#JustPublished!
Autumn #vaccination campaigns focused on older age groups and other high-risk populations are key to decrease impact of #COVID19.
Read full report: bit.ly/3ZJgEWk
Press release: bit.ly/3MdQjwJ
Autumn #vaccination campaigns focused on older age groups and other high-risk populations are key to decrease impact of #COVID19.
Read full report: bit.ly/3ZJgEWk
Press release: bit.ly/3MdQjwJ
To decrease the impact of #COVID19 hospitalisations and mortality, countries should plan for a continued roll-out of #COVID19vaccines.
Efforts should focus on protecting older adults & other vulnerable groups, such as those with underlying comorbidities & the immunocompromised.



Efforts should focus on protecting older adults & other vulnerable groups, such as those with underlying comorbidities & the immunocompromised.




According to #ECDC surveillance data, with every new wave of #COVID19 infection, individuals in older age groups are more likely to be hospitalised.
Data suggests persisting #SARSCoV2 transmission in EU/EEA & therefore, a continuous risk of severe disease for vulnerable groups.
Data suggests persisting #SARSCoV2 transmission in EU/EEA & therefore, a continuous risk of severe disease for vulnerable groups.

Mathematical models detailed in the report show that an autumn 2023 vaccination programme with very high vaccine uptake targeting individuals 60+ is expected to prevent up to 32% of #COVID19-related hospitalizations across the EU/EEA. 

Assuming a very high vaccine uptake, combining an autumn 2023 vaccination programme for 60+ with a spring 2023 vaccination campaign for 80+ is expected to prevent up to 44% of #COVID19-related hospitalizations. 
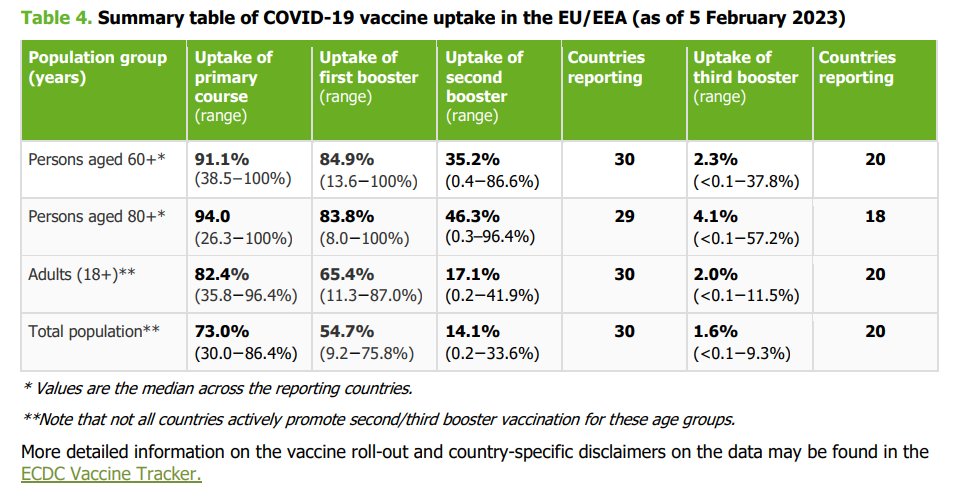
In conducting the mathematical modelling, #ECDC experts took into consideration the knowledge gathered on a number of factors including waning vaccine effectiveness, age groups targeted by the recent autumn/winter 2022/23 vaccine booster campaign & 2022 epidemiological situation. 

National decisions on the best strategies for the local epidemiological context should be undertaken taking into account their specific context, esp. considering the likely uptake. Uncertainties on future epidemiological developments remain & this may influence future decisions. 

#PublicHealth authorities may consider developing targeted communication focused on reaching high-priority groups through trusted channels, providing clear information on groups recommended for vaccination, the type of vaccines available & timing.
More: bit.ly/3MdQjwJ
More: bit.ly/3MdQjwJ
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh