The findings of this one suggest that weight loss during a high-intensity exercise program is likely to lead to improved substrate oxidation during exercise. 
- This study is a secondary analysis of the “Effects of SIT on substrate oxidation in adults living with and without obesity: i-FLEX study”...
...a clinical trial investigating changes in substrate oxidation and insulin sensitivity following 4 weeks of sprint interval training (SIT) between individuals with and without obesity.
- The primary objective of this analysis was to further understand the role short-term sprint interval training-induced weight loss has on resting and submaximal fat oxidation and investigate their association with exercise performance, body composition, and metabolic outcomes.
- 4 weeks of sprint interval training-induced weight loss were likely to lead to decreases in RER and increases in fat oxidation during submaximal exercise compared to sprint interval training without weight loss. 
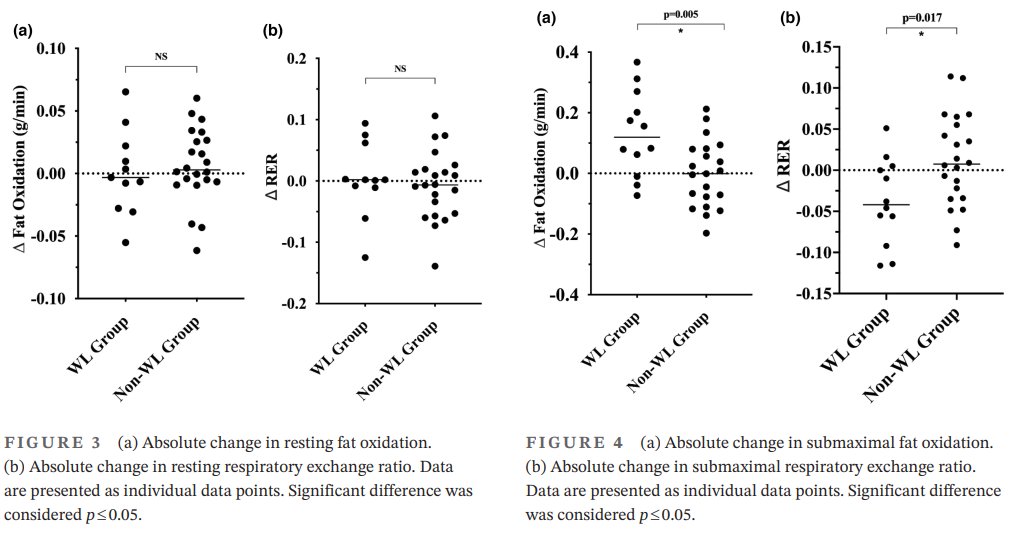
- Changes in fat oxidation following sprint interval training were correlated with exercise performance, changes in waist circumference, and fat mass. 

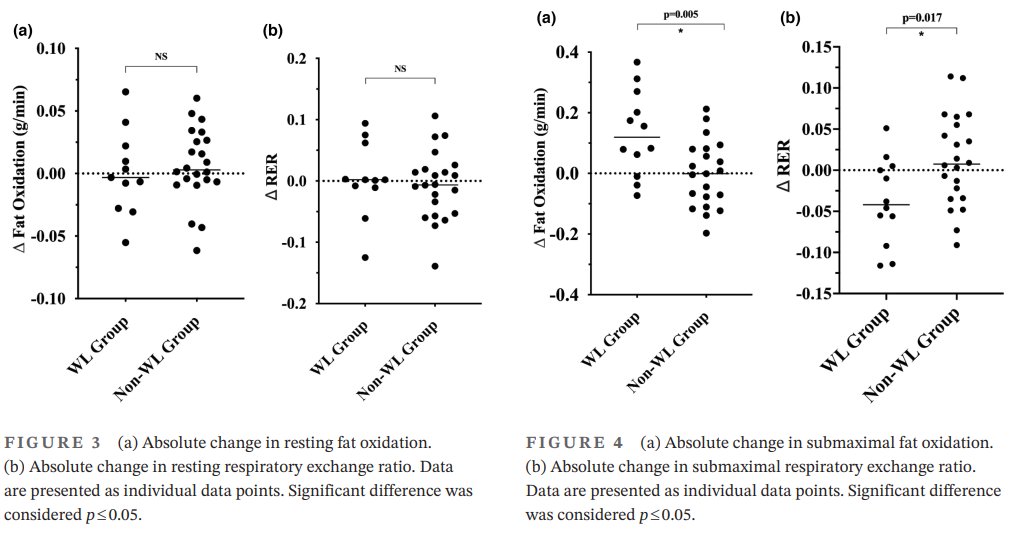
- No statistically significant improvements in substrate oxidation at rest were observed in either group.
The impact of sprint interval training with or without weight loss on substrate oxidation in adults: A secondary analysis of the i-FLEX study (open access)
doi.org/10.14814/phy2.…
#exercise #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit
doi.org/10.14814/phy2.…
#exercise #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter







