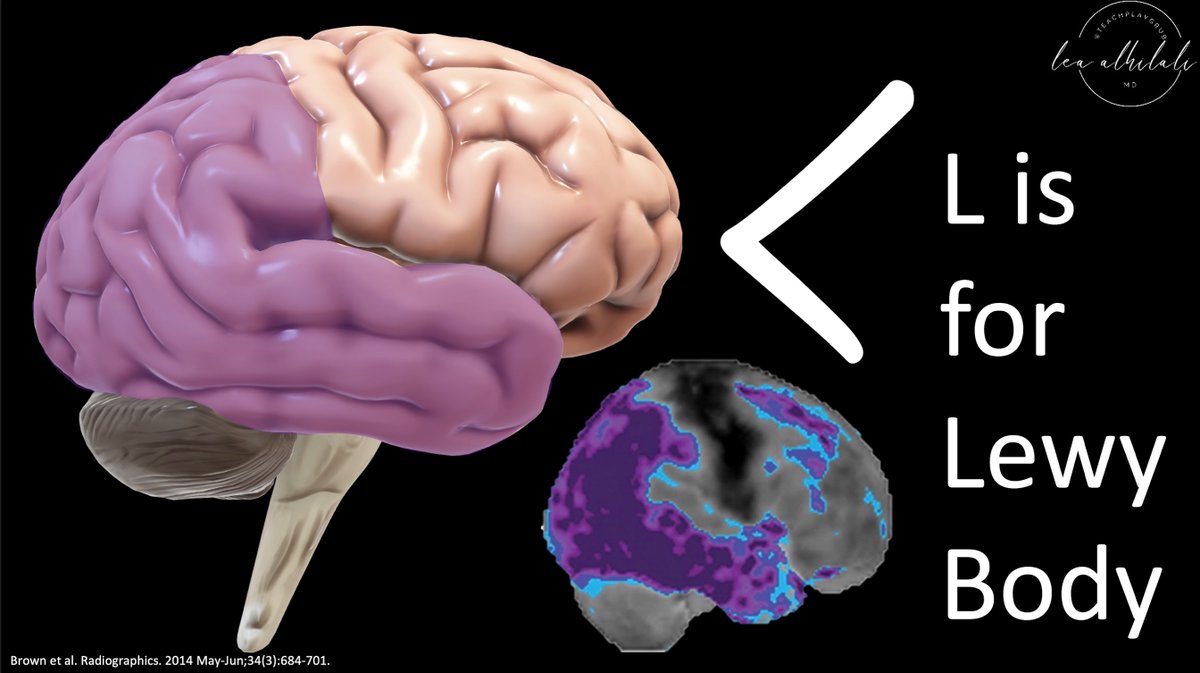
6/Dementia w/Lewy Bodies (DLB) also has temporoparietal hypometabolism—but it also involves the occipital cortex—a very specific finding for DLB. DLB also extends to the ant. temporal cortex.
Together, these regions of hypometabolism look more like an L. And Lewy starts w/an L
Together, these regions of hypometabolism look more like an L. And Lewy starts w/an L
7/Next is frontotemporal dementia. As one might expect, it has hypometabolism in…wait for it…the frontal & temporal regions. This is one for Captain Obvious. However, it is a little more complicated than that. 

8/Medially, frontotemporal dementia involves the anterior cingulate gyrus. I remember this bc the involvement of the anterior cingulate gyrus makes a hook—so it looks like a lowercase letter f—and frontotemporal starts with f 

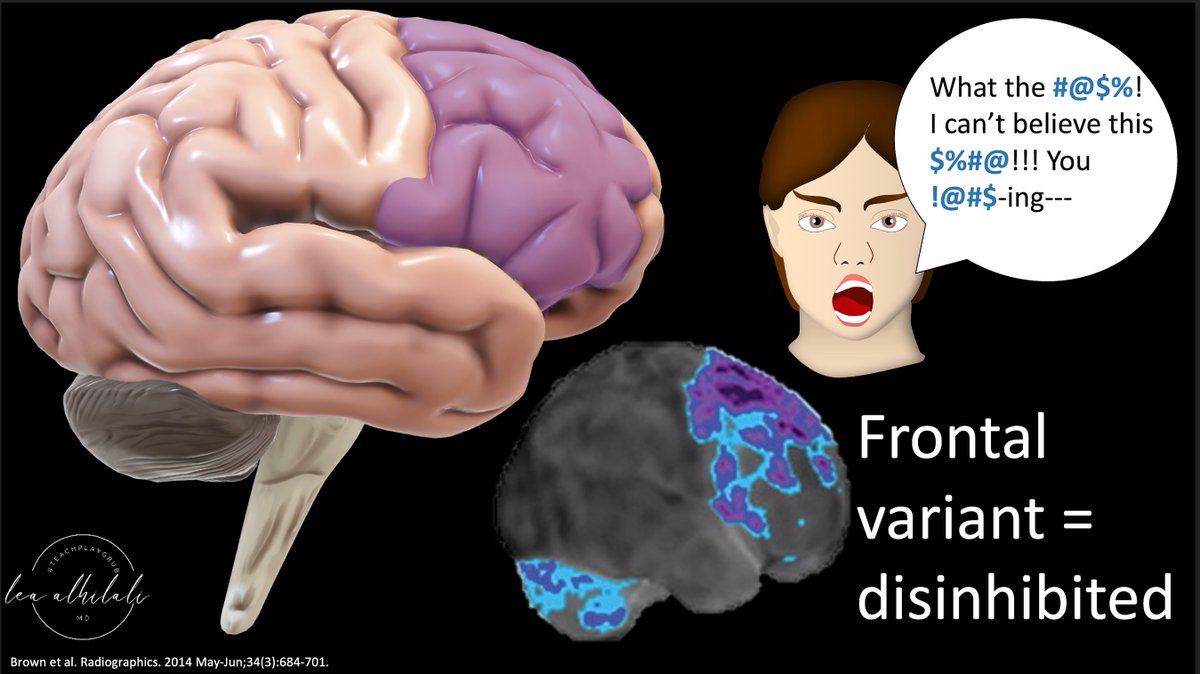
9/There are also variants of frontotemporal dementia that will not show the classic frontal & temporal involvement.
First, is the frontal variant. This only involves the frontal lobe. It presents w/disinhibition as one would expect to see with frontal lobe involvement
First, is the frontal variant. This only involves the frontal lobe. It presents w/disinhibition as one would expect to see with frontal lobe involvement
10/Temporal variant involves temporal lobe only. Language processing is here (Wernicke’s anyone?). So this presents w/language difficulties (semantic dementia)
So you DON’T have to have BOTH frontal & temporal involvement to have frontotemporal dementia bc there are variants
So you DON’T have to have BOTH frontal & temporal involvement to have frontotemporal dementia bc there are variants

11/Corticobasilar degeneration involves the sensorimotor cortex & basal ganglia.
I remember this bc CORTICObasilar goes along the CORTICOspinal tract—so it has hypometabolism at the home of the corticospinal tract, the sensorimotor cortex
I remember this bc CORTICObasilar goes along the CORTICOspinal tract—so it has hypometabolism at the home of the corticospinal tract, the sensorimotor cortex

12/You also see basal ganglia & thalamus hypometabolism in corticobasilar degeneration. This makes sense bc corticobasilar contains “BASilar” referring to the BASal ganglia
So the 2 regions of hypometabolism in corticobasilar degeneration are in the name—cortex & basal ganglia
So the 2 regions of hypometabolism in corticobasilar degeneration are in the name—cortex & basal ganglia

13/A rare dementia is posterior cerebral atrophy (PCA). As its name implies, hypometabolism is POSTERIOR—occipital cortex & post temporal lobe
I like to call it posterior CAPE atrophy bc the distribution looks a cape—w/arms (ant temporal lobes) sticking out from under the cape
I like to call it posterior CAPE atrophy bc the distribution looks a cape—w/arms (ant temporal lobes) sticking out from under the cape

14/You might say PCA looks like Lewy Body dementia—but PCA doesn’t usuallly involve the ant temporal lobes
So the ant temp lobe involvement that gave Lewy body its L shape is cut short—making the PCA distribution look more like a c than an L
Remember C is PCA & L is Lewy body
So the ant temp lobe involvement that gave Lewy body its L shape is cut short—making the PCA distribution look more like a c than an L
Remember C is PCA & L is Lewy body

15/Finally, vascular dementia has a variable distribution, depending on the regions infarcted (V is both for Vascular & Variable)
These patients may have wedged shaped regions of hypometabolism corresponding to cortical infarcts—remember this bc a wedge is just an inverted V.
These patients may have wedged shaped regions of hypometabolism corresponding to cortical infarcts—remember this bc a wedge is just an inverted V.

16/So now you know the patterns of hypometabolism on PET for the major dementias
This list isn’t all inclusive & there can be variations or even mixed dementias
But hopefully this gives you a starting point you won’t soon forget!
This list isn’t all inclusive & there can be variations or even mixed dementias
But hopefully this gives you a starting point you won’t soon forget!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















