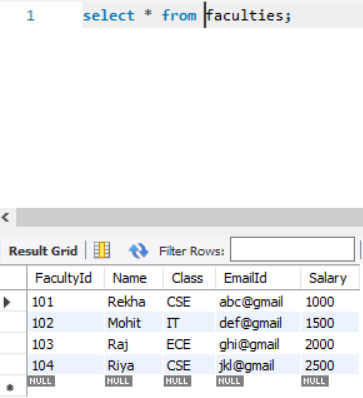
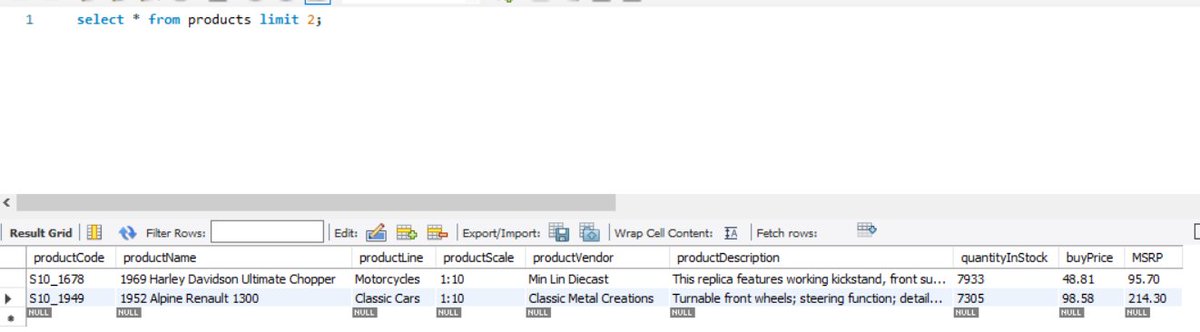
The topic of TRIGGERS is a level-up from creating queries and sub-queries in the handling databases.
A super-easy guide to triggers in SQL 🧵👇
A super-easy guide to triggers in SQL 🧵👇
☑️ What is a trigger in the laymen (standard) language?
When someone pokes you or does something to agitate you, there is a high chance that you might get 'triggered' automatically! Right?
When someone pokes you or does something to agitate you, there is a high chance that you might get 'triggered' automatically! Right?
☑️ Triggers in SQL
So, when we say TRIGGERS in SQL, it is simply a stored program that gets executed on its own when a triggering event occurs. Now, triggers are a part of PL/SQL.
PL/SQL is an extension of SQL where SQL queries are used and procedural statements/language.
So, when we say TRIGGERS in SQL, it is simply a stored program that gets executed on its own when a triggering event occurs. Now, triggers are a part of PL/SQL.
PL/SQL is an extension of SQL where SQL queries are used and procedural statements/language.
Stored Program is an SQL code that can be saved and reused multiple times.
For example, You have a query that has to be implemented numerous times, instead of writing it every single time, you can save it as a stored program and call that program to run that query when you want.
For example, You have a query that has to be implemented numerous times, instead of writing it every single time, you can save it as a stored program and call that program to run that query when you want.
Triggering Events -> Triggers are triggered/executed in response to DELETE, UPDATE and INSERT queries.
☑️ How to create a trigger?
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
{ BEFORE | AFTER} {INSERT | UPDATE| DELETE }
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
trigger_body;
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
{ BEFORE | AFTER} {INSERT | UPDATE| DELETE }
ON table_name FOR EACH ROW
trigger_body;
👉 Syntax Explanation: CREATE TRIGGER phrase is used to create the trigger, followed by the trigger's name. You can name your trigger whatever you want.
Decide when you want your trigger to be invoked, before or after, and likewise write that keyword.
Decide when you want your trigger to be invoked, before or after, and likewise write that keyword.
Follow that with either insert, delete or update event.
Trigger body would include the actions you want the trigger to perform.
Trigger body would include the actions you want the trigger to perform.
🌟 EXAMPLE!!
Let's create a table named 'allemployees'.
It has columns:-
Eid -> Employee ID
Contact -> Employee contact number
Name -> Employee Name
Refer the Image
Let's create a table named 'allemployees'.
It has columns:-
Eid -> Employee ID
Contact -> Employee contact number
Name -> Employee Name
Refer the Image
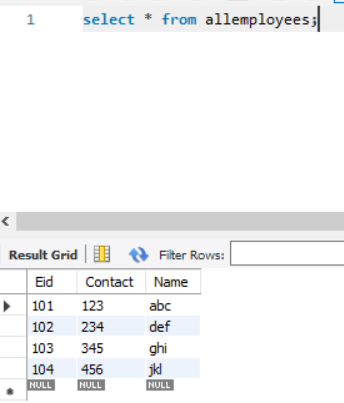
👉 Creating a TRIGGER before the insert query is executed.
(See the image for the code)
Explanation: A trigger named 'bef_insert_emp' is created on the table 'allemployees'
(See the image for the code)
Explanation: A trigger named 'bef_insert_emp' is created on the table 'allemployees'
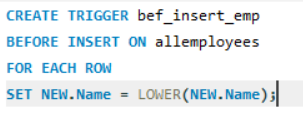
The trigger would be executed before the values are entered in the table and would perform the assigned function.
The assigned function is that whatever name is being inserted in the table should be in LOWER CASE.
For that, we use the SET keyword.
The assigned function is that whatever name is being inserted in the table should be in LOWER CASE.
For that, we use the SET keyword.
SET NEW.Name = LOWER(https://t.co/UOUAZLE9s2);
Here, NEW is a keyword for the latest values being filled in the table.
So, New.Name is referring to the latest value in the Name column.
Here, NEW is a keyword for the latest values being filled in the table.
So, New.Name is referring to the latest value in the Name column.
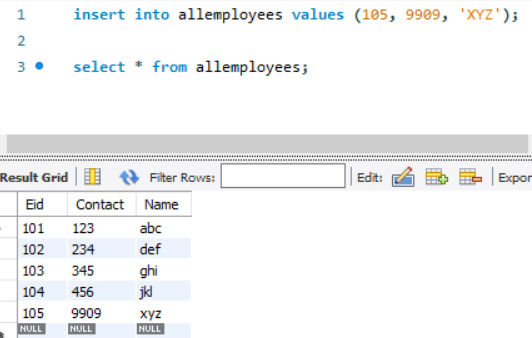
When we try to put an upper case name or a mixture of the upper and lower case name, the trigger will convert the name into the lower case before inserting it into the table. 
If you like the explanation and are interested in content related to Data Science, consider liking and retweeting the post.
Follow me too! 😁
Follow me too! 😁
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh