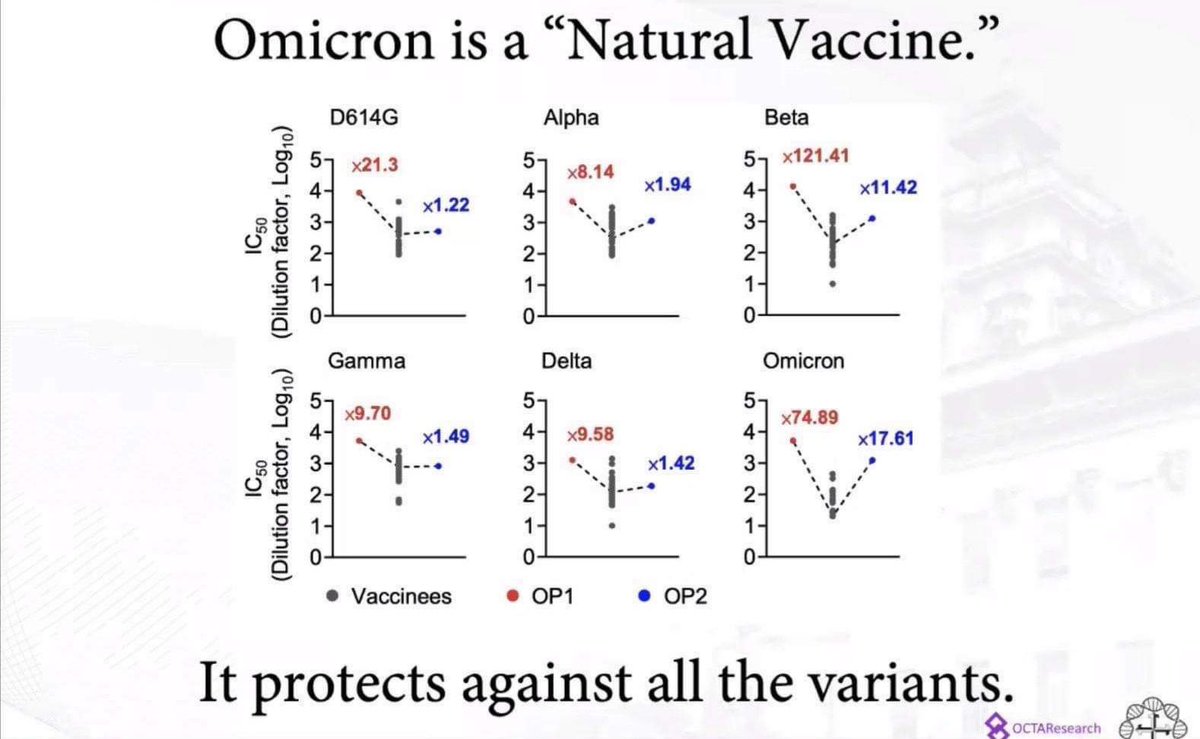
The word ‘endemic’ has become one of the most misused of the pandemic.
An endemic infection is one in which overall rates are static — not rising, not falling. More precisely, it means that the proportion of people who can get sick balances out the ‘Ro’ of the virus. 1/
An endemic infection is one in which overall rates are static — not rising, not falling. More precisely, it means that the proportion of people who can get sick balances out the ‘Ro’ of the virus. 1/
Assuming a population in which everyone could get sick. Yes, common colds are endemic. So are Lassa fever, malaria and polio. So was smallpox, until vaccines stamped it out. 2/
In other words, a disease can be endemic and both widespread and deadly. Malaria killed more than 600,000 people in 2020. Ten million fell ill with TB that same year and 1.5 million died. 3/
Endemic certainly does not mean that evolution has somehow tamed a pathogen so that life simply returns to ‘normal’. There’s more to global health policy than learning to live with endemic rotavirus, hepatitis C or measles. 4/
Stating that an infection will become endemic says nothing about how long it might take to reach stasis, what the case rates, morbidity levels or death rates will be or, crucially, how much of a population will be susceptible. 5/
Nor does it suggest guaranteed stability: there can still be disruptive waves from endemic infections, as seen with the US measles outbreak in 2019. 6/
The same virus can cause endemic, epidemic or pandemic infections: it depends on the interplay of a population’s behaviour, demographic structure, susceptibility and immunity, plus whether viral variants emerge. 7/
There is a widespread, rosy misconception that viruses evolve over time to become more benign. This is not the case: there is no predestined evolutionary outcome for a virus to become more benign. 8/
Take the case of SARS-CoV-2, in which most transmission happens before the virus causes severe disease. 9/
Much can be done to shift the evolutionary arms race in humanity’s favour.
1-We must set aside lazy optimism.
2-We must be realistic about the likely levels of death, disability and sickness. 10/
1-We must set aside lazy optimism.
2-We must be realistic about the likely levels of death, disability and sickness. 10/
3-We must use — globally — the formidable weapons available: effective vaccines, antivirals, diagnostic tests & a better understanding of how to stop an airborne virus through mask wearing, distancing, and air ventilation and filtration. 11/
4-We must invest in vaccines that protect against a broader range of variants.
5-We must ensure a vaccine equity, globally! 12/
5-We must ensure a vaccine equity, globally! 12/
Thinking that endemicity is both mild and inevitable is more than wrong, it is dangerous: it sets humanity up for many more years of disease, including unpredictable waves of outbreaks. 13/
It is more productive to consider how bad things could get if we keep giving the virus opportunities to outwit us. Then we might do more to ensure that this does not happen. 14/
A great piece worth to read by @ArisKatzourakis 👇
nature.com/articles/d4158…
A great piece worth to read by @ArisKatzourakis 👇
nature.com/articles/d4158…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh