a brilliant🧵 for your Monday morning:
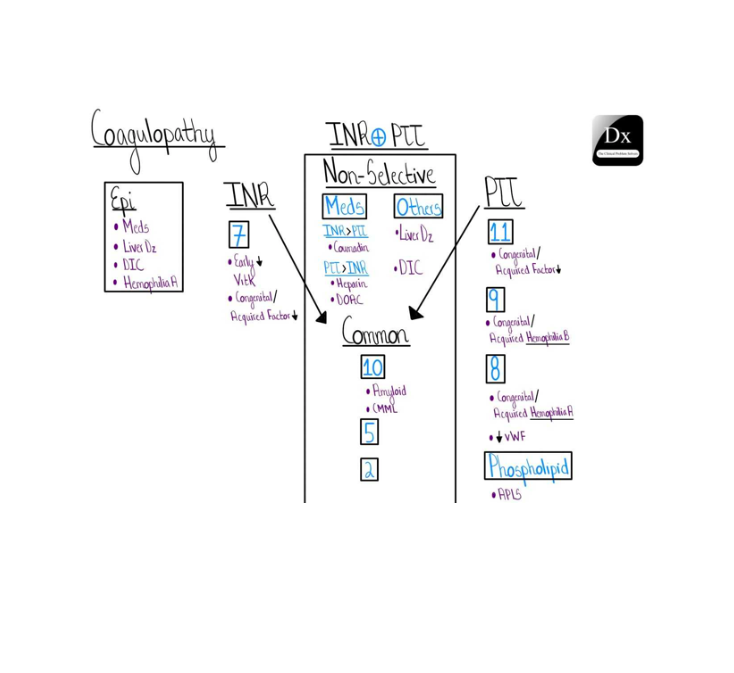
6/14 - bit.ly/3gR3UbQ #cpsvmrpearls Both TTP and HUS can p/w kidney injury + neurological Sx. To differentiate b/w them based on clinical Sx, remember that in TTP, the neuro Sx > renal Sx and in HUS, the renal Sx > neuro Sx
6/14 - bit.ly/3gR3UbQ #cpsvmrpearls Both TTP and HUS can p/w kidney injury + neurological Sx. To differentiate b/w them based on clinical Sx, remember that in TTP, the neuro Sx > renal Sx and in HUS, the renal Sx > neuro Sx

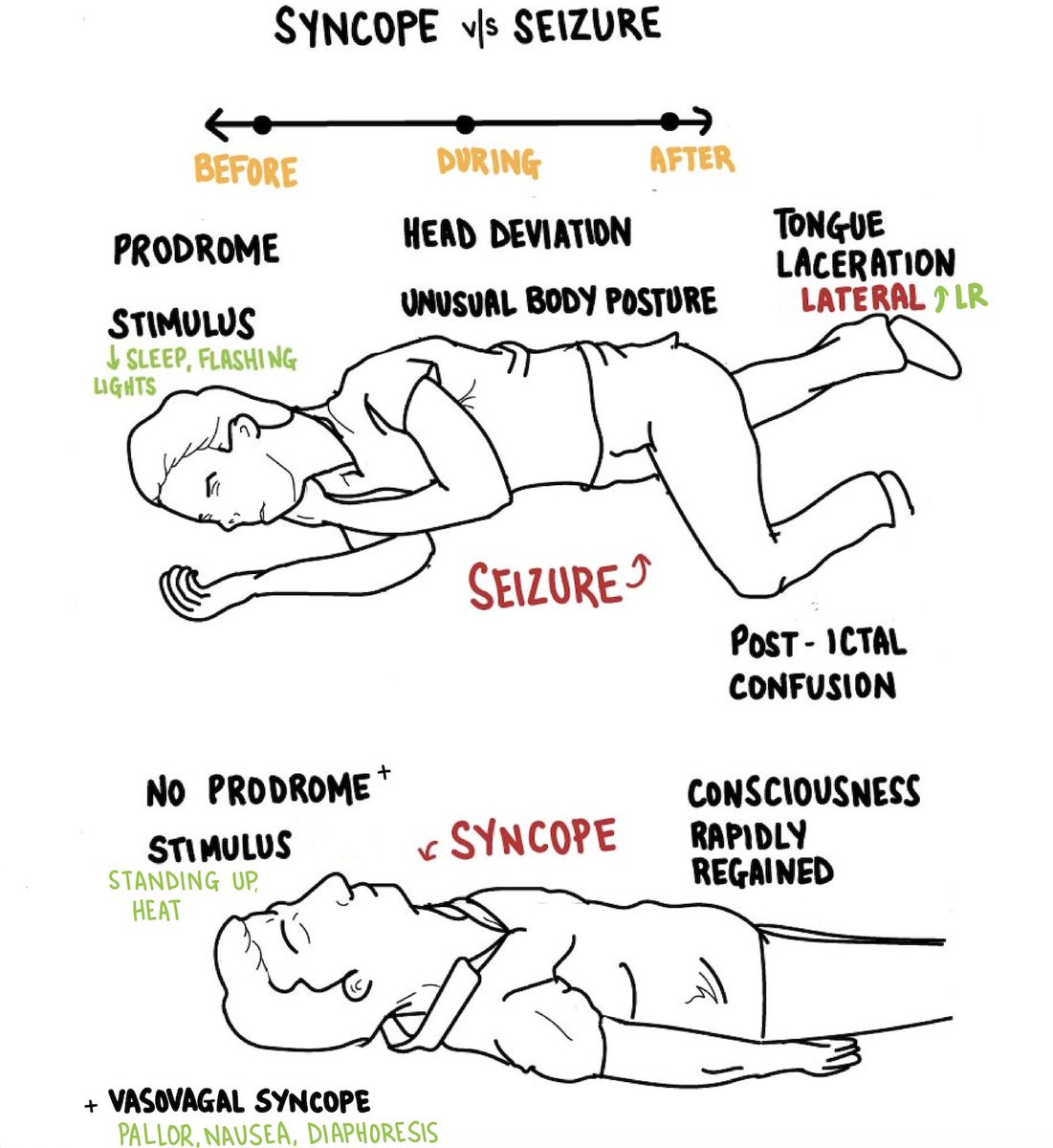
6/15 - bit.ly/3ql5IOU #cpsvmrpearls Consider CV & neuro causes when evaluating unwitnessed LOC. Presence & location of tongue bites can help differentiate b/w them: Bites on the a) lateral aspect of the tongue - seizure b) tip of the tongue - syncope c) lips/cheek - PNES 
6/16 - bit.ly/35CthJt #cpsvmrpearls CNS involvement is infrequent in small & medium vessel vasculitis which commonly p/w << systemic manifestations, but when present, CNS involvement is a predictor of poor prognosis & indication for aggressive immunosuppressive Tx. (1/2)
However, in large-vessel vasculitis, CNS involvement may benefit from vascular interventions > intensification of immunosuppressive Tx. (2/2)
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
6/17- bit.ly/35AXWa2 #cpsvmrpearls A nodule indicates deep dermal involvement which makes a systemic disease more likely, often a granulomatous pulmonary disease such as TB, NTM, or fungal infections. 

6/18 - bit.ly/3vH3ydu #cpsvmrpearls The MC cause of tricuspid regurg = functional regurg 2/2 to R-sided dilation. In the presence of severe regurg w/o RV dilation, think about primary valve disease (eg. ischemia, vegetation, trauma, congenital, rheumatic, CTD, Carcinoid)
6/19 - bit.ly/3gKf4Ag #cpsvmrpearls In a patient presenting with high-risk chest pain, if the EKG and troponin are not diagnostic of ACS, do not delay getting a CT chest. The CT chest can help diagnose emergent causes such as aortic dissection and pulmonary embolism. 

6/20 - #cpsvmrpearls A physical exam is helpful in differentiating b/w the ulcers of Leishmaniasis vs Sporotrichosis:
Cutaneous leishmaniasis - well-defined ulcers w/ elevated border
Sporotrichosis - nodules and ulcers along the lymphatic channels
Cutaneous leishmaniasis - well-defined ulcers w/ elevated border
Sporotrichosis - nodules and ulcers along the lymphatic channels
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh