Patellar maltracking is the most common complication of primary TKA.
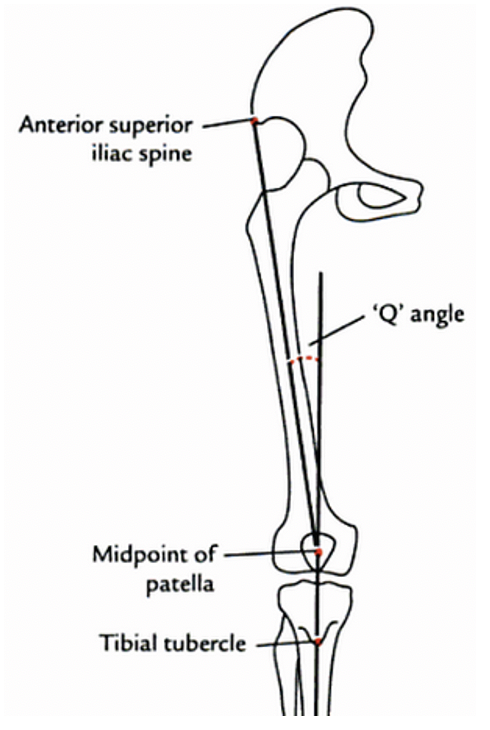
The dynamic forces affecting patellar tracking are represented by the Q-angle, formed by a line from the ASIS to the patella and from the tibial tubercle to the patella. A normal Q-angle is between 12-20°.
2/
The dynamic forces affecting patellar tracking are represented by the Q-angle, formed by a line from the ASIS to the patella and from the tibial tubercle to the patella. A normal Q-angle is between 12-20°.
2/
The static transverse stabilizers of the patella include the medial/lateral retinaculum and medial/lateral patellofemoral ligaments.
The dynamic transverse stabilizers include the IT band and vastus medialis/lateralis.
3/
The dynamic transverse stabilizers include the IT band and vastus medialis/lateralis.
3/

What position of rotation should the femoral component be placed in to improve patellar tracking:
How should the femoral and tibial components be placed to improve patellar tracking:
How should the patellar component be placed to improve patellar tracking:
The risk of lateral maltracking can be decreased by maintaining an anatomical Q-angle and lateralizing the trochlear groove.
This can be accomplished by lateralization and ER of the femoral and tibial components and medialization of the patellar button.
This can be accomplished by lateralization and ER of the femoral and tibial components and medialization of the patellar button.
If maltracking persists a lateral retinacular release may be performed to improve patellar tracking.
8/
8/
An inflated pneumatic tourniquet may shorten the quadriceps and affect patellar tracking, studies have shown decreased rates of lateral retinacular releases when tracking is performed after tourniquet deflation.
9/
9/

A study by Husted et al (2005) noted that 16/100 patients undergoing TKA were found to have patellar maltracking intraoperatively. Deflation improved tracking in all patients and corrected the maltracking in 5 of the patients and prevented lateral releases in these patients (2)
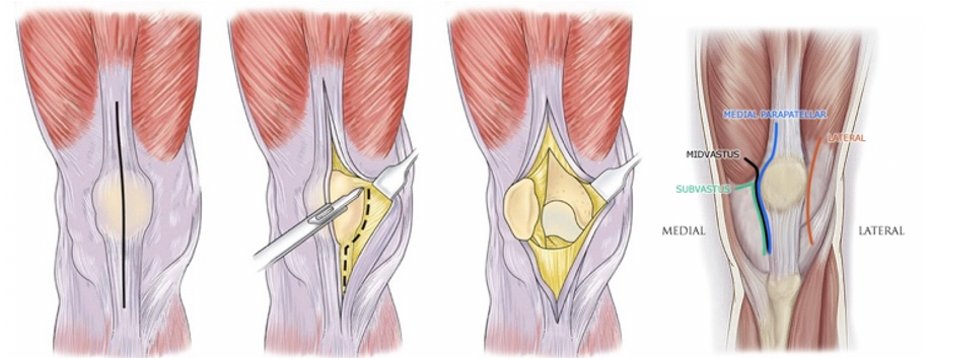
Studies have also proposed that the medial parapatellar approach may increase the risk of patellar maltracking and the need for lateral retinacular releases when compared to the mid-vastus and sub-vastus approaches.
11/
11/
Studies have shown that towel clip testing of patellar tracking which utilizes a towel clip to approximate the medial retinaculum may also decrease the need for lateral releases.
12/
12/

A study by Archibeck et al (2003) showed that in 200 primary TKA the no-thumbs test overpredicted the need for lateral retinacular release by 32.5%. (6)
13/
13/
References:
1)ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
2)arthroplastyjournal.org/article/S0883-…
3)jsesarthroplasty.org/article/S1045-…
4)https://t.co/Ych6xwjEUp
5)ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
6)pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12966289/
1)ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
2)arthroplastyjournal.org/article/S0883-…
3)jsesarthroplasty.org/article/S1045-…
4)https://t.co/Ych6xwjEUp
5)ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
6)pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12966289/
If you enjoyed this review please like or retweet and give the page a follow.
Author: @CSMorford
#OrthoTwitter #MedTwitter #MedEd #Tweetorial
@MedTweetorials #Ortho #TKA #JointReplacement
Author: @CSMorford
#OrthoTwitter #MedTwitter #MedEd #Tweetorial
@MedTweetorials #Ortho #TKA #JointReplacement
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh