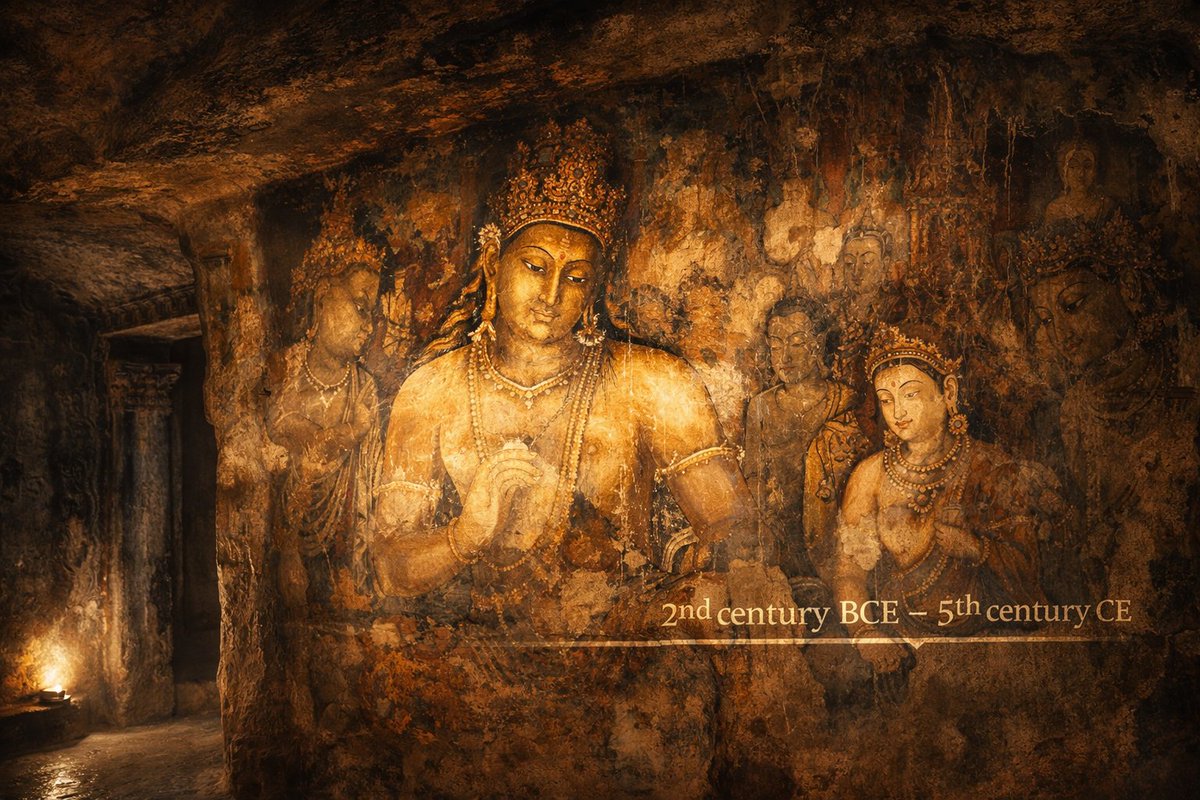
Bandhavgarh Madhyapradesh had a modern society 2000 years ago. Man made Water bodies besides other #Hindu Artefacts have been found.
InPic Sleeping #Vishnu
#Archaeology
freepressjournal.in/india/madhya-p…
InPic Sleeping #Vishnu
#Archaeology
freepressjournal.in/india/madhya-p…

Varah with Conch shell
Bandhavgarh, Madhyapradesh
300-600 ce
#Archaeology #Hinduism #हिंदुत्व
/2
timesnownews.com/viral/2000-yea…
Bandhavgarh, Madhyapradesh
300-600 ce
#Archaeology #Hinduism #हिंदुत्व
/2
timesnownews.com/viral/2000-yea…

Varah
Bandhavgarh, Madhyapradesh
300-600 ce
#Archaeology #hindutva #हिंदुत्व
/3
dailypioneer.com/2022/pioneer-e…
Bandhavgarh, Madhyapradesh
300-600 ce
#Archaeology #hindutva #हिंदुत्व
/3
dailypioneer.com/2022/pioneer-e…

Murtis of #Hindu Bhagwan including Ganesh and Parvati found in Bandhavgarh, Madhyapradesh
#Archaeology #hindutva #हिंदुत्व
4/
#Archaeology #hindutva #हिंदुत्व
4/

An inscription in one of the caves found in Bandhavgarh Madhyapradesh
#Archaeology #Hindutva #हिंदुत्व
5/
#Archaeology #Hindutva #हिंदुत्व
https://twitter.com/ASIGoI/status/1575130296013312000?t=uPg25k_EBGqQ7hFwx-ZzKw&s=19
5/

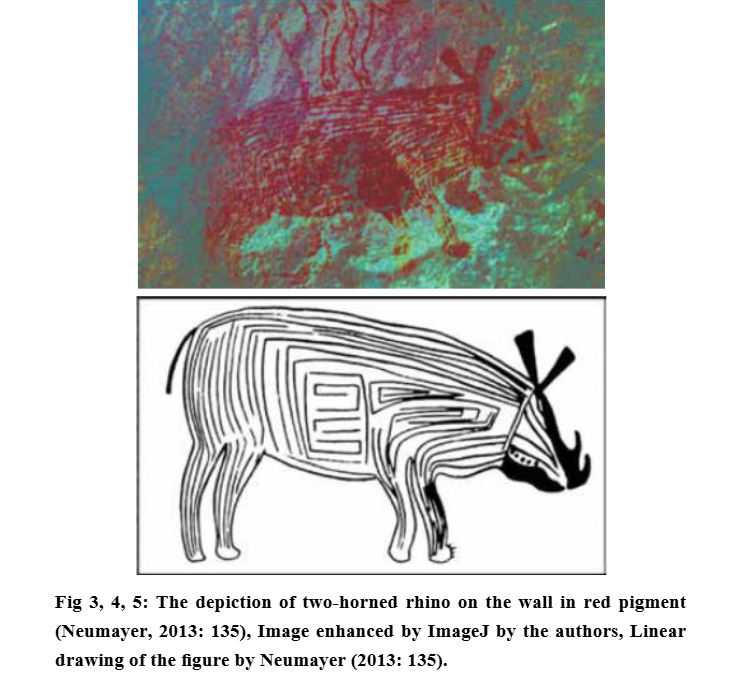
Master of Animals or #Krishna with his herd on Bandhavgarh Caves, Madhyapradesh.
This depiction was earliest noted 12000 ybp in Konkan Petroglyphs and later in IVSC seals 4500 ybp.
It also confirms #continuity of Hindu beliefs.
#Archaeology #Hindutva
#हिंदूत्व
6/
This depiction was earliest noted 12000 ybp in Konkan Petroglyphs and later in IVSC seals 4500 ybp.
It also confirms #continuity of Hindu beliefs.
#Archaeology #Hindutva
#हिंदूत्व
6/

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh