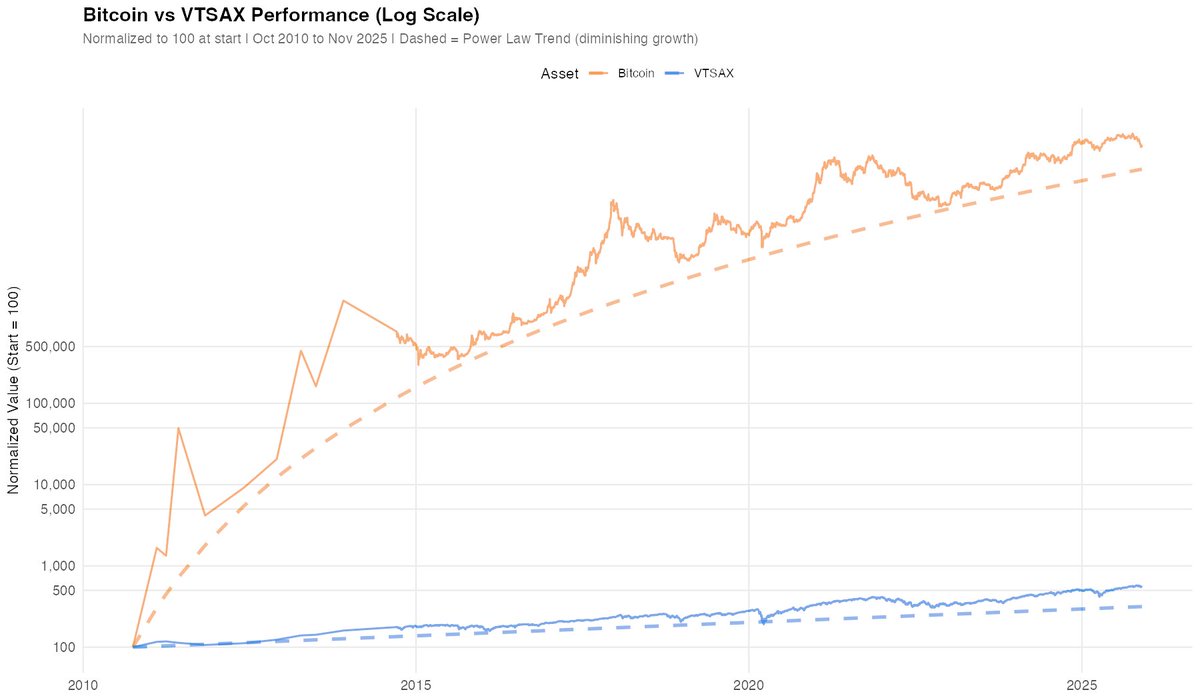
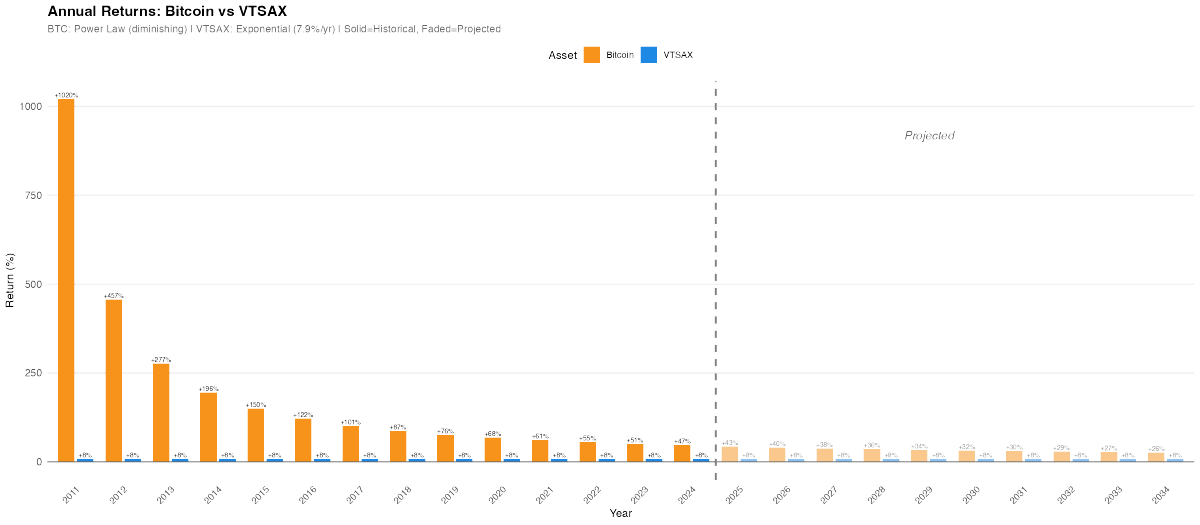
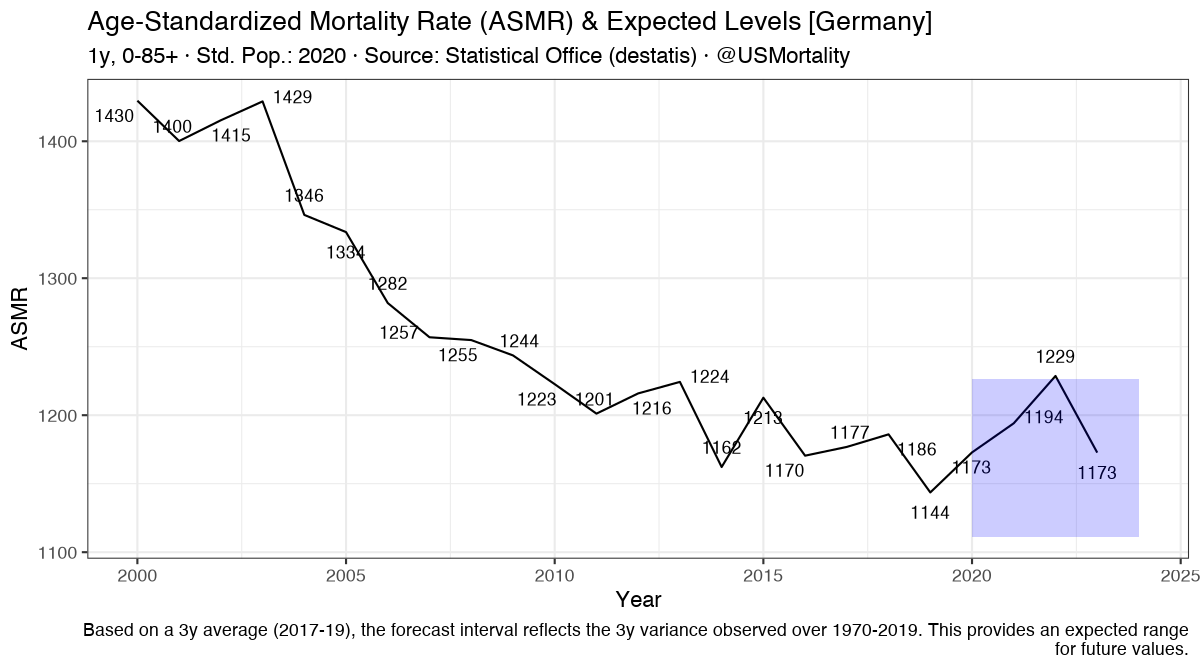
Thread on how to calculate Vaccine Efficiacy (VE) as defined by CDC, and deep dive into MA Barnstable County MWWR outbreak case data.
⬇️⬇️⬇️ 1/n
#Covid #Covid19 #Covid_19 #Corona #Coronavirus
⬇️⬇️⬇️ 1/n
#Covid #Covid19 #Covid_19 #Corona #Coronavirus
In order to Calculate VE, we need to calculate Risk Ratio (RR).
CDC, in their epidemiological handbook, gives this definition/example for Varicella:
CDC, in their epidemiological handbook, gives this definition/example for Varicella:

I've rebuilt above example in Google Sheets:
- VE for this varicella example/outbreak is at 73%.
- Not statistically significant at 90%, but close.
Now we should be able to do the same for Covid19 right?
- VE for this varicella example/outbreak is at 73%.
- Not statistically significant at 90%, but close.
Now we should be able to do the same for Covid19 right?

I'm using the CDC MWWR Case Study of the Massachussets/Barnstable County outbreak, as that had quite a lot of data.
Unfortunately they do not disclose the # of negative tests per group - so we can try to estimate them.
Unfortunately they do not disclose the # of negative tests per group - so we can try to estimate them.
So we know that about 60k people were in the county.
CDC also discloses the % of vaccinated/unvaccinated.
So we can calculate the absolute size of the two groups.
Now, the question is, what's the proportion of people in each group that got tested? We don't know.. let's use 10%
CDC also discloses the % of vaccinated/unvaccinated.
So we can calculate the absolute size of the two groups.
Now, the question is, what's the proportion of people in each group that got tested? We don't know.. let's use 10%

Using 10%, gives us the total # of tests, and we can finally calculate VE.
VE is calculated the same way as before. So what's the result? --> -26%
So if the proportion of people tested is equal, the VE is negative! WOW
VE is calculated the same way as before. So what's the result? --> -26%
So if the proportion of people tested is equal, the VE is negative! WOW

So to get to a CDC defined minimum VE of 50%, the amount of people tested in the vaccinated group would have had to be at least 2.5x times (10% vs 4%) higher.
Is that realistic?
Is that realistic?

So unfortunately CDC does not know or publish the # of tests by vaccine group.
What do you think?
Please let me know your thoughts in the comments?
Spreadsheet/Sources here: docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d…
What do you think?
Please let me know your thoughts in the comments?
Spreadsheet/Sources here: docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d…
FYI, I'm planning to FOIA the numbers from MA or CDC.. So I'd appreciate to get some thoughts before ;)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh