Based off of Run the List Episode 24, here is a #tweetorial on💘Tachyarrhythmias💘
🎧Full episode: bit.ly/3b6svs0
Let's start with an EKG 👇 (@medicine_strong). For more practice, check out: bit.ly/35mxD7P
Thanks to @Gurleen_Kaur96 for this week's edition!
🎧Full episode: bit.ly/3b6svs0
Let's start with an EKG 👇 (@medicine_strong). For more practice, check out: bit.ly/35mxD7P
Thanks to @Gurleen_Kaur96 for this week's edition!

❓What tachyarrhythmia is shown on that EKG above❓
Keep these things in mind when interpreting:
🔶Rate
🔶Regularity
🔶Width of QRS complex
🔶Relationship of P wave to QRS complex
And continue reading this 🧵 for the correct answer...
Keep these things in mind when interpreting:
🔶Rate
🔶Regularity
🔶Width of QRS complex
🔶Relationship of P wave to QRS complex
And continue reading this 🧵 for the correct answer...
First, let's review some 🔑 principles:
🥇Always assess if patient is hemodynamically stable!
✅Hypotension
✅Altered Mental Status
✅Chest pain
✅Shortness of breath
If unstable ➡️ cardioversion or defibrillation
🥇Always assess if patient is hemodynamically stable!
✅Hypotension
✅Altered Mental Status
✅Chest pain
✅Shortness of breath
If unstable ➡️ cardioversion or defibrillation
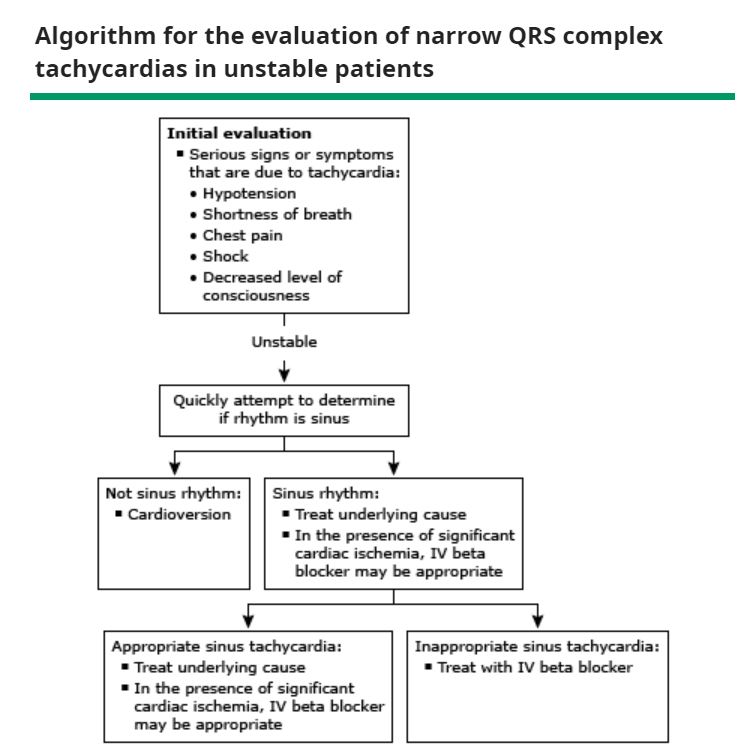
Now an aside on terminology:
💓Tachycardia💓 = HR >100, physiologic or pathologic
💘Tachyarrhythmia💘 = Heart rhythm disorder causing *pathologic* tachycardia
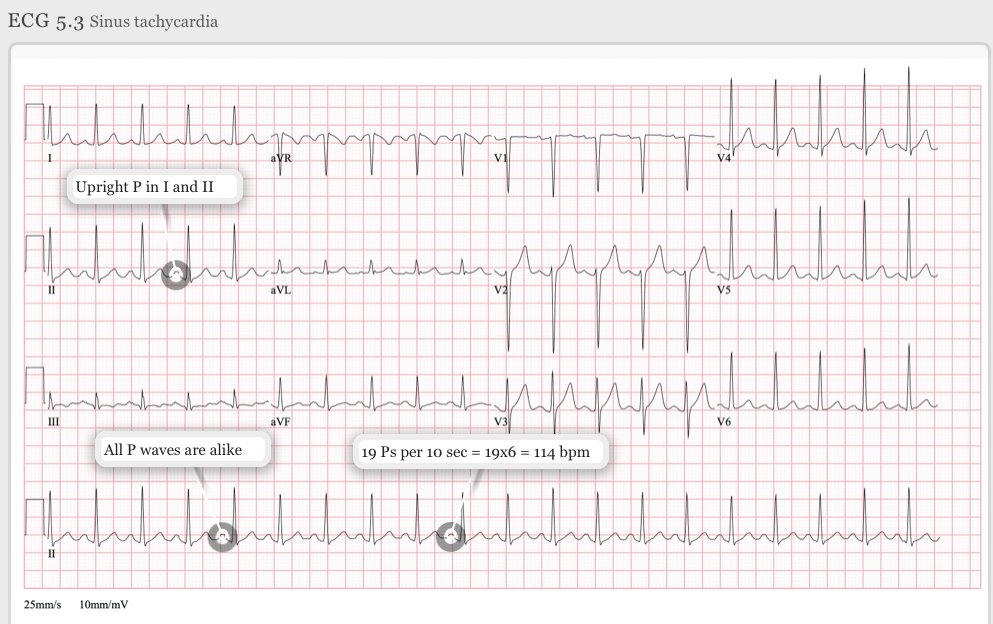
If sinus rhythm:
➡️P before each QRS wave
➡️QRS following each P
➡️P wave upright in lead II
Then ⏩ Sinus Tachycardia


💓Tachycardia💓 = HR >100, physiologic or pathologic
💘Tachyarrhythmia💘 = Heart rhythm disorder causing *pathologic* tachycardia
If sinus rhythm:
➡️P before each QRS wave
➡️QRS following each P
➡️P wave upright in lead II
Then ⏩ Sinus Tachycardia
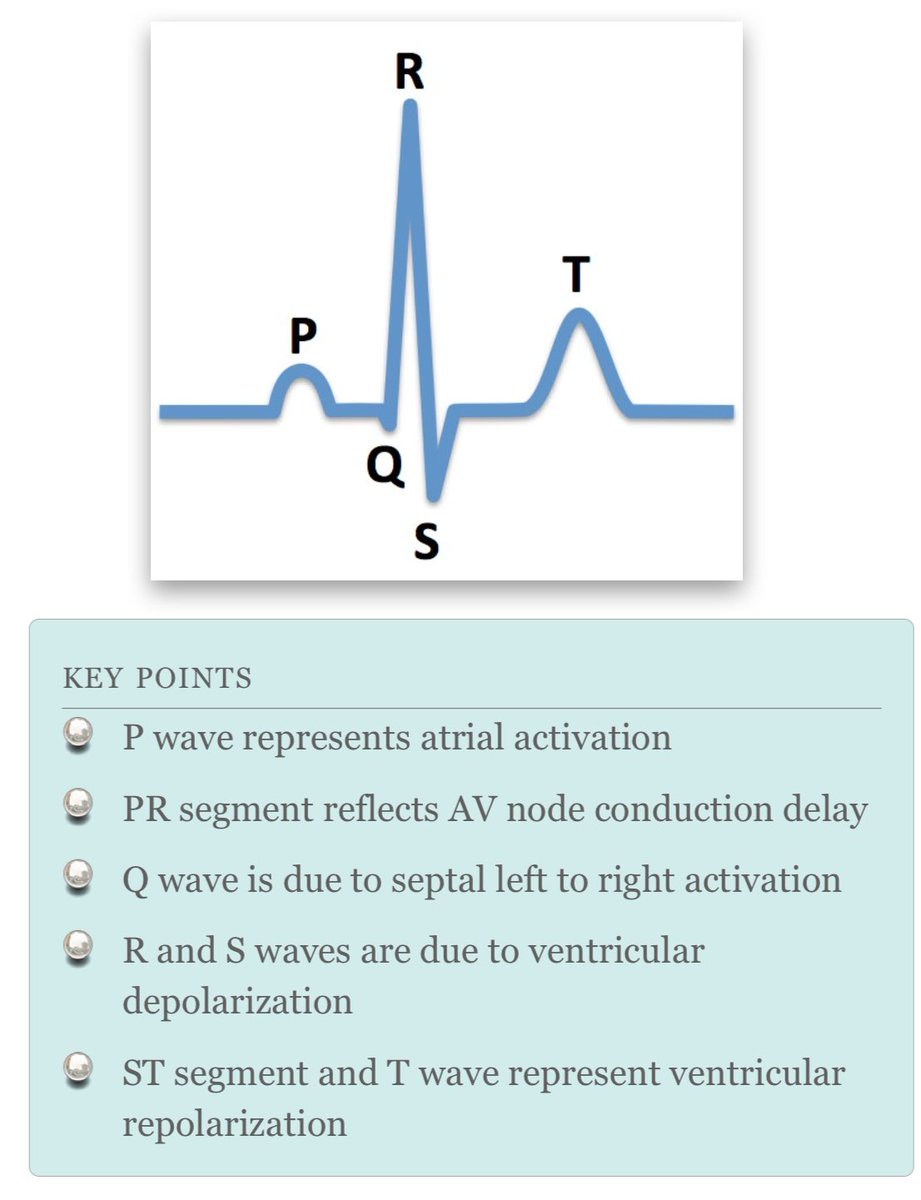

🧠Let's develop a diagnostic framework for tachyarrhythmias
QRS complex on EKG is 💯
🔹Narrow complex (QRS <120ms): SVT
🔷Wide complex (QRS >120ms): SVT w/ aberrancy or ventricular tachycardia (V. tach)
Check out this ⤵️schema from @CPSolvers
QRS complex on EKG is 💯
🔹Narrow complex (QRS <120ms): SVT
🔷Wide complex (QRS >120ms): SVT w/ aberrancy or ventricular tachycardia (V. tach)
Check out this ⤵️schema from @CPSolvers

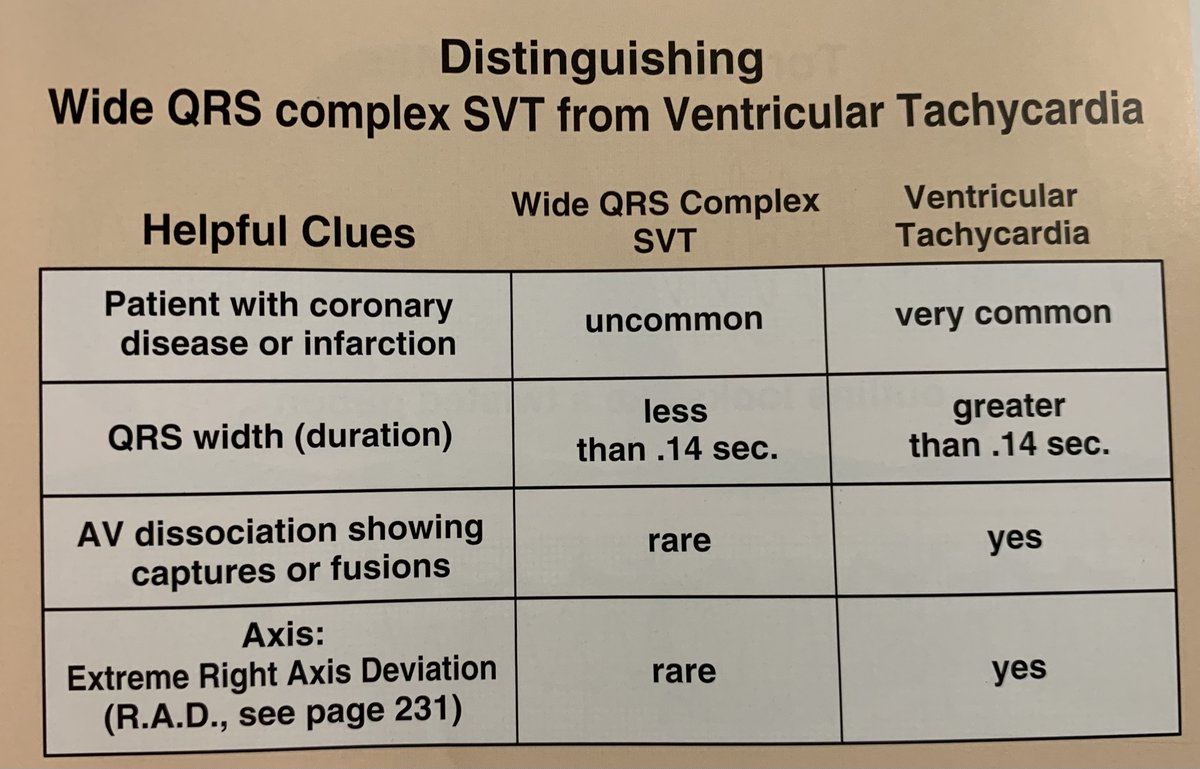
SVT 🆚 V. tach
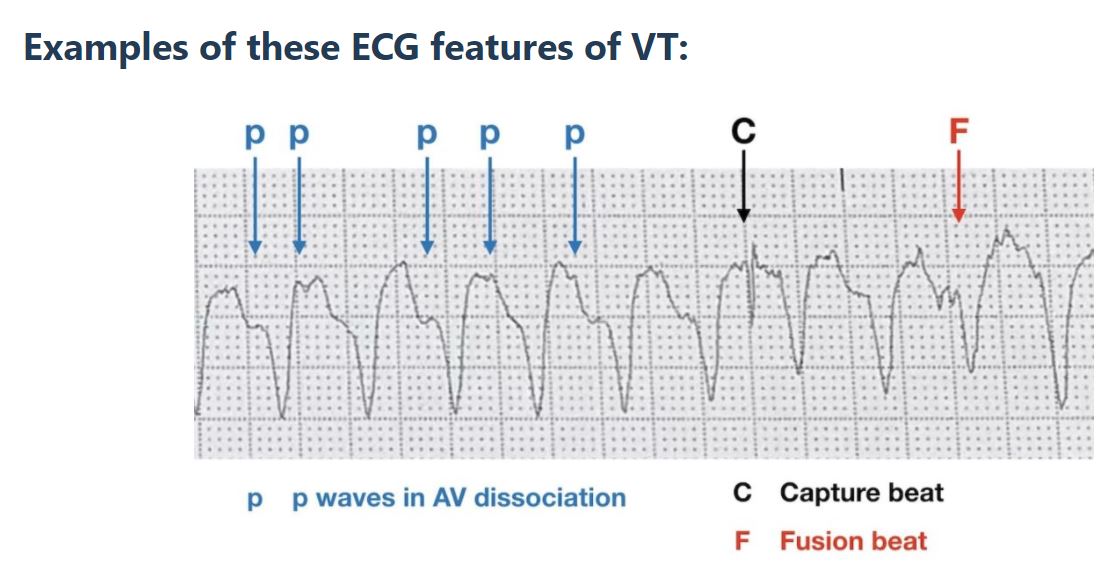
Quick tricks to identify V. tach on EKG:
✏️Concordance of precordial leads (all QRS complexes ➕ or all ➖)
✏️QRS complex ➖ in all inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
✏️AV dissociation w/ capture (QRS of normal duration) or fusion beats
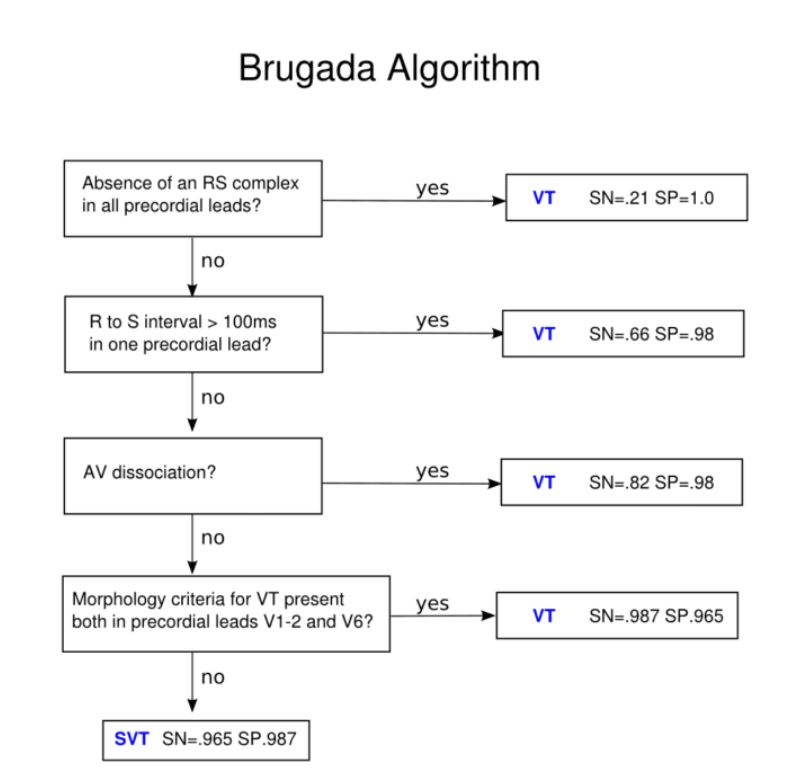
Brugada Algorithm ⤵️



Quick tricks to identify V. tach on EKG:
✏️Concordance of precordial leads (all QRS complexes ➕ or all ➖)
✏️QRS complex ➖ in all inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
✏️AV dissociation w/ capture (QRS of normal duration) or fusion beats
Brugada Algorithm ⤵️

For *narrow* complex, next determine if irregular or regular
RTL schema by @haematognomist ⤵️
--
Ways to differentiate?
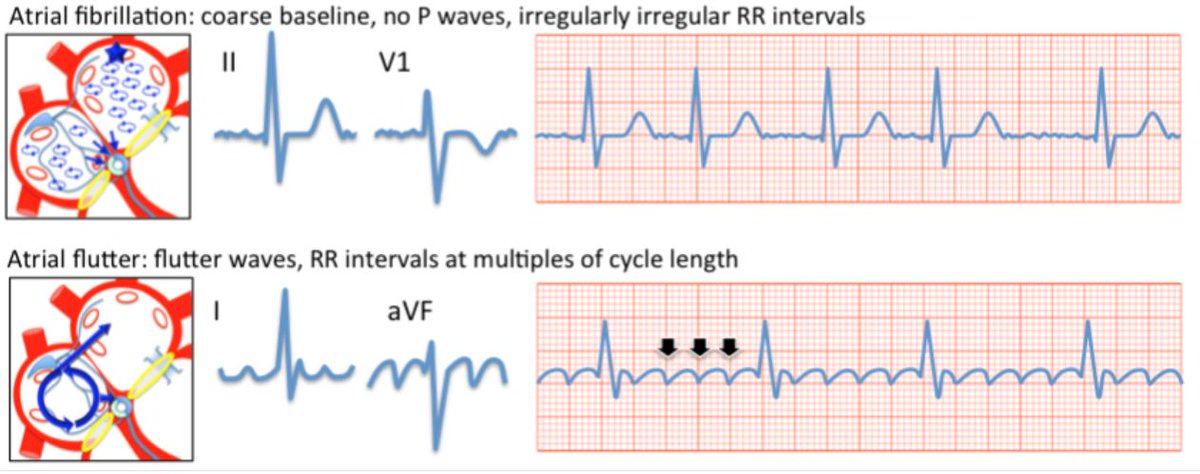
🪚Sawtooth pattern in inferior leads – A flutter
🌌Ectopic p wave – Atrial tachycardia
❎No p waves – A fib
🌈Irregularly regular, 3+ p waves – MAT



RTL schema by @haematognomist ⤵️
--
Ways to differentiate?
🪚Sawtooth pattern in inferior leads – A flutter
🌌Ectopic p wave – Atrial tachycardia
❎No p waves – A fib
🌈Irregularly regular, 3+ p waves – MAT


Now, back to the earlier EKG...
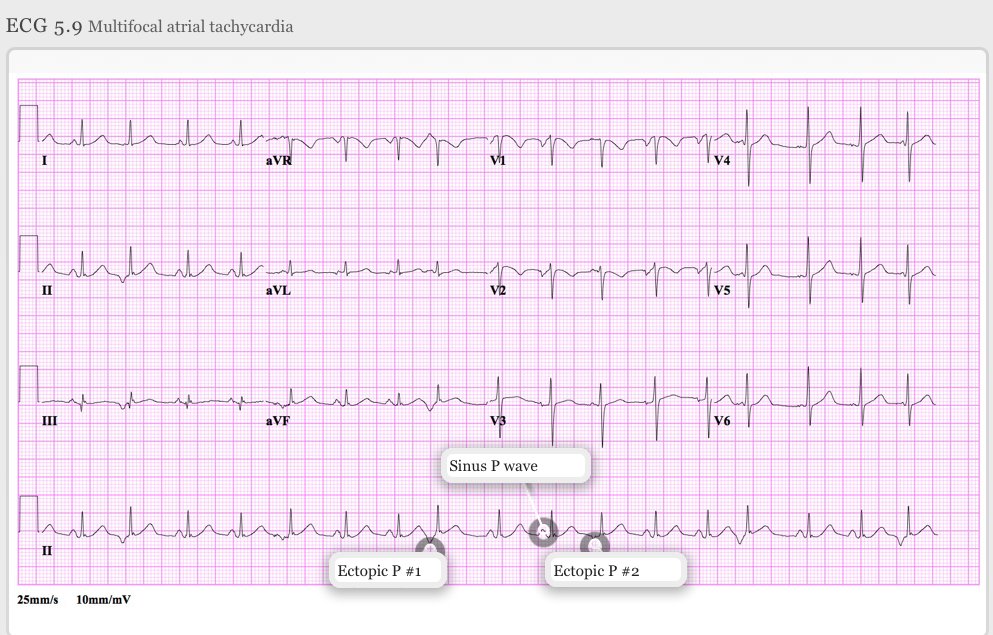
Answer❓ Multifocal Atrial Tachy (MAT)!
♦️Unknown MoA, triggered activity from delayed afterdepolarizations
Etiologies:
🫁COPD exacerbation, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism
💘CHF exacerbation
💊theophylline
♦️No one predominant P wave morphology!
Answer❓ Multifocal Atrial Tachy (MAT)!
♦️Unknown MoA, triggered activity from delayed afterdepolarizations
Etiologies:
🫁COPD exacerbation, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism
💘CHF exacerbation
💊theophylline
♦️No one predominant P wave morphology!

🪂Now, let's take a deeper dive into AVNRT🪂
🔷Most common SVT
🔷More common in younger women
🔷Spontaneous events or by ☕️🤸🍵
🔷AV node re-entry circuit
90% Typical:
-slow AV pathway for anterograde
-fast path. for retrograde
10% Atypical:
-fast anterograde
-slow retrograde


🔷Most common SVT
🔷More common in younger women
🔷Spontaneous events or by ☕️🤸🍵
🔷AV node re-entry circuit
90% Typical:
-slow AV pathway for anterograde
-fast path. for retrograde
10% Atypical:
-fast anterograde
-slow retrograde
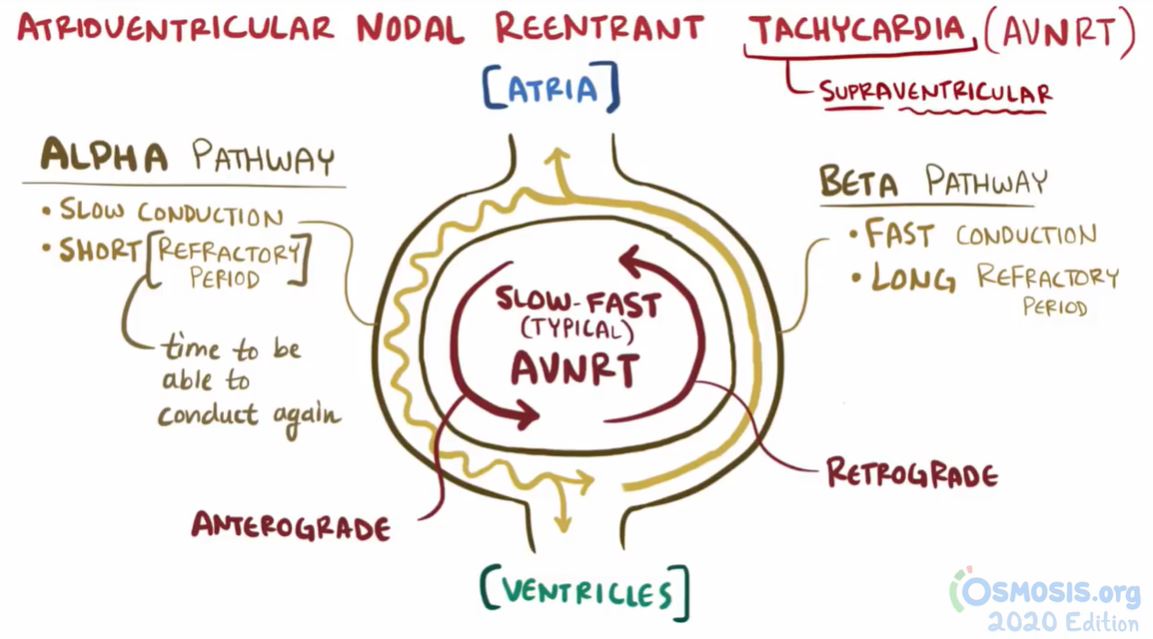
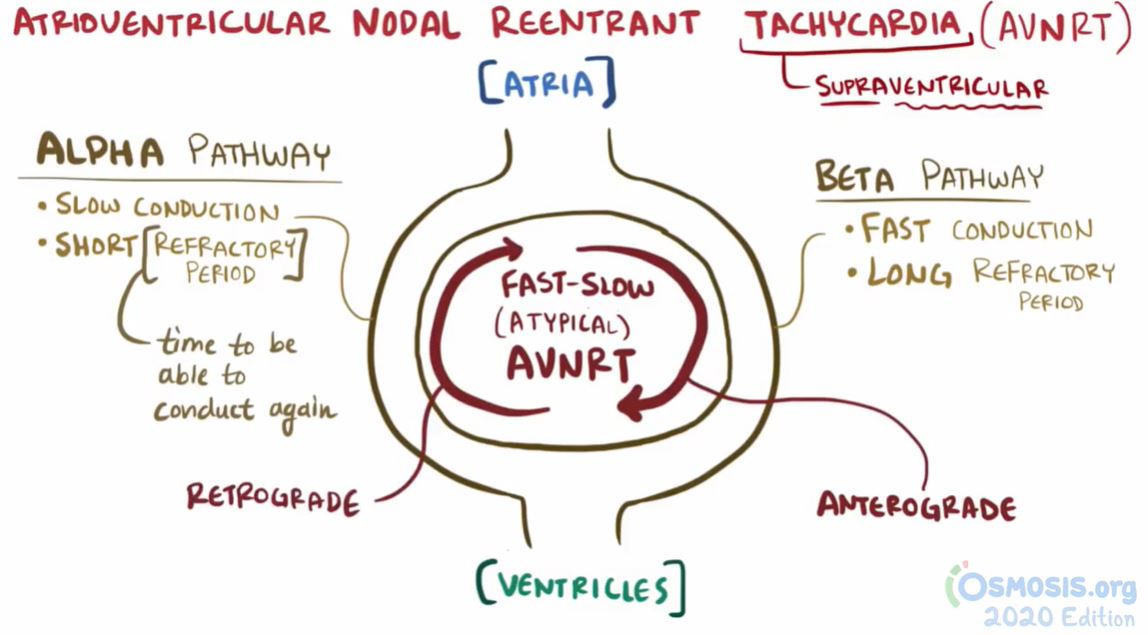
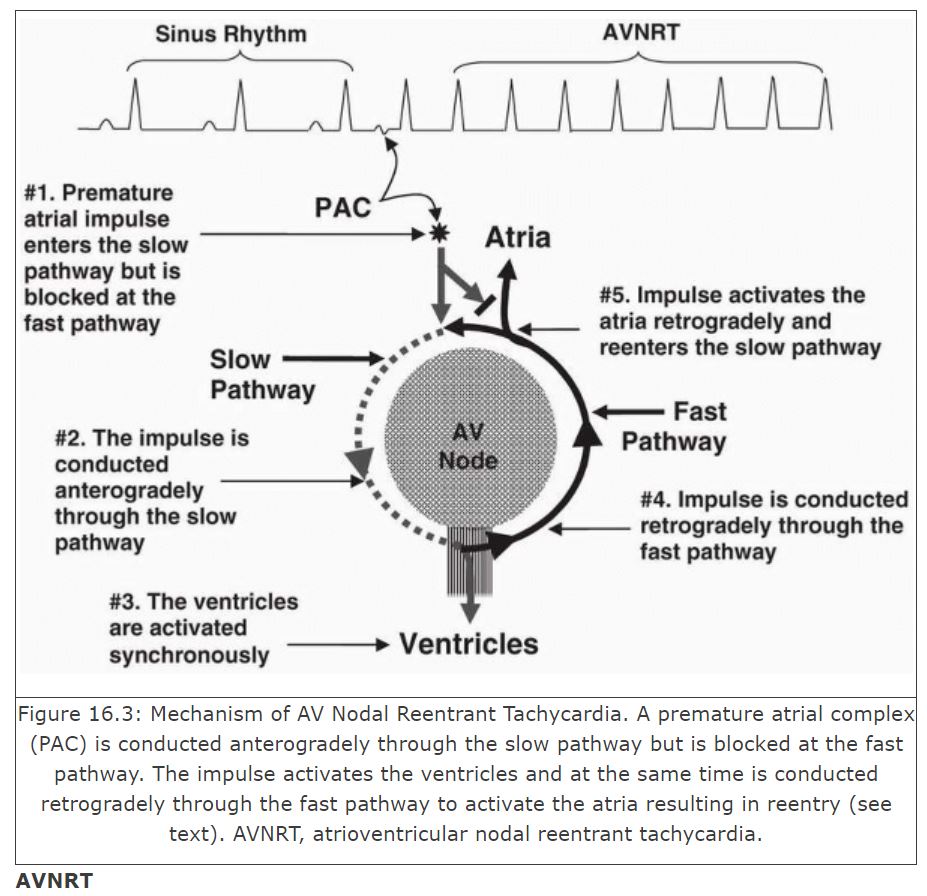
For typical AVNRT:
Retrograde ⬅️ conduction typically occurs in the fast 🚀 pathway
Atria are activated either simultaneously with or just after the ventricles so P wave is in the ST segment or *buried* within the QRS complex
🔥So on EKG, the RP interval < PR interval🔥

Retrograde ⬅️ conduction typically occurs in the fast 🚀 pathway
Atria are activated either simultaneously with or just after the ventricles so P wave is in the ST segment or *buried* within the QRS complex
🔥So on EKG, the RP interval < PR interval🔥


We've covered a lot! Hopefully you're not😴
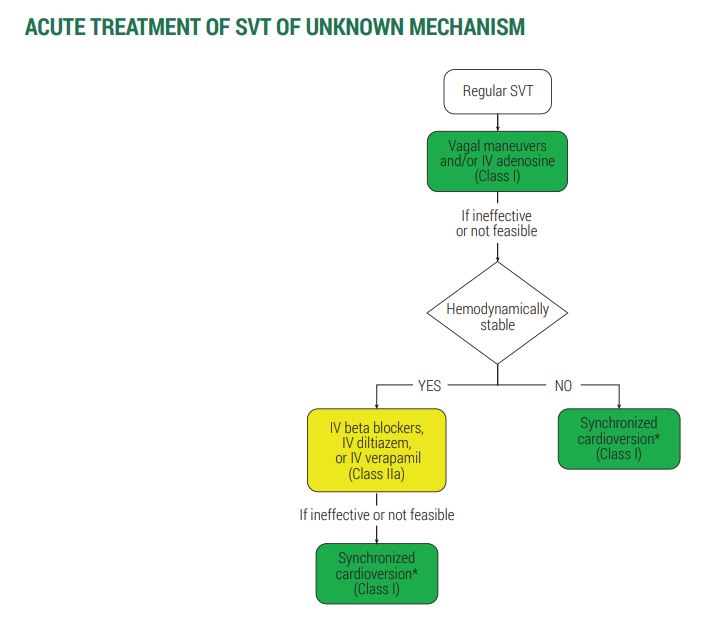
Let's hit it home with the treatment of SVT 🎯
Acute: Vagal stimulation (carotid sinus massage, Valsalva maneuver) or adenosine
💊Beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers can also suppress AVNRT event by blocking/slowing the AV node
Let's hit it home with the treatment of SVT 🎯
Acute: Vagal stimulation (carotid sinus massage, Valsalva maneuver) or adenosine
💊Beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers can also suppress AVNRT event by blocking/slowing the AV node
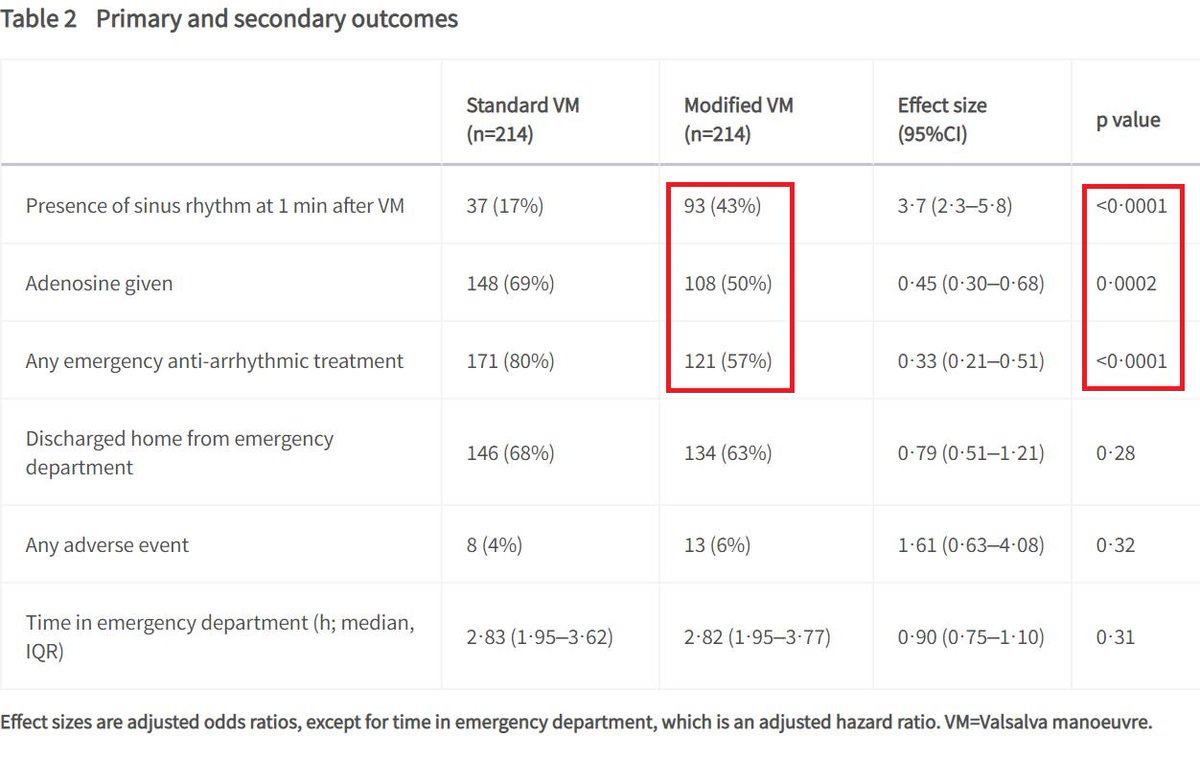
⁉️ Modified Valsalva ⁉️
The REVERT study from 🇬🇧 randomized patients presenting w/ SVT to either modified or standard Valsalva
Conclusion:
-Modified Valsalva should be considered as first-line treatment!
Video of Modified Valsalva: bit.ly/3hJuaVN

The REVERT study from 🇬🇧 randomized patients presenting w/ SVT to either modified or standard Valsalva
Conclusion:
-Modified Valsalva should be considered as first-line treatment!
Video of Modified Valsalva: bit.ly/3hJuaVN

Radiofrequency catheter ablation 🔪 is first-line therapy for symptomatic chronic AVNRT (palpitations, SOB, neck pulsations)
📢 Large registry studies report >95% success rates of slow-pathway ablation (preferred 🎯), with a <1% risk of AV block
🧊Cryoablation is alternative🧊
📢 Large registry studies report >95% success rates of slow-pathway ablation (preferred 🎯), with a <1% risk of AV block
🧊Cryoablation is alternative🧊

💥Summary/pearls for Tachyarrhythmias💥
1. Assess hemodynamic instability
2. EKG is 🗝️ - wide or narrow QRS
3. If narrow, determine if regular or irregular rhythm
Other labs/imaging: BMP, TSH, Troponin, BNP, urine toxicology, Echo
RTL Episode Handout: bit.ly/35cEAbw
1. Assess hemodynamic instability
2. EKG is 🗝️ - wide or narrow QRS
3. If narrow, determine if regular or irregular rhythm
Other labs/imaging: BMP, TSH, Troponin, BNP, urine toxicology, Echo
RTL Episode Handout: bit.ly/35cEAbw

REFs (1/3):
[1,8]
[3]uptodate.com/contents/overv…
[4,7,10] Mikhail Torosoff & Steven A. Fein. "I Read ECGs An interactive practical guide to the electrocardiogram interpretation".
[5]clinicalproblemsolving.com/dx-schema-supr…
[6]litfl.com/vt-versus-svt-…
[1,8]
[3]uptodate.com/contents/overv…
[4,7,10] Mikhail Torosoff & Steven A. Fein. "I Read ECGs An interactive practical guide to the electrocardiogram interpretation".
[5]clinicalproblemsolving.com/dx-schema-supr…
[6]litfl.com/vt-versus-svt-…
REFs (2/3):
[6]Dale Dubin "Rapid Interpretation of EKGs". 6th edition.
[7] litfl.com/atrial-tachyca…
[9]osmosis.org/learn/AV_reent…
[9]litfl.com/supraventricul…
[9]aafp.org/afp/2010/1015/…
[6]Dale Dubin "Rapid Interpretation of EKGs". 6th edition.
[7] litfl.com/atrial-tachyca…
[9]osmosis.org/learn/AV_reent…
[9]litfl.com/supraventricul…
[9]aafp.org/afp/2010/1015/…
REFs (3/3):
[9] Baltazar RF. Supraventricular Tachycardia due to Reentry. In: Basic and Bedside Electrocardiography. 1st ed.; 2009. doctorlib.info/cardiology/ele….
[10]ucsfmed.wordpress.com/2017/07/18/mof…
[11,13]ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
[12]thelancet.com/journals/lance…
[9] Baltazar RF. Supraventricular Tachycardia due to Reentry. In: Basic and Bedside Electrocardiography. 1st ed.; 2009. doctorlib.info/cardiology/ele….
[10]ucsfmed.wordpress.com/2017/07/18/mof…
[11,13]ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.11…
[12]thelancet.com/journals/lance…
@MedTweetorials @cardionerds @medicine_strong @CPSolvers @COREIMpodcast @CuriousClinPod @DxRxEdu @rabihmgeha @tony_breu @AvrahamCooperMD @medrants @AmitGoyalMD @Dr_DanMD
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh