2/
Most of us go through life without ever experiencing a "windfall".
We don't start billion dollar companies.
Or win lotteries.
Or become highly paid sportsmen or movie stars.
Heck, most of us never even have a tweet go viral.
Most of us go through life without ever experiencing a "windfall".
We don't start billion dollar companies.
Or win lotteries.
Or become highly paid sportsmen or movie stars.
Heck, most of us never even have a tweet go viral.
3/
For "ordinary" folks like us, the most promising path to a comfortable retirement boils down to 3 things:
a) Planning ahead and starting early,
b) Living consistently below our means (ie, saving diligently), and
c) Investing our savings intelligently over many years.
For "ordinary" folks like us, the most promising path to a comfortable retirement boils down to 3 things:
a) Planning ahead and starting early,
b) Living consistently below our means (ie, saving diligently), and
c) Investing our savings intelligently over many years.
4/
This thread is about the first point above -- planning ahead.
In my mind, planning for retirement is a 2-step process:
Step 1. Set a "retirement goal", and
Step 2. Figure out a path to reach that goal.
This thread is about the first point above -- planning ahead.
In my mind, planning for retirement is a 2-step process:
Step 1. Set a "retirement goal", and
Step 2. Figure out a path to reach that goal.
5/
Step 1 -- setting a retirement goal -- usually means coming up with something like this:
Retirement Goal: To build a portfolio of size X dollars, within Y years from now.
What should X and Y be?
Well, that varies from person to person.
Step 1 -- setting a retirement goal -- usually means coming up with something like this:
Retirement Goal: To build a portfolio of size X dollars, within Y years from now.
What should X and Y be?
Well, that varies from person to person.
6/
For example, suppose we want to retire 10 years from now -- in 2031.
And to live comfortably in retirement, say we need $50K per year -- in today's dollars.
If we expect inflation to run at roughly 3% per year, that's $50K * (1.03^10) = ~$67K in 2031 dollars.
For example, suppose we want to retire 10 years from now -- in 2031.
And to live comfortably in retirement, say we need $50K per year -- in today's dollars.
If we expect inflation to run at roughly 3% per year, that's $50K * (1.03^10) = ~$67K in 2031 dollars.
7/
Of that ~$67K, suppose we expect ~$25K to come from our social security benefits.
The remaining $67K - $25K = $42K will have to come from our retirement portfolio.
So, how large should our portfolio be, so it can generate this $42K for us, year after year?
Of that ~$67K, suppose we expect ~$25K to come from our social security benefits.
The remaining $67K - $25K = $42K will have to come from our retirement portfolio.
So, how large should our portfolio be, so it can generate this $42K for us, year after year?
8/
There are some "Rules" to help us answer that.
For example, there's the "3% Rule". It says our portfolio should be ~33.3 times our yearly withdrawal.
That means, for our $42K yearly withdrawal, we'll need a 33.3 * $42K = ~$1.4M portfolio.
For more:
There are some "Rules" to help us answer that.
For example, there's the "3% Rule". It says our portfolio should be ~33.3 times our yearly withdrawal.
That means, for our $42K yearly withdrawal, we'll need a 33.3 * $42K = ~$1.4M portfolio.
For more:
https://twitter.com/10kdiver/status/1287043526153273344
9/
So, that can be our "retirement goal": To amass a $1.4M portfolio within 10 years.
That's Step 1 -- setting the goal.
Here's a recap of how we arrived at this goal:
So, that can be our "retirement goal": To amass a $1.4M portfolio within 10 years.
That's Step 1 -- setting the goal.
Here's a recap of how we arrived at this goal:

10/
On to Step 2 -- figuring out a path to our goal.
This path involves both Saving and Investing.
Here's a simple model:
Between now and retirement (say, T years from now), we save $S each year.
These savings go into our retirement portfolio, which compounds at I% per year.
On to Step 2 -- figuring out a path to our goal.
This path involves both Saving and Investing.
Here's a simple model:
Between now and retirement (say, T years from now), we save $S each year.
These savings go into our retirement portfolio, which compounds at I% per year.
11/
I like to call this the "SIT model", because the model has 3 parameters:
a) Our Savings: $S per year,
b) Our Investment returns: I% per year, and
c) Our Time horizon: T years until retirement.
Here's a flowchart of this model:
I like to call this the "SIT model", because the model has 3 parameters:
a) Our Savings: $S per year,
b) Our Investment returns: I% per year, and
c) Our Time horizon: T years until retirement.
Here's a flowchart of this model:
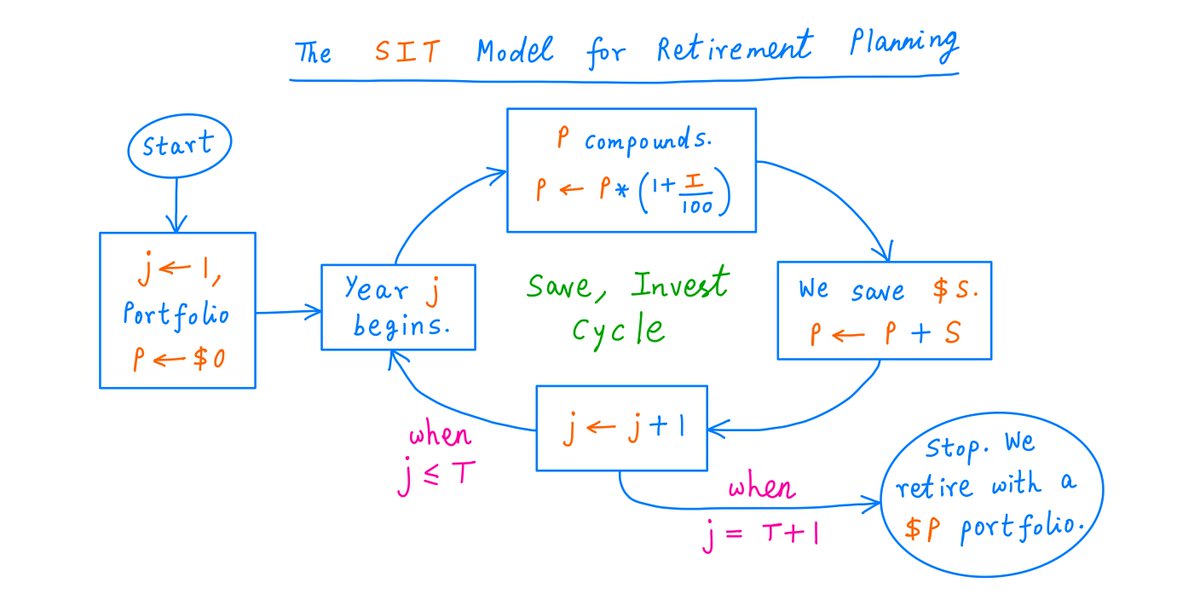
12/
For example, let's take our "$1.4M by 2031" goal.
To achieve this goal, suppose we save S = $75K per year -- every year from 2021 through 2030.
And suppose our portfolio grows at I = 10% per year.
For example, let's take our "$1.4M by 2031" goal.
To achieve this goal, suppose we save S = $75K per year -- every year from 2021 through 2030.
And suppose our portfolio grows at I = 10% per year.
13/
Here's how this will pan out.
We begin 2021 with a $0 portfolio.
During 2021, we save S = $75K.
At the end of 2021, we add this $75K to our $0 portfolio.
So, at the end of 2021, our portfolio will be worth $75K.
Here's how this will pan out.
We begin 2021 with a $0 portfolio.
During 2021, we save S = $75K.
At the end of 2021, we add this $75K to our $0 portfolio.
So, at the end of 2021, our portfolio will be worth $75K.
14/
In 2022, this $75K will grow by I = 10% -- and turn into 1.1 * $75K = $82.5K.
To this $82.5K, we'll add our $75K of 2022 savings.
So, at the end of 2022, our portfolio will be worth $82.5K + $75K = $157.5K.
In 2022, this $75K will grow by I = 10% -- and turn into 1.1 * $75K = $82.5K.
To this $82.5K, we'll add our $75K of 2022 savings.
So, at the end of 2022, our portfolio will be worth $82.5K + $75K = $157.5K.
15/
This continues in 2023.
Our $157.5K portfolio grows into 1.1 * $157.5K = $173.25K.
To that, we add another $75K in savings -- leaving us with $173.25K + $75K = $248.25K at the end of 2023.
And so on -- until the end of 2030.
That's the SIT model.
This continues in 2023.
Our $157.5K portfolio grows into 1.1 * $157.5K = $173.25K.
To that, we add another $75K in savings -- leaving us with $173.25K + $75K = $248.25K at the end of 2023.
And so on -- until the end of 2030.
That's the SIT model.
16/
So, finally, when we retire in 2031, how much will our portfolio be worth?
To calculate that, we could cycle through the flowchart several more times -- until we get to the end of 2030.
But where's the fun in that?
So, finally, when we retire in 2031, how much will our portfolio be worth?
To calculate that, we could cycle through the flowchart several more times -- until we get to the end of 2030.
But where's the fun in that?
17/
There's a much faster way -- a formula that directly tells us how much our portfolio will be worth at retirement.
Here it is:
There's a much faster way -- a formula that directly tells us how much our portfolio will be worth at retirement.
Here it is:
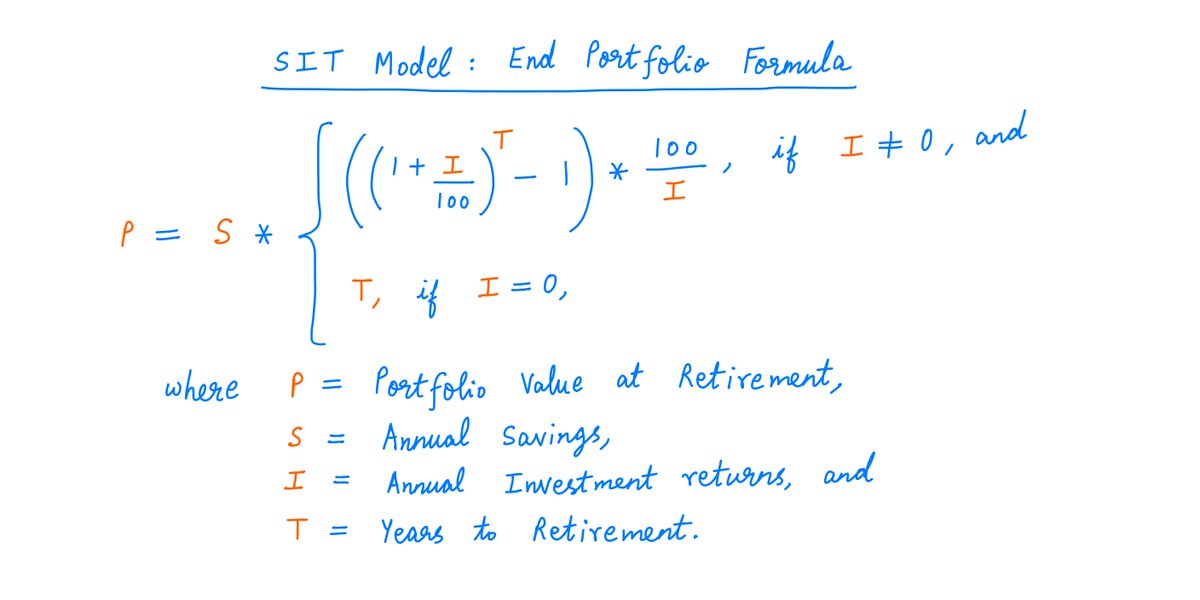
18/
Applying this formula, we see that saving S = $75K per year (and growing the portfolio at I = 10% per year) gets us only to ~$1.195M by 2031.
This is *short* of our $1.4M goal.
Applying this formula, we see that saving S = $75K per year (and growing the portfolio at I = 10% per year) gets us only to ~$1.195M by 2031.
This is *short* of our $1.4M goal.
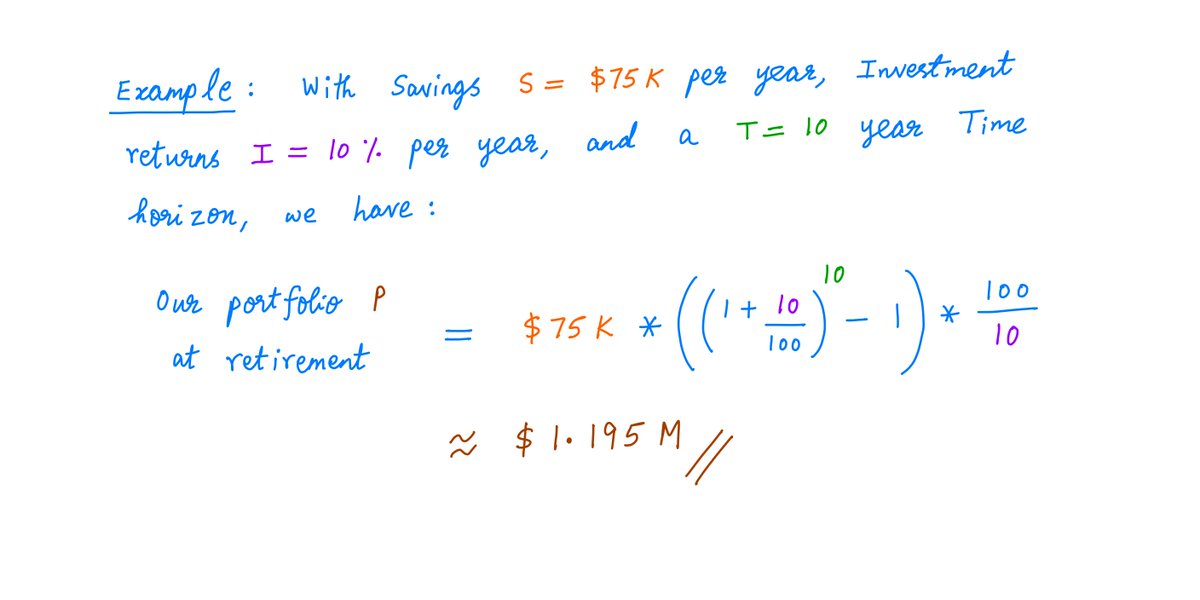
19/
Therefore, to reach our goal, we should either save more or invest better.
If we can't save more (ie, S is capped at $75K), then we need I to be ~13.3%. 10% won't cut it.
And if we can't invest better (ie, I is capped at 10%), then S has to be ~$88K. $75K won't cut it.
Therefore, to reach our goal, we should either save more or invest better.
If we can't save more (ie, S is capped at $75K), then we need I to be ~13.3%. 10% won't cut it.
And if we can't invest better (ie, I is capped at 10%), then S has to be ~$88K. $75K won't cut it.
20/
There's a trade-off here.
If we're very good at investing, we can get away with lower savings.
For example, if we can generate an I = 20% return per year, we only need to save S = $54K per year to reach our goal.
There's a trade-off here.
If we're very good at investing, we can get away with lower savings.
For example, if we can generate an I = 20% return per year, we only need to save S = $54K per year to reach our goal.
21/
And vice-versa.
If we're very good savers, we can tolerate a lower investment return and still achieve our goal.
For example, if we're able to save S = $120K per year, we'll reach our goal even if our portfolio only compounds at I = 3.5% annually.
And vice-versa.
If we're very good savers, we can tolerate a lower investment return and still achieve our goal.
For example, if we're able to save S = $120K per year, we'll reach our goal even if our portfolio only compounds at I = 3.5% annually.
22/
So, here's the thing:
To reach a particular retirement goal, there isn't "one true path".
Many combinations of S and I can get us to our goal.
Good savers can be mediocre investors, and vice-versa.
There's hope for all of us.
So, here's the thing:
To reach a particular retirement goal, there isn't "one true path".
Many combinations of S and I can get us to our goal.
Good savers can be mediocre investors, and vice-versa.
There's hope for all of us.
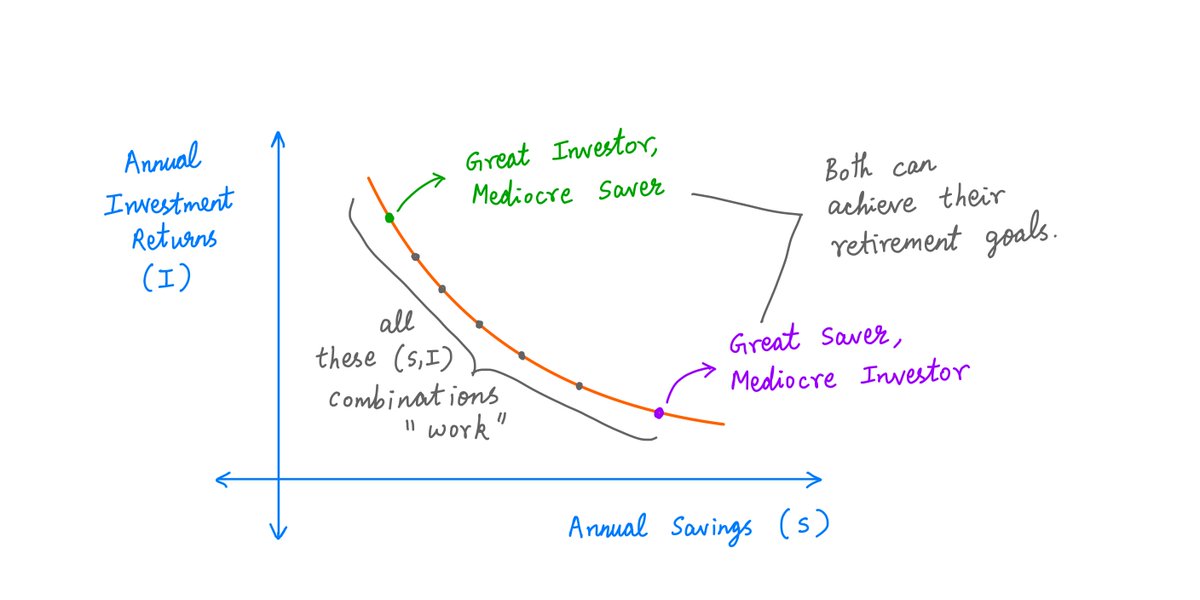
23/
The other key dimension is Time (T).
The earlier we start planning, saving, and investing for retirement, the more we let compounding do the heavy lifting for us.
As long as we start early enough, we don't have to be super good at *either* saving or investing.
The other key dimension is Time (T).
The earlier we start planning, saving, and investing for retirement, the more we let compounding do the heavy lifting for us.
As long as we start early enough, we don't have to be super good at *either* saving or investing.
24/
For example, say our goal is to retire with a portfolio that can safely yield us $50K per year (in 2021 dollars).
At 3% annual inflation and 10% annual investment returns, following the 3% Rule, here's how much we need in annual savings S for various time horizons T:
For example, say our goal is to retire with a portfolio that can safely yield us $50K per year (in 2021 dollars).
At 3% annual inflation and 10% annual investment returns, following the 3% Rule, here's how much we need in annual savings S for various time horizons T:
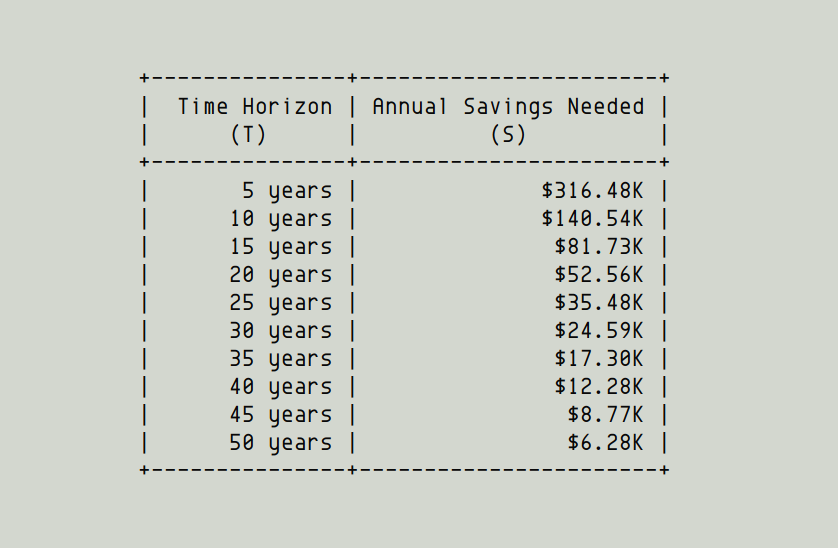
25/
If our time horizon is short (eg, we need to retire in 5 or 10 years), the only way to safely do so is by saving hundreds of thousands of dollars per year.
But if we're planning 40 years ahead, we only need to save ~$12K per year to retire with the same level of comfort.
If our time horizon is short (eg, we need to retire in 5 or 10 years), the only way to safely do so is by saving hundreds of thousands of dollars per year.
But if we're planning 40 years ahead, we only need to save ~$12K per year to retire with the same level of comfort.
26/
Time is indeed a super power.
For example, here's the inspiring story of a janitor who built a fortune by compounding small savings over decades.
It's from @morganhousel's book, The Psychology of Money.
If I quote this any more often, Morgan's going to want a royalty!
Time is indeed a super power.
For example, here's the inspiring story of a janitor who built a fortune by compounding small savings over decades.
It's from @morganhousel's book, The Psychology of Money.
If I quote this any more often, Morgan's going to want a royalty!

27/
As Buffett says, he doesn't try to jump over 7-foot bars. He looks around for 1-foot bars that he can just step over.
If we start planning for retirement early, the S and I we need will be low hurdles that we can comfortably clear -- the equivalent of 1-foot bars.
As Buffett says, he doesn't try to jump over 7-foot bars. He looks around for 1-foot bars that he can just step over.
If we start planning for retirement early, the S and I we need will be low hurdles that we can comfortably clear -- the equivalent of 1-foot bars.
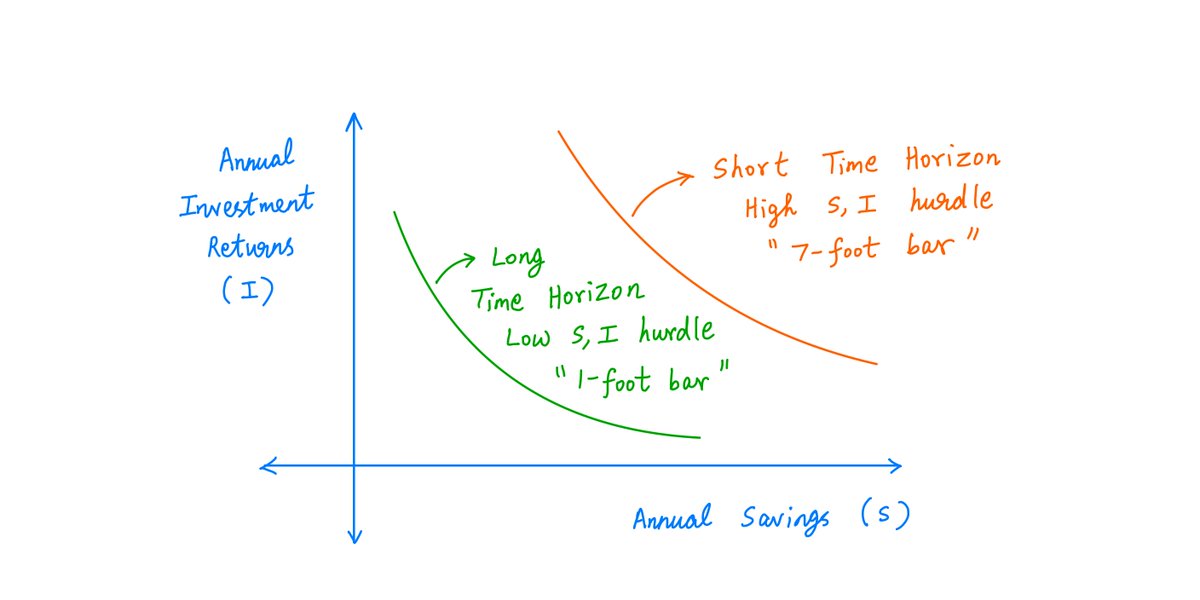
28/
The SIT model can be a very useful retirement planning tool.
But we should always remember: it's only a model.
In reality, S and I won't be constant for decades. They'll change every year.
For more on such path-dependence (aka, sequence risk):
The SIT model can be a very useful retirement planning tool.
But we should always remember: it's only a model.
In reality, S and I won't be constant for decades. They'll change every year.
For more on such path-dependence (aka, sequence risk):
https://twitter.com/10kdiver/status/1353169429287211009
29/
Still, I like the simplicity of the SIT model.
It's a great way to crunch the numbers to get us in the ballpark of a decent retirement plan.
Of course, as with all plans, it's important to periodically monitor our progress and make mid-course corrections as needed.
Still, I like the simplicity of the SIT model.
It's a great way to crunch the numbers to get us in the ballpark of a decent retirement plan.
Of course, as with all plans, it's important to periodically monitor our progress and make mid-course corrections as needed.
30/
For many people, retirement planning is a low hanging fruit. It can dramatically improve financial security and well-being.
I hope this thread covered the basics in an actionable and digestible way.
Thank you very much. Please stay safe. Enjoy your weekend!
/End
For many people, retirement planning is a low hanging fruit. It can dramatically improve financial security and well-being.
I hope this thread covered the basics in an actionable and digestible way.
Thank you very much. Please stay safe. Enjoy your weekend!
/End
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh