BREAKING🔔 The 19th paper from G2P-Japan🇯🇵 is out at Lancet Infectious Diseases @TheLancetInfDis . We elucidated the virological characteristics of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of interest, XBB.1.16 (aka #Arcturus) Please RT🔥 1/
thelancet.com/journals/lanin…
thelancet.com/journals/lanin…
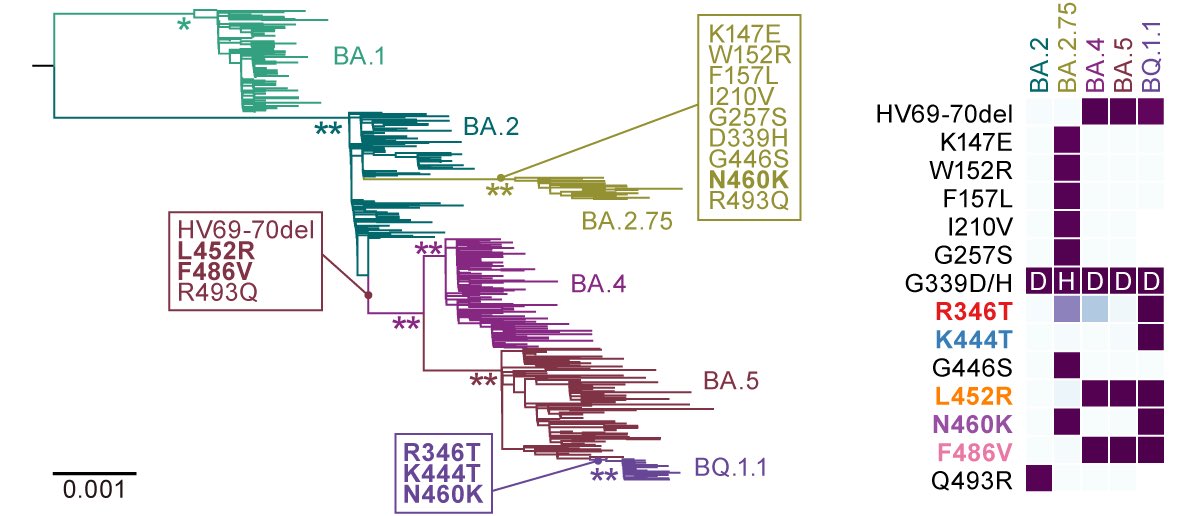
XBB.1.16 = XBB.1 + #F486P, #E180V, and #T478K in spike.
cf. XBB.1.5 = XBB.1 + #F486P in spike (i.e., XBB.1.16 = XBB.1.5 + #E180V and #T478K in spike). 2/
cf. XBB.1.5 = XBB.1 + #F486P in spike (i.e., XBB.1.16 = XBB.1.5 + #E180V and #T478K in spike). 2/

The relative basic reproduction number (Re) of XBB.1.16 is greater than that of XBB.1.5 in 🇮🇳🇺🇸🇸🇬🇦🇺, suggesting that XBB.1.16 will outcompete XBB.1.5 in the future. 4/ 

Pseudovirus experiments showed the increased infectivity by #T478K mutation. In contrast, #E180V decreased the infectivity. In total, the infectivity of XBB.1.16 was comparable to that of XBB.1.5. 5/ 

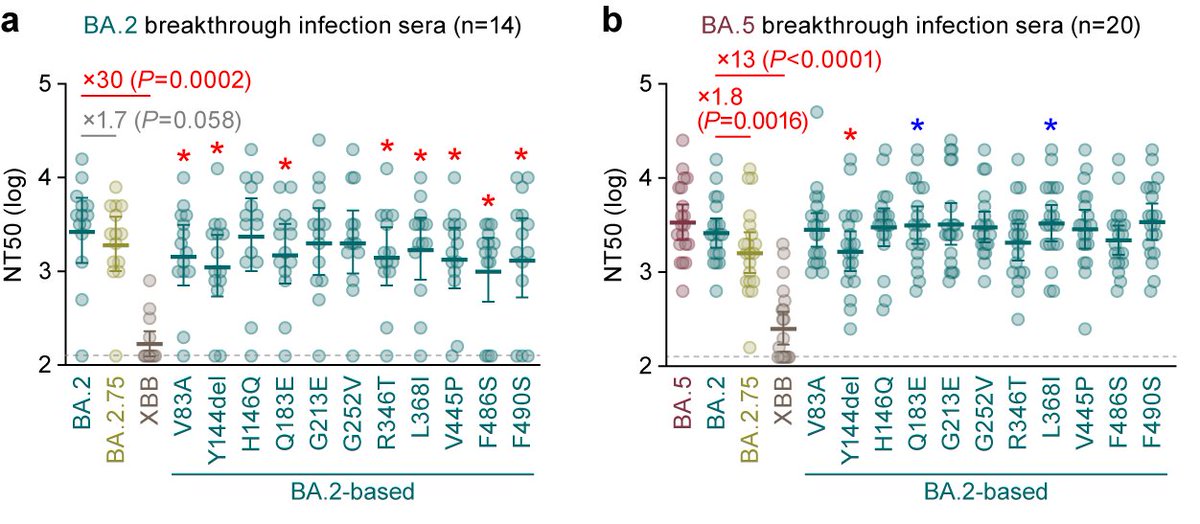
Neutralization assay showed that XBB.1.16 is robustly resistant to BA.2 breakthru infection sera (18-fold vs B.1.1) and BA.5 breakthru infection sera (37-fold vs B.1.1). 6/ 

Antigenic cartography shows that the antigenicity of XBB.1.16 is slightly different from that of XBB.1.5. 7/ 

Importantly, XBB.1.16 as well as the other XBB subvariants are sensitive to #sotrovimab, a therapeutic monoclonal antibody. 8/ 
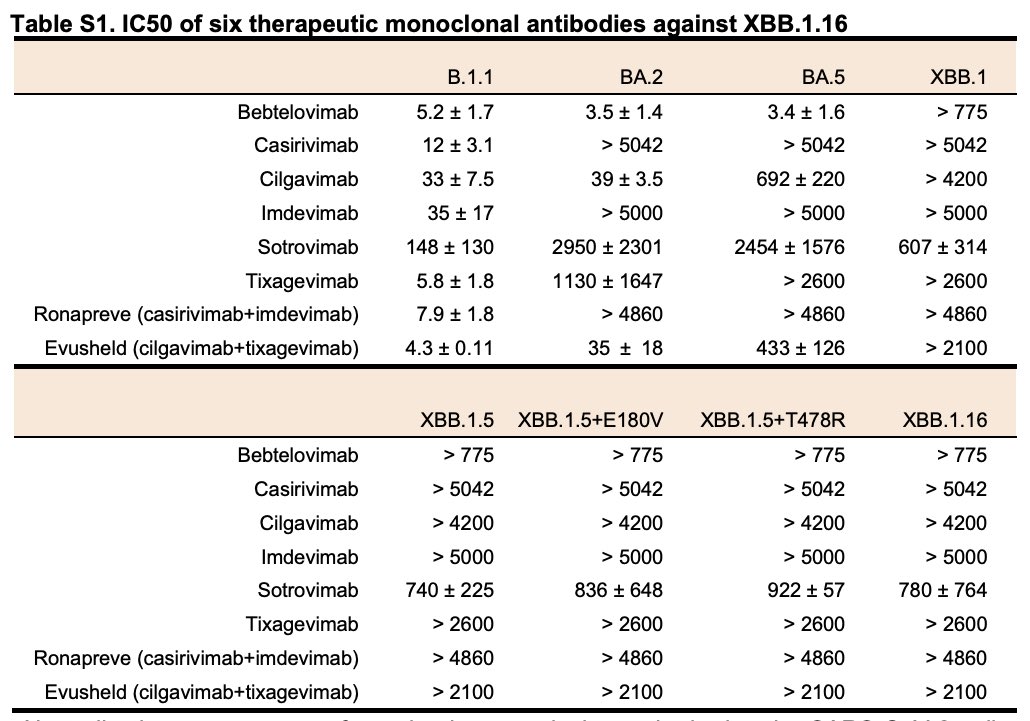
In sum, our results suggest the increased fitness of XBB.1.16 may be due to (1) different antigenicity from XBB.1.5; and/or (2) the mutations in the non-S viral protein(s) that may contribute to increased viral growth efficiency. 9/9
PS - Yunlong @yunlong_cao explains more about XBB.1.16 and other new variants based on his data. This should add to and increase our knowledge🔥
https://twitter.com/yunlong_cao/status/1649523529422082048
Correction!
XBB.1.16 = XBB.1 + #F486P, #E180V, and #T478R in spike. cf. XBB.1.5 = XBB.1 + #F486P in spike (i.e., XBB.1.16 = XBB.1.5 + #E180V and #T478R in spike).
XBB.1 and XBB.1.5 harbor T478'K', while XBB.1.16 harbors T478'R'.
XBB.1.16 = XBB.1 + #F486P, #E180V, and #T478R in spike. cf. XBB.1.5 = XBB.1 + #F486P in spike (i.e., XBB.1.16 = XBB.1.5 + #E180V and #T478R in spike).
XBB.1 and XBB.1.5 harbor T478'K', while XBB.1.16 harbors T478'R'.
Correction (again)!
Pseudovirus experiments showed the increased infectivity by #T478R (not T478’K’!) mutation. In contrast, #E180V decreased the infectivity. In total, the infectivity of XBB.1.16 was comparable to that of XBB.1.5. 5/
Pseudovirus experiments showed the increased infectivity by #T478R (not T478’K’!) mutation. In contrast, #E180V decreased the infectivity. In total, the infectivity of XBB.1.16 was comparable to that of XBB.1.5. 5/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter