
Comparative Semiticist trying to leave his dark Indo-Europeanist past behind him. /ˈsuʃɑɹd/, /ˈsyʃɑɹt/, or /syˈʃaʁ/ preferred; /ˈsʌkhɑɹd/ dispreferred.
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


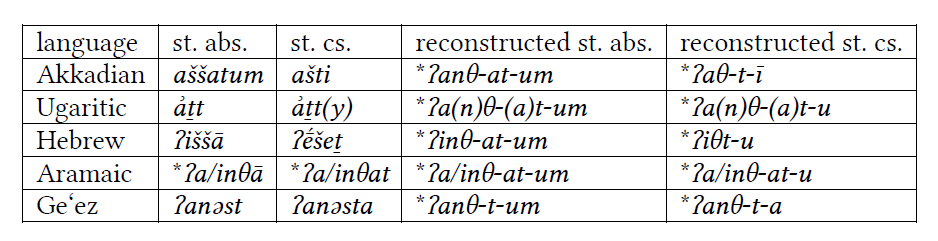
 This *-(a)t- is the feminine suffix. From the same consonantal root, we also find some other words: #Arabic ʔunθā 'feminine', #Amorite(!) /taʔnīθ-um/, predictably bizarre Modern South Arabian forms like #Jibbali teθ, etc. (for Ancient South Arabian, see below). 2/11
This *-(a)t- is the feminine suffix. From the same consonantal root, we also find some other words: #Arabic ʔunθā 'feminine', #Amorite(!) /taʔnīθ-um/, predictably bizarre Modern South Arabian forms like #Jibbali teθ, etc. (for Ancient South Arabian, see below). 2/11

 The pronunciations like Yahawashi etc. come from the idea that in the #Hebrew alphabet (especially the Paleo-Hebrew one), every letter represents a syllable. You can then read the original form of the name, יהושע (Paleo 𐤉𐤄𐤅𐤔𐤏) ‘Joshua’, as Ya-ha-wa-sha-i. Or something. 2/14
The pronunciations like Yahawashi etc. come from the idea that in the #Hebrew alphabet (especially the Paleo-Hebrew one), every letter represents a syllable. You can then read the original form of the name, יהושע (Paleo 𐤉𐤄𐤅𐤔𐤏) ‘Joshua’, as Ya-ha-wa-sha-i. Or something. 2/14 

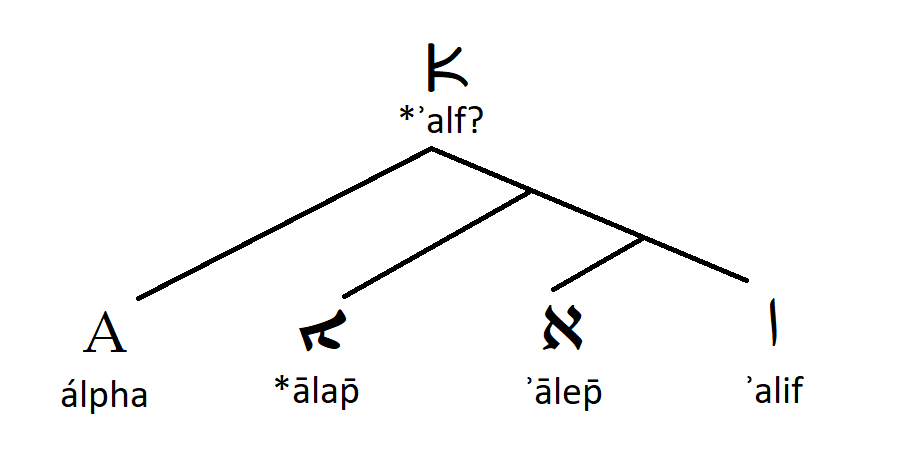
 That goes for names like "aleph". Sometimes you'll see reconstructed forms, like "ʾalp", which are closer to the #Greek names and partially also attested in the Septuagint of Psalm 119 (118 in Gk)—but there they're actually Hebrew too, of course. 2/10 en.katabiblon.com/us/index.php?t…
That goes for names like "aleph". Sometimes you'll see reconstructed forms, like "ʾalp", which are closer to the #Greek names and partially also attested in the Septuagint of Psalm 119 (118 in Gk)—but there they're actually Hebrew too, of course. 2/10 en.katabiblon.com/us/index.php?t…
https://twitter.com/bnuyaminim/status/1455915480208838665?s=20The III-weak plural ending ܘ- -aw as in ܚܙܘ ḥzaw 'they saw' turns into -au- before suffixes, written -ܐܘ- -ʔw- with an extra alaph to spell the hiatus (two vowels in a row). At least, this is the traditional explanation; forms like *ḥzaw-y turning to ḥzauy. 2/10

https://twitter.com/d_stoekl/status/1402892647744815109After a summary of his original argument, @IdanDershowitz moves on to discussing some major points of criticism.


 In Arabic, the *-iyu of the imperfect contracts to -ī, while the imperative adds i- before the cluster:
In Arabic, the *-iyu of the imperfect contracts to -ī, while the imperative adds i- before the cluster:
 For example, should Biblical Aramaic אַנְתְּה 'you (m.sg.)' be read as Ɂant or Ɂantə? (Yes, there's an extra ה at the end and yes, the Masoretes read shwa as a full vowel, not [ə]; that's all not relevant right now, you know what I mean.) 2/6
For example, should Biblical Aramaic אַנְתְּה 'you (m.sg.)' be read as Ɂant or Ɂantə? (Yes, there's an extra ה at the end and yes, the Masoretes read shwa as a full vowel, not [ə]; that's all not relevant right now, you know what I mean.) 2/6

 This talk is about #Biblical #Aramaic, attested in the books of #Ezra and #Daniel. Scholars have long debated the linguistic background of these texts, nearly always focusing on the consonantal text. But in the case of Biblical Aramaic, that only tells you half the story.
This talk is about #Biblical #Aramaic, attested in the books of #Ezra and #Daniel. Scholars have long debated the linguistic background of these texts, nearly always focusing on the consonantal text. But in the case of Biblical Aramaic, that only tells you half the story. 