
1/
Just out today (free) in @JAMASurgery
@Guyettef @Jjasonsperrymd @joshua_b_brown et al.
#TXA During Prehospital Transport in Patients at Risk for Hemorrhage After Injury: A Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial
jamanetwork.com/journals/jamas…
#staamptrial
Just out today (free) in @JAMASurgery
@Guyettef @Jjasonsperrymd @joshua_b_brown et al.
#TXA During Prehospital Transport in Patients at Risk for Hemorrhage After Injury: A Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial
jamanetwork.com/journals/jamas…
#staamptrial
2/
The role of #TXA has been the subject of varying debate.
This study asks if giving #TXA to #bleeding trauma patients in the #prehospital setting affects 30-day outcomes
This is a critical questions as #trauma remains a leading cause of death around the world
#StopTheBleed
The role of #TXA has been the subject of varying debate.
This study asks if giving #TXA to #bleeding trauma patients in the #prehospital setting affects 30-day outcomes
This is a critical questions as #trauma remains a leading cause of death around the world
#StopTheBleed
3/
It is crucial we look at point-of-injury methods to control hemorrhage and hopefully affect outcome.
Remember, as this paper shows, there is a significant portion of patients in the prehospital setting that suffer potentially preventable death
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25058244/
It is crucial we look at point-of-injury methods to control hemorrhage and hopefully affect outcome.
Remember, as this paper shows, there is a significant portion of patients in the prehospital setting that suffer potentially preventable death
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25058244/
4/
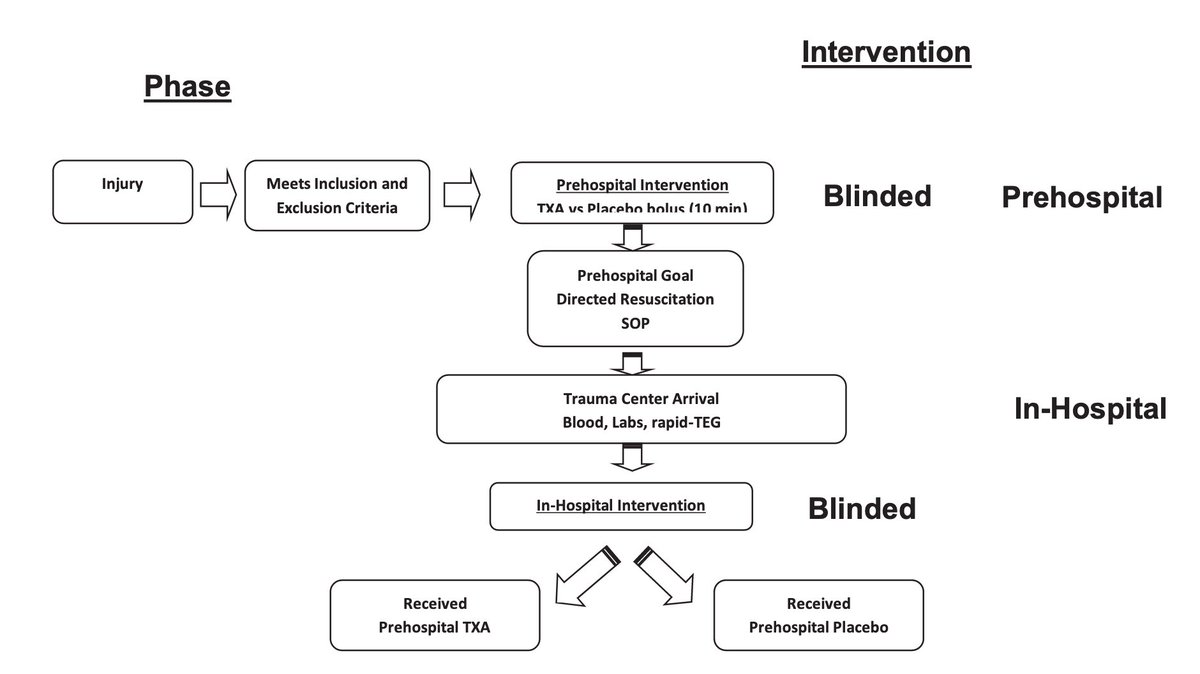
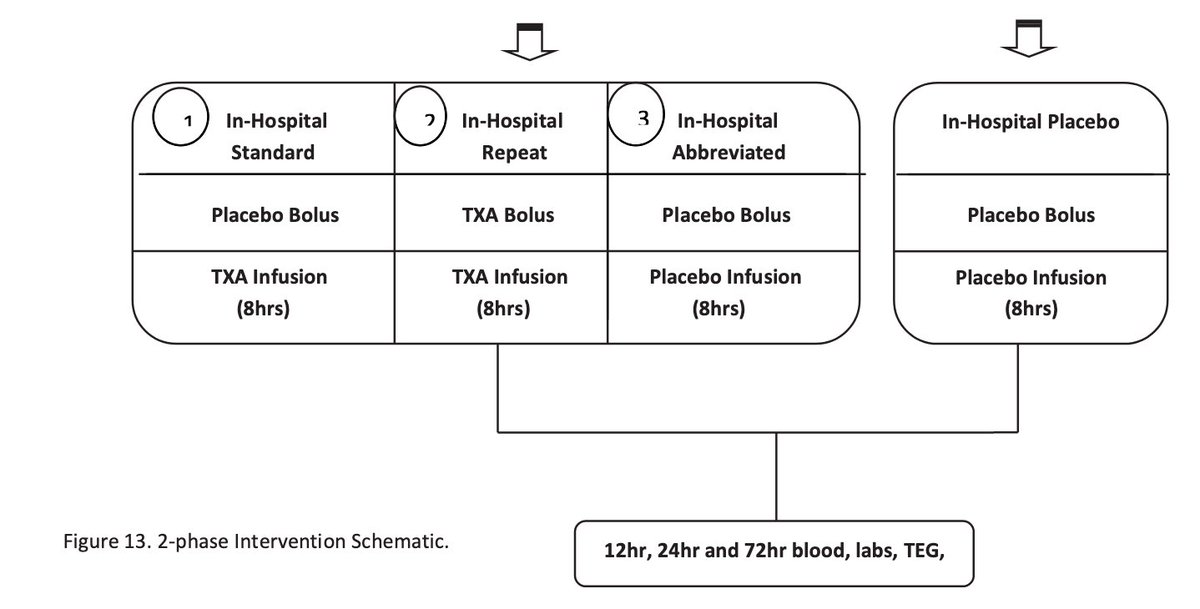
The authors conducted a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled RCT
4 US L1TC
May 1, 2015 to October 31, 2019
Treatment arm: 1g #TXA during helicopter transport.
On arrival to L1TC, this arm got either:
-no further #TXA
-1g infusion only
-1g bolus then 1g infusion

The authors conducted a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled RCT
4 US L1TC
May 1, 2015 to October 31, 2019
Treatment arm: 1g #TXA during helicopter transport.
On arrival to L1TC, this arm got either:
-no further #TXA
-1g infusion only
-1g bolus then 1g infusion
5/
Inclusion:
-injured pts at transported from scene or w/i 2h from outside ED to L1TC
-at least 1 episode of SBP<90 or HR >110
-age 18-90 years
Exclusion:
-lack of IV/IO access
-isolated fall from standing, drowning, hanging
-traumatic arrest>5min
-penetrating TBI
-opted out
Inclusion:
-injured pts at transported from scene or w/i 2h from outside ED to L1TC
-at least 1 episode of SBP<90 or HR >110
-age 18-90 years
Exclusion:
-lack of IV/IO access
-isolated fall from standing, drowning, hanging
-traumatic arrest>5min
-penetrating TBI
-opted out
6/
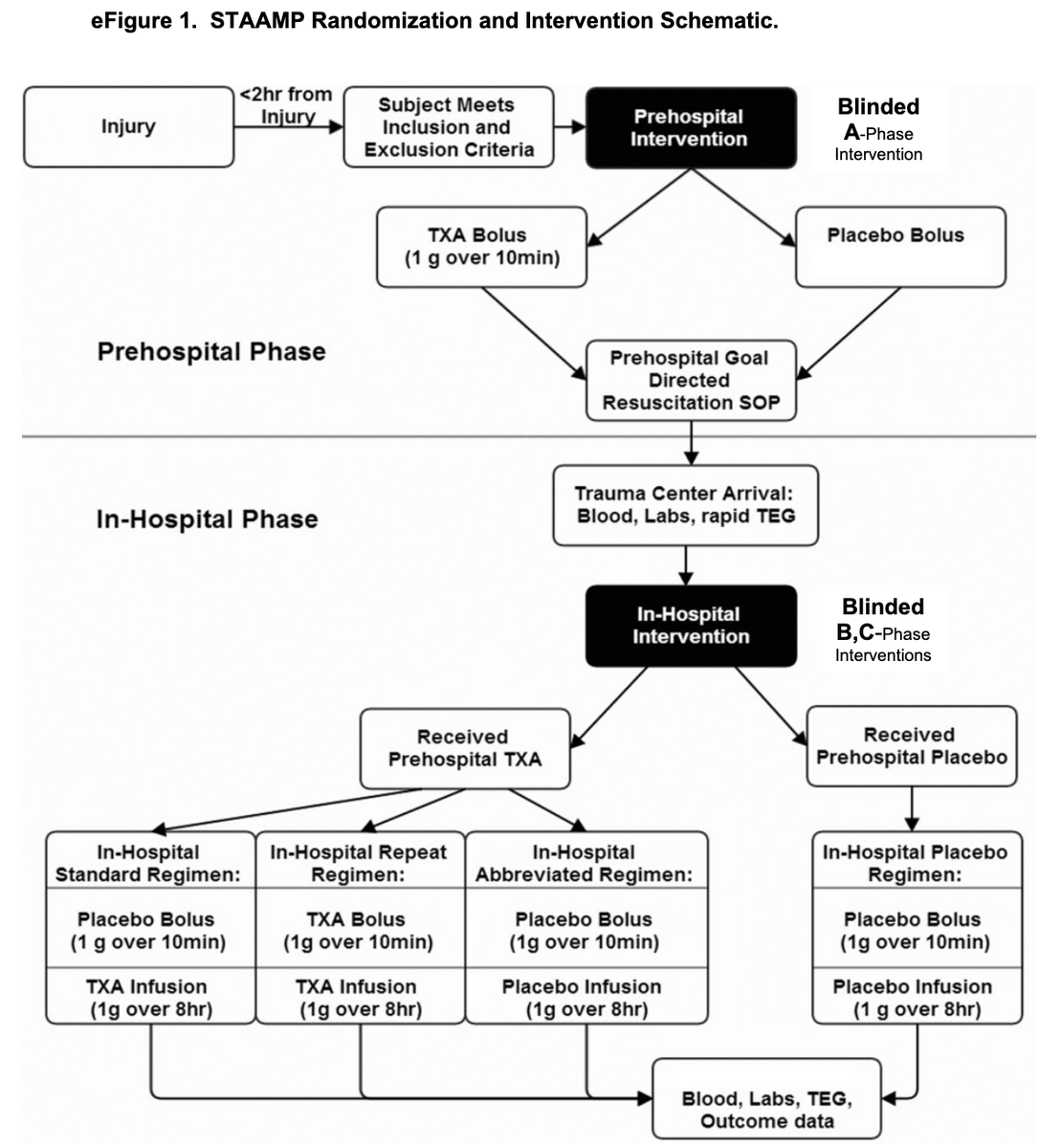
Methods:
-randomized 1:1:1:1 with block size 12
-computerized randomization
-sealed drug kits according to allocation sequence
Community consultation was done for approval with an exception from informed consent clause
Intention to treat analysis
Methods:
-randomized 1:1:1:1 with block size 12
-computerized randomization
-sealed drug kits according to allocation sequence
Community consultation was done for approval with an exception from informed consent clause
Intention to treat analysis
7/
Outcomes:
1º outcome: 30-day mortality
2º outcomes:
-24h & in-hospital mortality
-blood volumes at 6/24h
-crystalloid volumes at 24h
-incidence of multiorgan failure, ARDS, infection, seizures, PE/DVT, coagulopathy/hyperfibrinolysis
Outcomes:
1º outcome: 30-day mortality
2º outcomes:
-24h & in-hospital mortality
-blood volumes at 6/24h
-crystalloid volumes at 24h
-incidence of multiorgan failure, ARDS, infection, seizures, PE/DVT, coagulopathy/hyperfibrinolysis
8/
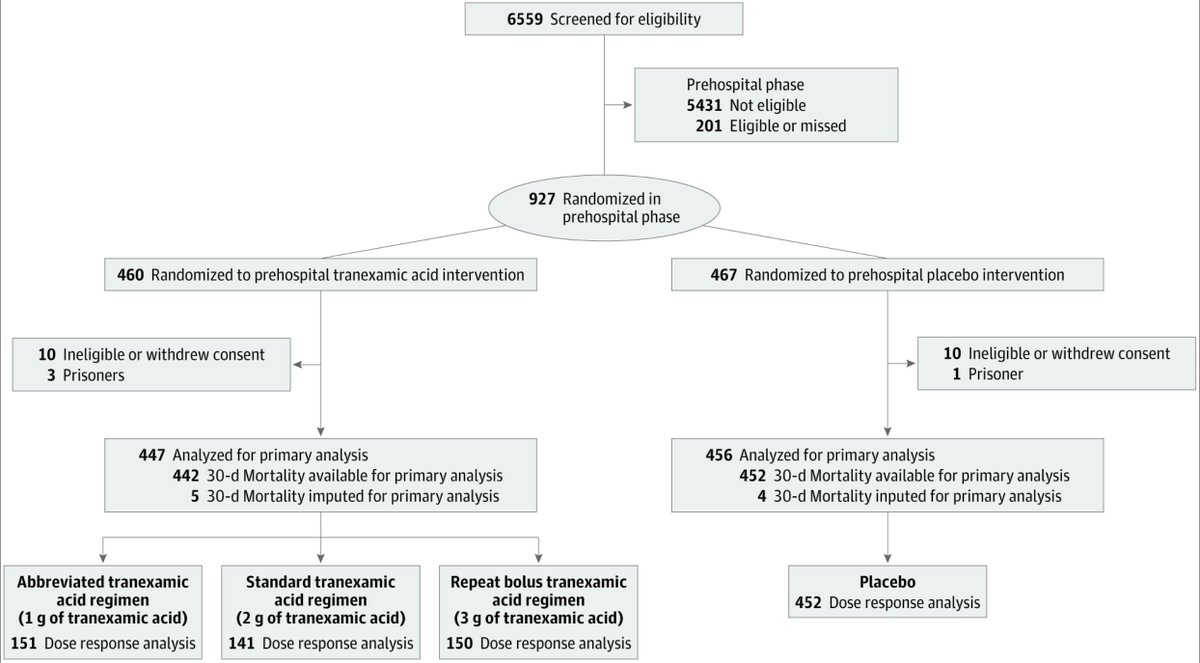
Results:
927 enrolled (24 excluded)
-447 to #TXA, 456 to placebo
Trial was halted at 93% enrollment due to financial limitations and slow enrollment
Patient characteristics below:

Results:
927 enrolled (24 excluded)
-447 to #TXA, 456 to placebo
Trial was halted at 93% enrollment due to financial limitations and slow enrollment
Patient characteristics below:
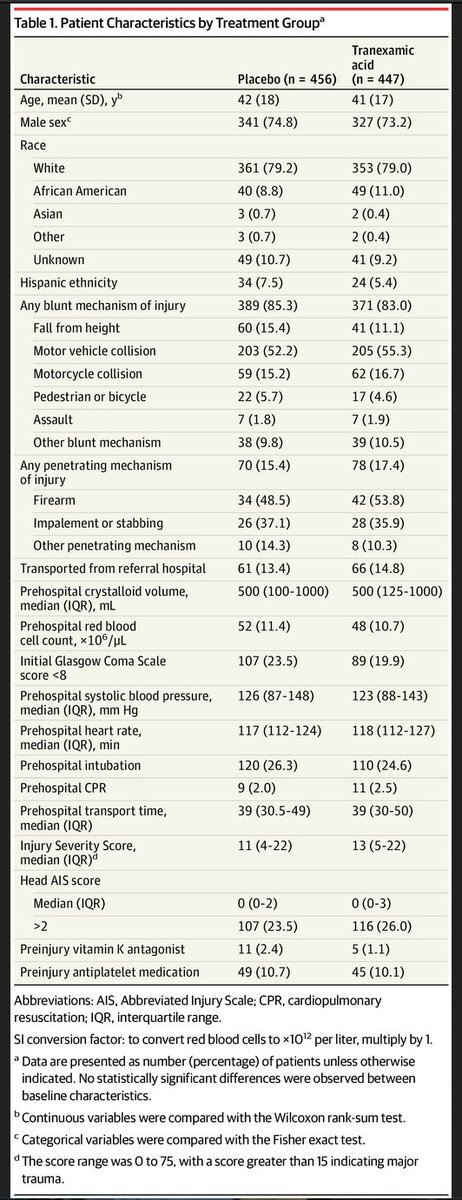
9/
Key numbers for all patients:
Median ISS: 12
All cause 30-day mortality: 9.1%
Initial prehospital SBP<90: 22%
Required blood in 1st 24h: 34%
Operative procedure in 1st 24h: 45%
Key numbers for all patients:
Median ISS: 12
All cause 30-day mortality: 9.1%
Initial prehospital SBP<90: 22%
Required blood in 1st 24h: 34%
Operative procedure in 1st 24h: 45%
10/
Key numbers TXA arm:
TXA delivered in 98% assigned patients
>92% in each sub-arm received their assigned TXA dose
30 day mortality: 8% (vs 10% placebo) difference: −1.8; 95% CI: −5.6% to 1.9%; P = .17
Assignment to the TXA group didn't change hazards of 30-day mortality

Key numbers TXA arm:
TXA delivered in 98% assigned patients
>92% in each sub-arm received their assigned TXA dose
30 day mortality: 8% (vs 10% placebo) difference: −1.8; 95% CI: −5.6% to 1.9%; P = .17
Assignment to the TXA group didn't change hazards of 30-day mortality
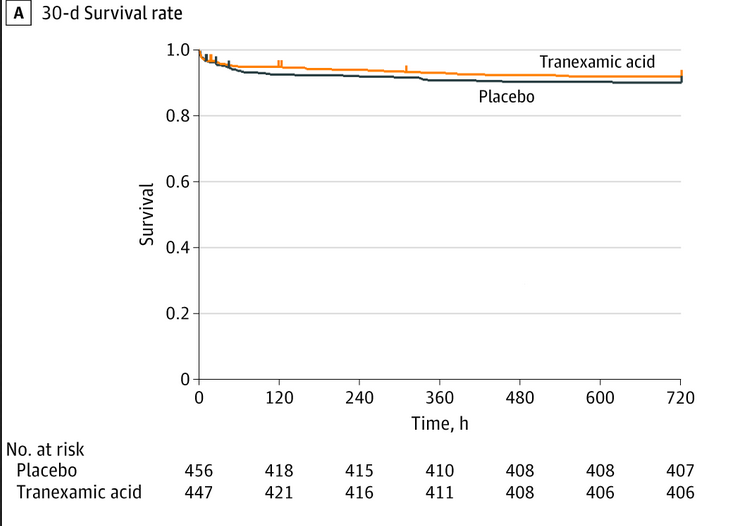
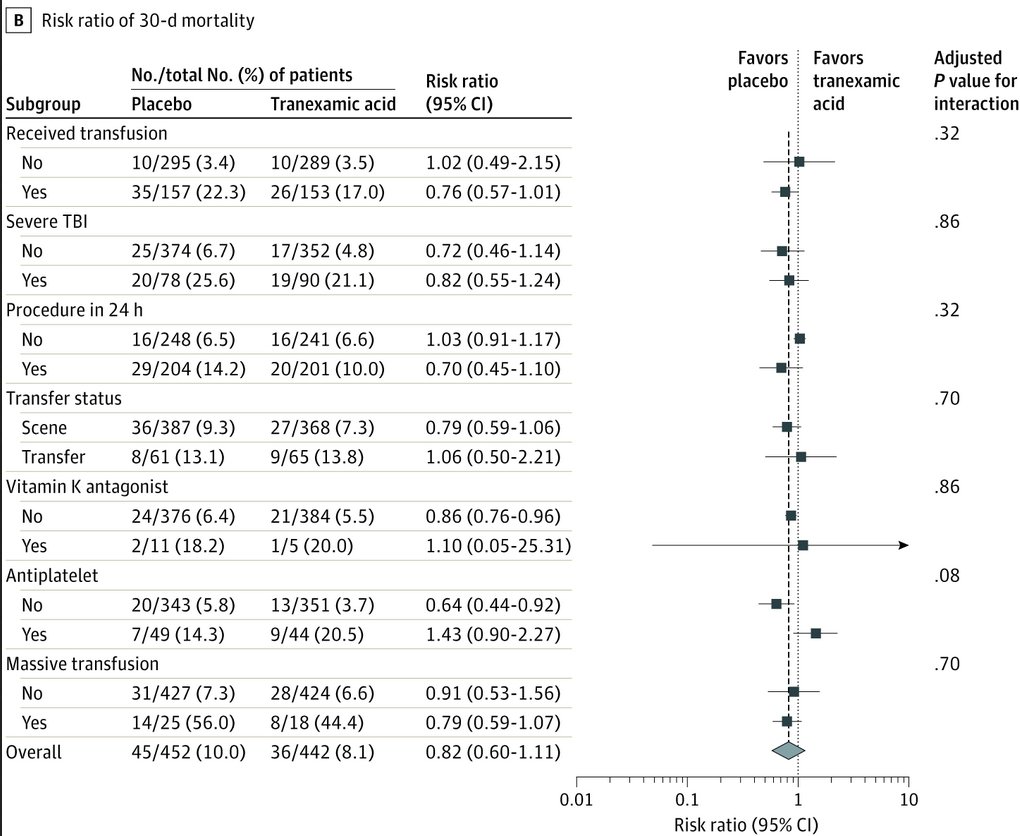
11/
There were also
-no group differences in 24-hour mortality (difference: 0.15; 95% CI: −2.3 to 2.6; adjusted P = .98) or in-hospital mortality (difference: 1.1; 95% CI: −2.7 to 4.9; P = .94)
-similar 6- and 24h blood transfusion requirements in both groups
There were also
-no group differences in 24-hour mortality (difference: 0.15; 95% CI: −2.3 to 2.6; adjusted P = .98) or in-hospital mortality (difference: 1.1; 95% CI: −2.7 to 4.9; P = .94)
-similar 6- and 24h blood transfusion requirements in both groups
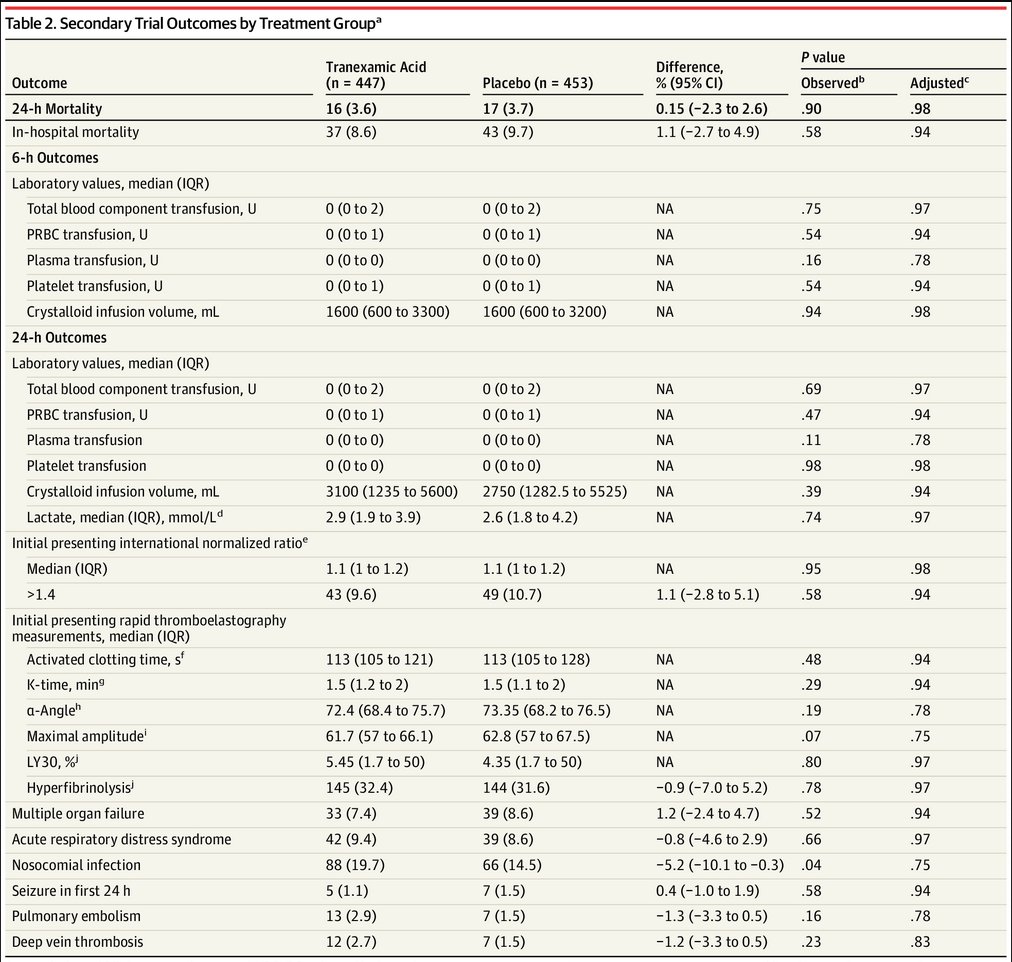
12/
No differences overall in incidence of:
- PE/DVT (hear that 🇺🇸😉)
- seizures
- multiorgan failure
- infection
No differences overall in incidence of:
- PE/DVT (hear that 🇺🇸😉)
- seizures
- multiorgan failure
- infection
13/
Interestingly-when comparing each TXA regimen to placebo, that group that received both prehospital and repeat bolus regimens had lower 30-day mortality after adjusting for site (7.3% vs 10.0%; difference: −2.7%; 95% CI: −5.0% to −0.4%; P = .04)
Interestingly-when comparing each TXA regimen to placebo, that group that received both prehospital and repeat bolus regimens had lower 30-day mortality after adjusting for site (7.3% vs 10.0%; difference: −2.7%; 95% CI: −5.0% to −0.4%; P = .04)
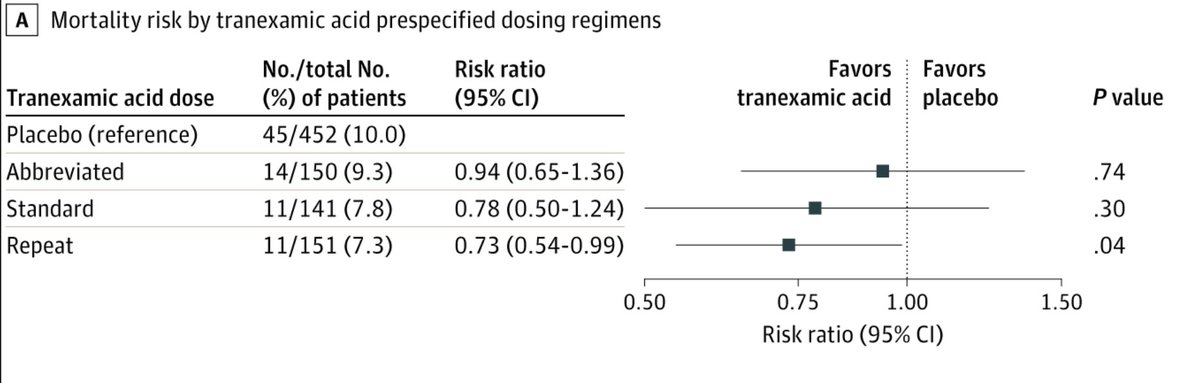
14/
Also when comparing for time to treatment & shock, there was a ↓ 30-day mortality in:
-group that received #TXA w/i 1h (4.6% vs 7.6%; difference, −3.0%; 95% CI, −5.7% to −0.3%; P < .002)
-those in severe shock (SBP<70) (18.5% vs 35.5%; 95% CI: −25.8% to −8.1%; P < .003)
Also when comparing for time to treatment & shock, there was a ↓ 30-day mortality in:
-group that received #TXA w/i 1h (4.6% vs 7.6%; difference, −3.0%; 95% CI, −5.7% to −0.3%; P < .002)
-those in severe shock (SBP<70) (18.5% vs 35.5%; 95% CI: −25.8% to −8.1%; P < .003)
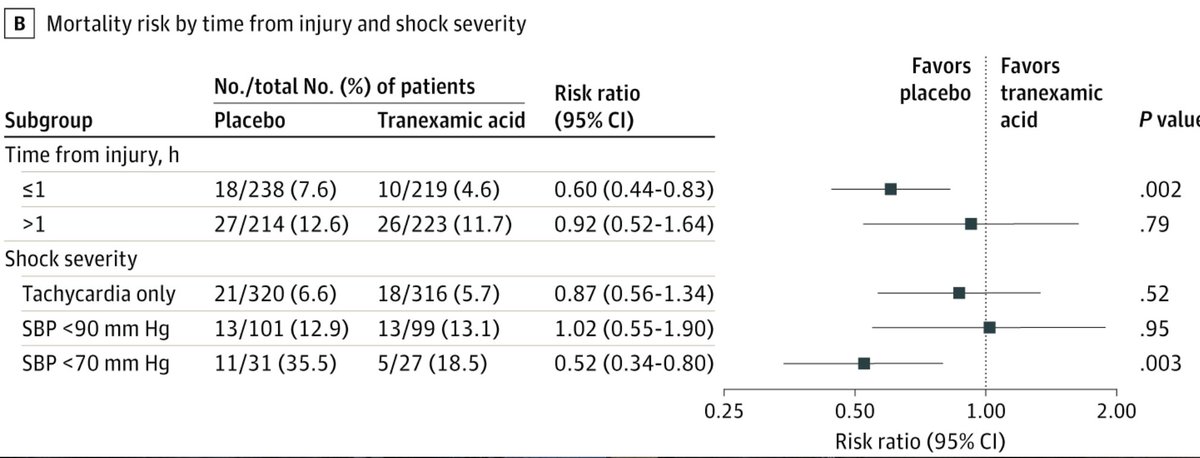
15/
Overall these results (similar overall 30-day mortality b/w groups) is similar to other trials.
Importantly (for 🇺🇸!!)- the VTE risk was no greater in the TXA group
Specific advantage may be found in giving #TXA early (w/i 1hr of injury) and in sicker (SBP<70) patients
Overall these results (similar overall 30-day mortality b/w groups) is similar to other trials.
Importantly (for 🇺🇸!!)- the VTE risk was no greater in the TXA group
Specific advantage may be found in giving #TXA early (w/i 1hr of injury) and in sicker (SBP<70) patients
16/
The trial is of course limited by
-low overall injury severity
-low blood transfusion requirement
-overall low mortality rates
-variations in Rx at individual centers
-variable adaptability to other (esp US) EMS systems
-some missing data
-underpowering of study
The trial is of course limited by
-low overall injury severity
-low blood transfusion requirement
-overall low mortality rates
-variations in Rx at individual centers
-variable adaptability to other (esp US) EMS systems
-some missing data
-underpowering of study
17/
Nevertheless, hats off to the investigators.
This trial certainly adds to the literature addressing #TXA's role in major trauma, and importantly highlights the critical importance of pushing the envelope in research and delivery of life-saving interventions at point of care
Nevertheless, hats off to the investigators.
This trial certainly adds to the literature addressing #TXA's role in major trauma, and importantly highlights the critical importance of pushing the envelope in research and delivery of life-saving interventions at point of care
18/
And of course don't forget the read the excellent accompanying editorial by @PMH_Trauma_RPD and @docmartin22
jamanetwork.com/journals/jamas…
And of course don't forget the read the excellent accompanying editorial by @PMH_Trauma_RPD and @docmartin22
jamanetwork.com/journals/jamas…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh







