1.
#Thread on the occasion of 586th anniversary of coronation of Kapilendra Gajapati
One of the greatest Hindu rulers from Odisha, he kept the Bengal & Bahmani Sultanates on toes, & patronised the Odia Culture.
#Odisha #KapilendraGajapati #Hindutva #History
#Thread on the occasion of 586th anniversary of coronation of Kapilendra Gajapati
One of the greatest Hindu rulers from Odisha, he kept the Bengal & Bahmani Sultanates on toes, & patronised the Odia Culture.
#Odisha #KapilendraGajapati #Hindutva #History

2.
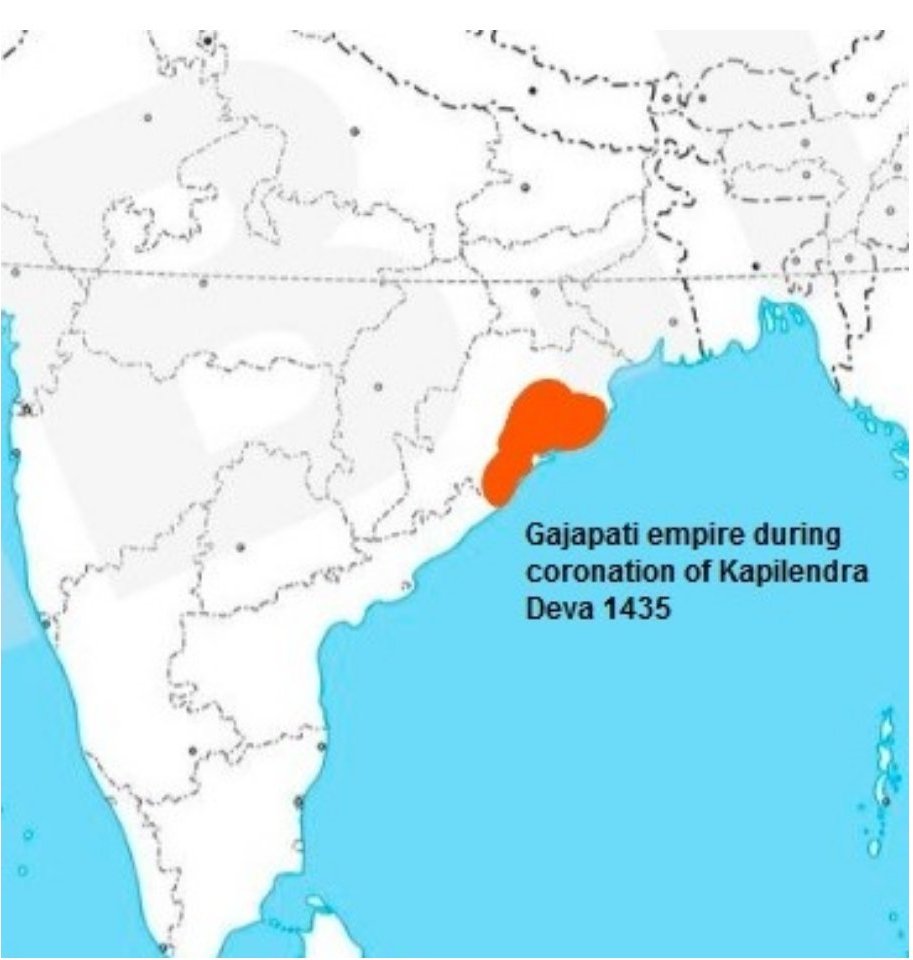
1435, Jun 29: Kapilendra Gajapati was coronated at Cuttack when the king Bhanudeva IV was away on southern campaigns.
1435, Jun 29: Kapilendra Gajapati was coronated at Cuttack when the king Bhanudeva IV was away on southern campaigns.

3.
At the time of his accession, the Gajapati kingdom was being hard-pressed by the Jaunpur, Bengal Sultanates from the north, and Bahmani Sultanate from the south-west. Vijayanagara Empire had also conquered the eastern coast upto Godavari delta.

At the time of his accession, the Gajapati kingdom was being hard-pressed by the Jaunpur, Bengal Sultanates from the north, and Bahmani Sultanate from the south-west. Vijayanagara Empire had also conquered the eastern coast upto Godavari delta.
4.
Since the accession was contested, Kapilendra Gajapati earnestly commenced to bring Odia nobles under control.
1436: Bengal Sultanate's Shamsuddin Ahmad Shah's invasion of Odisha was repelled by his able minister and general, Gopinath Mahapatra. The kingdom expanded to Ganga.
Since the accession was contested, Kapilendra Gajapati earnestly commenced to bring Odia nobles under control.
1436: Bengal Sultanate's Shamsuddin Ahmad Shah's invasion of Odisha was repelled by his able minister and general, Gopinath Mahapatra. The kingdom expanded to Ganga.
5.
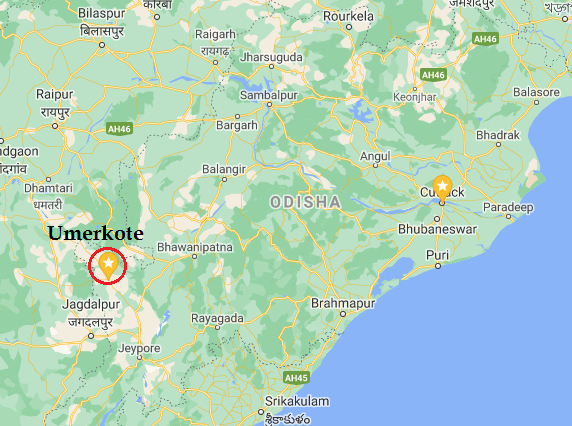
1440-41: Gopinath Mahapatra was deployed on western border to check the invasion by Malwa, which was repelled successfully as well! Gajapati borders extended to Umerkote in Odisha.
1440-41: Gopinath Mahapatra was deployed on western border to check the invasion by Malwa, which was repelled successfully as well! Gajapati borders extended to Umerkote in Odisha.
6.
1441-43: Kapilendra brought under his control all the chiefs previously loyal to Bhanudeva IV - Shilavamshis, Matsyas, Vishnuvardhan-Chakravartins, and some others. The empire now stretched from Ganga to Vishakhapatnam
1444: Jaunpur Sultan's invasion (J1h@d) was repelled.
1441-43: Kapilendra brought under his control all the chiefs previously loyal to Bhanudeva IV - Shilavamshis, Matsyas, Vishnuvardhan-Chakravartins, and some others. The empire now stretched from Ganga to Vishakhapatnam
1444: Jaunpur Sultan's invasion (J1h@d) was repelled.

7.
1447: Kapilendra attacked Bengal & defeated Sultan Nasiruddin Muhammad Shah. The Gopinathpur inscription honours him with 'Gaudamardi' & 'Gaudendra' titles. 👇
1448: Andhra kingdom conquered by Gajapatis. The Bahmani governor Sanjar Khan was suppressing independence of ...
1447: Kapilendra attacked Bengal & defeated Sultan Nasiruddin Muhammad Shah. The Gopinathpur inscription honours him with 'Gaudamardi' & 'Gaudendra' titles. 👇
1448: Andhra kingdom conquered by Gajapatis. The Bahmani governor Sanjar Khan was suppressing independence of ...

8.
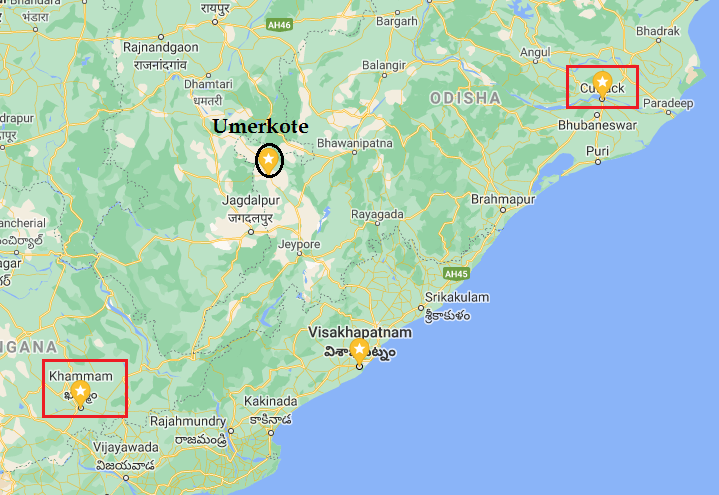
...Hindu chiefs of Telangana. He ignored Bahmani Sultan’s instructions not to incite Kapilendra’s wrath. Result? - Battle of Khammamet took place between Gajapatis & Bahmanis.
Kapilendra’s son Hamvira, & Gajaravu Tippa (Velama chief) subjugated the Bahmanis!


...Hindu chiefs of Telangana. He ignored Bahmani Sultan’s instructions not to incite Kapilendra’s wrath. Result? - Battle of Khammamet took place between Gajapatis & Bahmanis.
Kapilendra’s son Hamvira, & Gajaravu Tippa (Velama chief) subjugated the Bahmanis!


9.
1454: Kondavidu, Vinukonda, Addanki brought under Gajapati control.
1459-60: Bahmanis invade Telangana. Hindu Velama chiefs appealed to Kapilendra Gajapati for help. Bahmanis besieged Devarakonda fort. Hindu army arrived. At Battle of Devarakonda, Bahmanis were sandwiched ...
1454: Kondavidu, Vinukonda, Addanki brought under Gajapati control.
1459-60: Bahmanis invade Telangana. Hindu Velama chiefs appealed to Kapilendra Gajapati for help. Bahmanis besieged Devarakonda fort. Hindu army arrived. At Battle of Devarakonda, Bahmanis were sandwiched ...
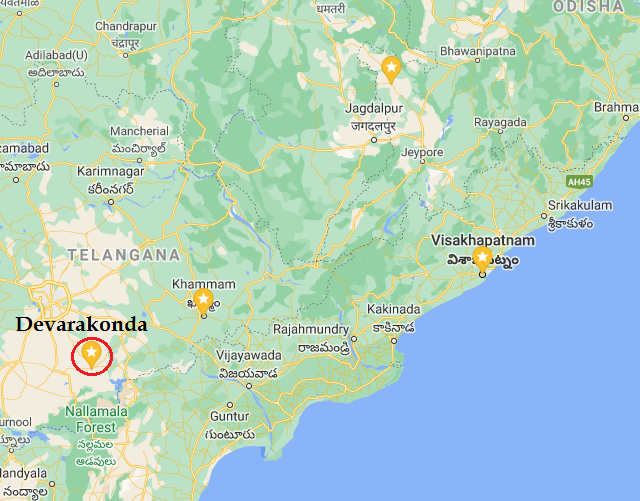
10.
between Velama & Odia Hindus. Bahmani army was routed & chased for 80 miles. 6-7k cavalry was k!lled. Kapilendra assumed the title of ‘Kalavargeshwara’ (Lord of Kalavarga or Gulbarga)
Hamvira Gajapati conquers Warangal Fort by defeating Bahmani officer Khwaja Mahmud Gawan.
between Velama & Odia Hindus. Bahmani army was routed & chased for 80 miles. 6-7k cavalry was k!lled. Kapilendra assumed the title of ‘Kalavargeshwara’ (Lord of Kalavarga or Gulbarga)
Hamvira Gajapati conquers Warangal Fort by defeating Bahmani officer Khwaja Mahmud Gawan.

11.
1461: Malwa had invaded Bahmanis; the Telangana chiefs again allied with Gajapatis to invade Bahmanis! The Hindu armies reached near the Bahmani capital at Bidar.
Just then, news arrived of Jaunpur's invasion of Odisha. Hence, the Hindu armies withdrew from Bidar.
1461: Malwa had invaded Bahmanis; the Telangana chiefs again allied with Gajapatis to invade Bahmanis! The Hindu armies reached near the Bahmani capital at Bidar.
Just then, news arrived of Jaunpur's invasion of Odisha. Hence, the Hindu armies withdrew from Bidar.

12.
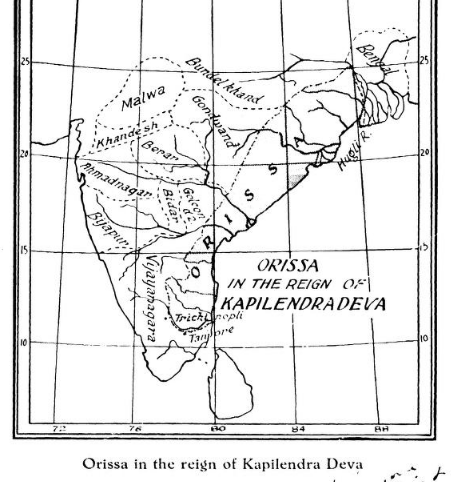
1464: Since the-then Vijayanagara emperor Mallikarjuna Raya wasn't strong, Kapilendra Gajapati invaded his territory till Hampi. He acquired a large territory along the eastern coast till Tiruchirapalli.

1464: Since the-then Vijayanagara emperor Mallikarjuna Raya wasn't strong, Kapilendra Gajapati invaded his territory till Hampi. He acquired a large territory along the eastern coast till Tiruchirapalli.

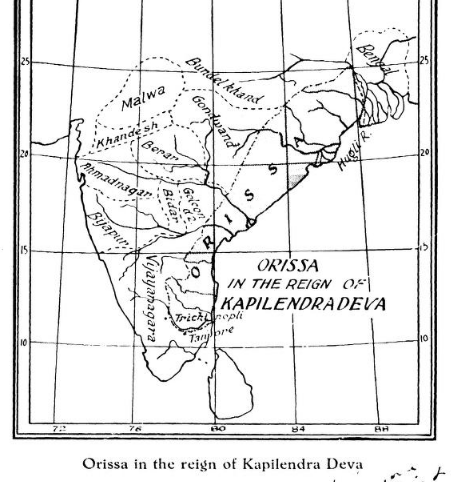
13.
Gajapati empire now reached its heights, and boasted borders from river Ganga to Kaveri!
His conquests enabled Kapilendra to assume the titles of "Gajapati Gaudeshwara Navakoti Karnata Kalavargeshwara" (Lord of the Elephants; Lord of Gauda, 9 peoples of Karnata & Gulbarga)
Gajapati empire now reached its heights, and boasted borders from river Ganga to Kaveri!
His conquests enabled Kapilendra to assume the titles of "Gajapati Gaudeshwara Navakoti Karnata Kalavargeshwara" (Lord of the Elephants; Lord of Gauda, 9 peoples of Karnata & Gulbarga)
14.
After 1464, amidst internal revolts & reconquest of southern territories by Vijayanagar, Kapilendra declared his younger son, Purushottamdeva to be successor in 1466.
1468, Jan 12: Kapilendra Gajapati passes away.
After 1464, amidst internal revolts & reconquest of southern territories by Vijayanagar, Kapilendra declared his younger son, Purushottamdeva to be successor in 1466.
1468, Jan 12: Kapilendra Gajapati passes away.

15.
Although a very active warrior, Kapilendra had also authored a Sanskrit work - Parshuram Bijaya.
He adopted Odia language as state language. Odia Mahabharata as well as Ramayana was written by great Odia poet Sarala Das during the reign of Kapilendradeva.

Although a very active warrior, Kapilendra had also authored a Sanskrit work - Parshuram Bijaya.
He adopted Odia language as state language. Odia Mahabharata as well as Ramayana was written by great Odia poet Sarala Das during the reign of Kapilendradeva.


16.
Interesting to note:- Maharana Kumbha (r.1433-68) was a contemporary of Kapilendra Gajapati (r.1435-68). The two Hindu heroes were subjugating majority of Sultanates in the subcontinent simultaneously!
Maharana Kumbha - Gujarat, Malwa
Kapilendra Gajapati - Bahmanis, Bengal

Interesting to note:- Maharana Kumbha (r.1433-68) was a contemporary of Kapilendra Gajapati (r.1435-68). The two Hindu heroes were subjugating majority of Sultanates in the subcontinent simultaneously!
Maharana Kumbha - Gujarat, Malwa
Kapilendra Gajapati - Bahmanis, Bengal


17.
Credits to @Param_Chaitanya for help in making thread.
Credits to @Param_Chaitanya for help in making thread.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh























