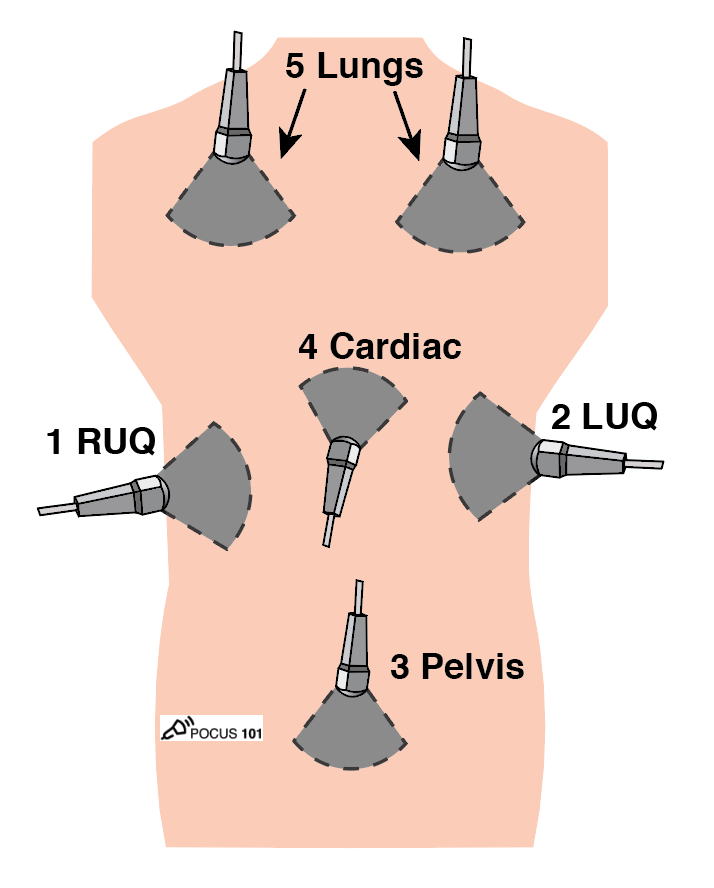
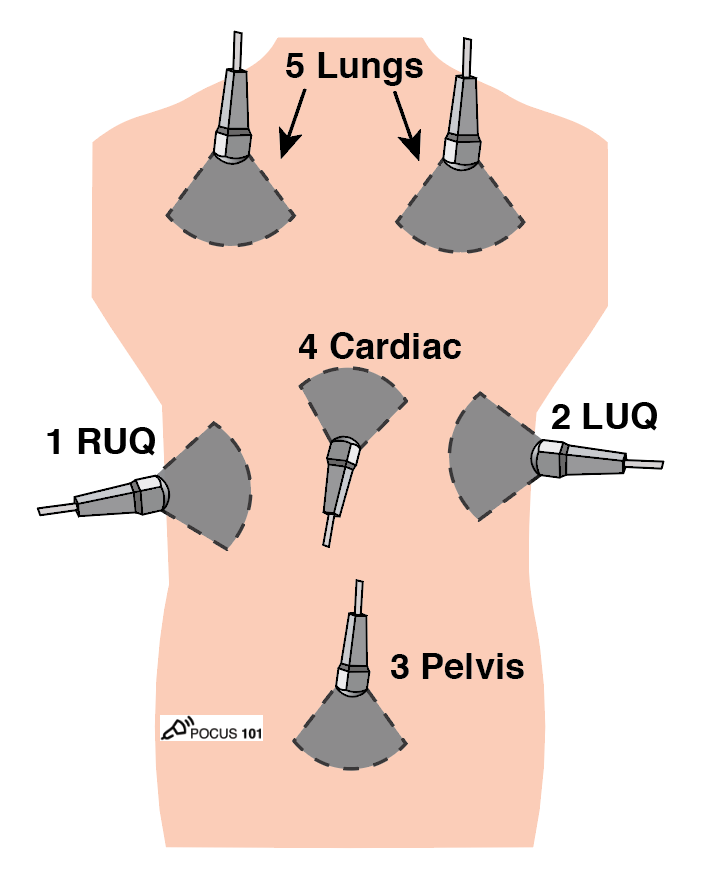
Having Problems Getting all those Cardiac (Echo)🫀Views on your Shock⚡️Patients?
1⃣Learn The Common Echo Views
2⃣Learn the IVC View
3⃣Estimate EF and CVP
4⃣Dx Massive PE
5⃣Dx Cardiac Tamponade
✅New #POCUS Blog Post!
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
#medtweetorial 👇(1/n)


1⃣Learn The Common Echo Views
2⃣Learn the IVC View
3⃣Estimate EF and CVP
4⃣Dx Massive PE
5⃣Dx Cardiac Tamponade
✅New #POCUS Blog Post!
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
#medtweetorial 👇(1/n)



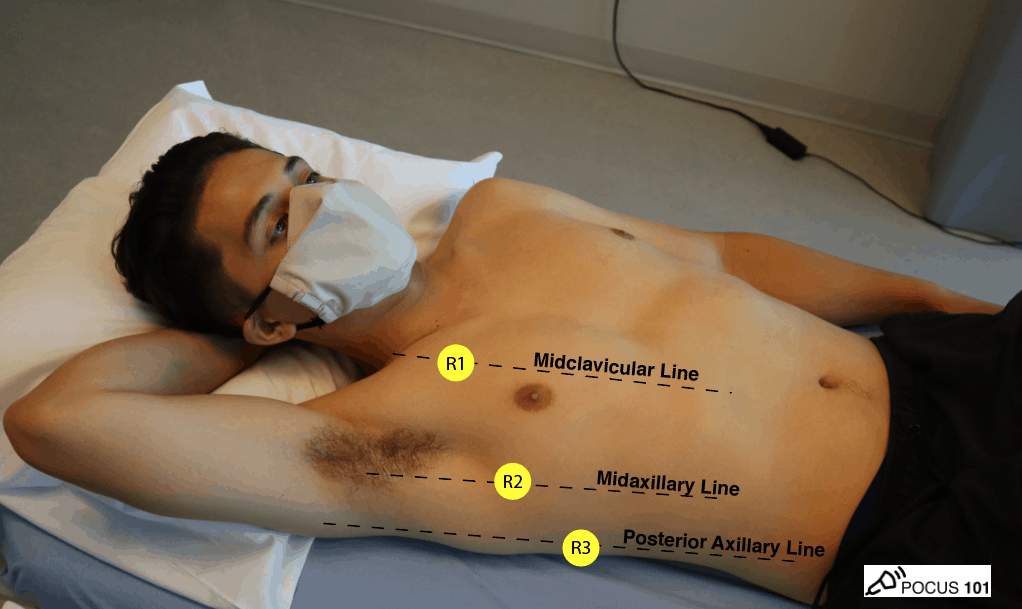
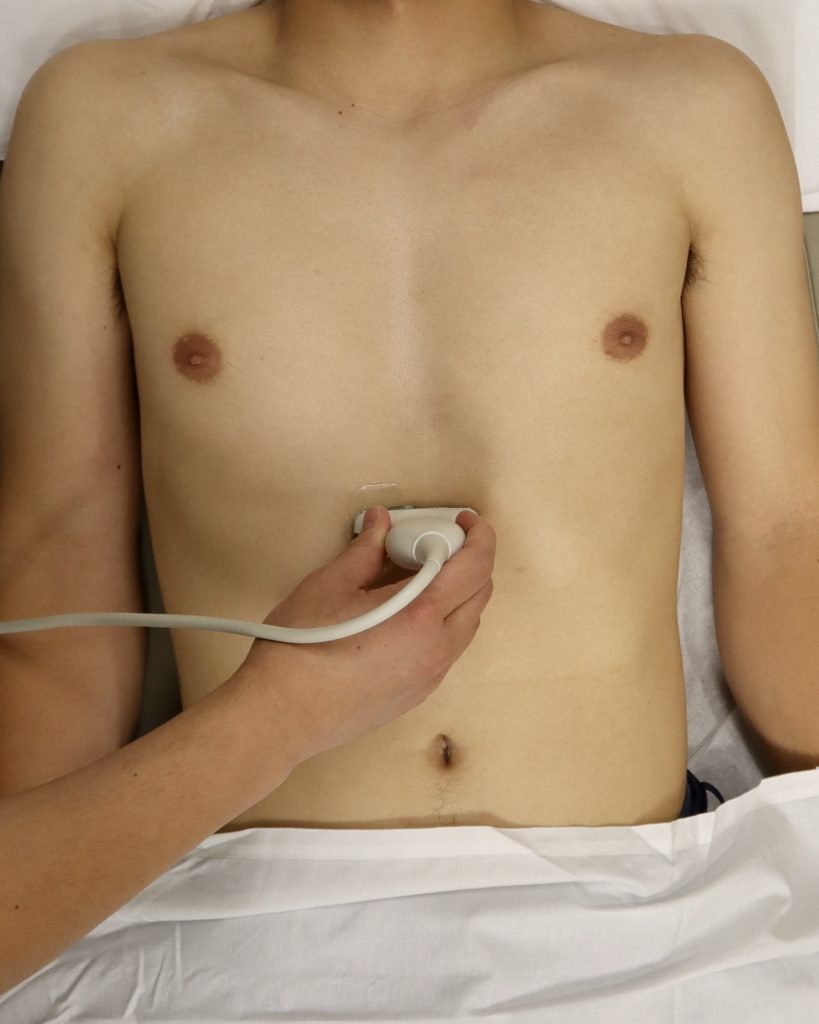
Use the phased array (Cardiac/echo) probe and make sure you are in the cardiac preset with the indicator orientation marker to the right of the screen.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

Remember the 4 chambers (RA, RV, LA, LV) and 4 valves (mitral, tricuspid, pulmonic, aortic) of the heart as you scan your patient.
Also, the heart is much more medial (towards the sternum) than you may realize.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

Also, the heart is much more medial (towards the sternum) than you may realize.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac


For the Parasternal Long Axis view. Point the indicator towards the pt's RIGHT shoulder. Identify RV, LV, LA, Aortic valve, Mitral valve, pericardium, and descending aorta.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

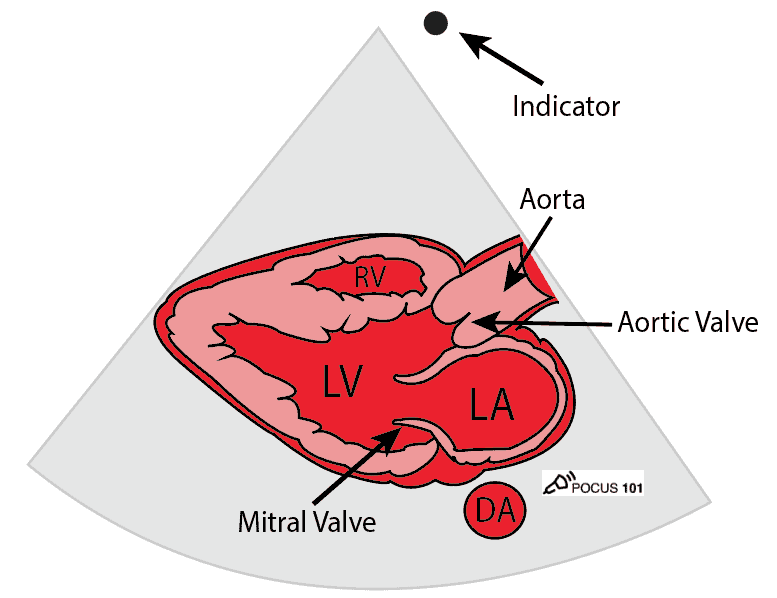
If you are having trouble orienting yourself, just remember “the 3 L‘s“: For the Parasternal Long Axis view, the Left Ventricle is on the Left side of the screen.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
To get the Parasternal SHORT axis view, rotate your probe 90 degrees clockwise so that the indicator is now pointing towards the patient’s left shoulder.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

The three main parasternal short axis levels you will see are the Mid-Papillary, Mitral valve (fish mouth), and Aortic Valve (mercedes benz) levels.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

For Apical 4 chamber (A4C) slide the probe down towards the apex while keeping the indicator towards the patient's left. Identify the RV, RA, LV, LA, mitral valve, and tricuspid valve.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac


If you are having trouble getting the Apical 4 Chamber view, try placing the patient in the left lateral decubitus position. It will reduce lung artifact and bring the heart more proximal to your ultrasound probe, usually giving you an optimal view.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
Subxiphoid (Subcostal) view:
With the patient’s knees bent, position the probe under the costal arch (beneath the xiphoid process) with the indicator pointing towards the left shoulder.
Identify the RV, LV, RA, LA, tricuspid valve and mitral valve.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

With the patient’s knees bent, position the probe under the costal arch (beneath the xiphoid process) with the indicator pointing towards the left shoulder.
Identify the RV, LV, RA, LA, tricuspid valve and mitral valve.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac


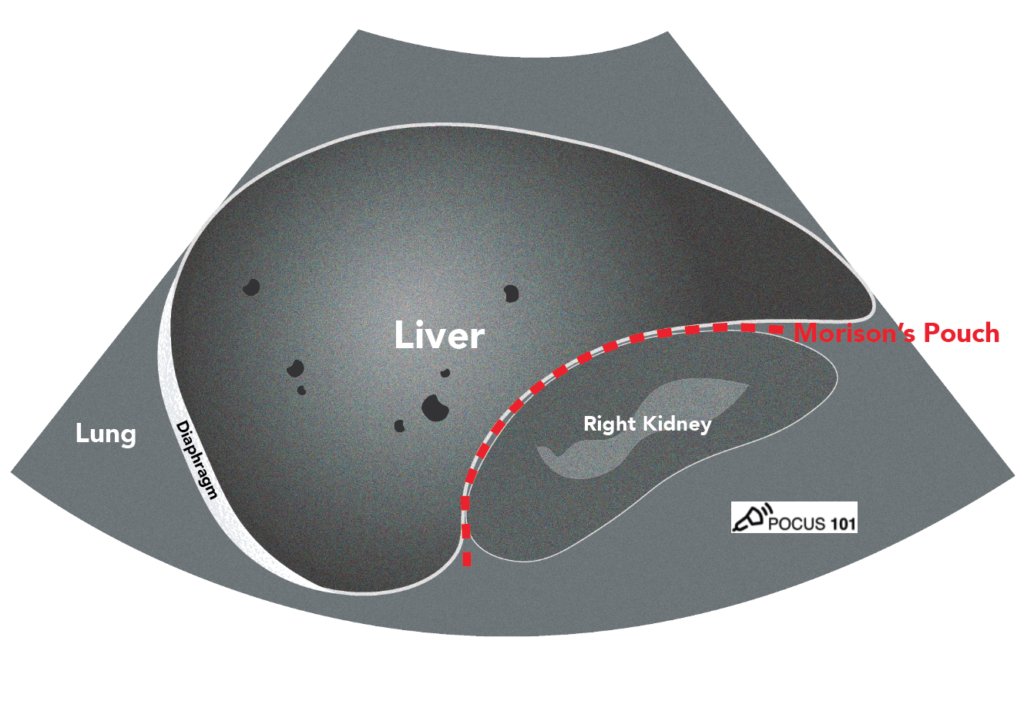
For the subxiphoid view, make sure to use liver as acoustic window. If you are still having trouble getting a clear image, try applying gentle downward pressure on the probe.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
For the IVC view, position the probe in the subxiphoid area and point the indicator towards the patient's feet. Identify the RA and IVC (also sometimes the hepatic vein).
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac


Evaluate the IVC diameter and collapsibility.
Estimate the ejection fraction of your patients.
Ejection fraction (EF) in percentage is defined as: EF(%) = SV/EDV x 100
The more you see the easier it gets!
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
Ejection fraction (EF) in percentage is defined as: EF(%) = SV/EDV x 100
The more you see the easier it gets!
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

For pulmonary embolism, you can sometimes directly see a clot in the pulmonary artery or a clot in transit.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
Another indirect sign of PE is McConnell's sign showing hypo/akinesis of the RV free wall and preserved function of the RV apex.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
For pericardial effusion. Remember the rate of accumulation is much more important than the absolute size.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac

Make sure to identify the descending aorta to differentiate between pericardial and pleural effusion.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
A pericardial fat pad can be a false positive for pericardial effusion. It is usually located anteriorly, echogenic, and appears to move with the heart contractions.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
One of the first signs of echocardiographic tamponade is right atrial systolic collapse.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
The other sign of echocardiographic tamponade is right ventricular diastolic collapse.
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
🔗👉pocus101.com/Cardiac
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh