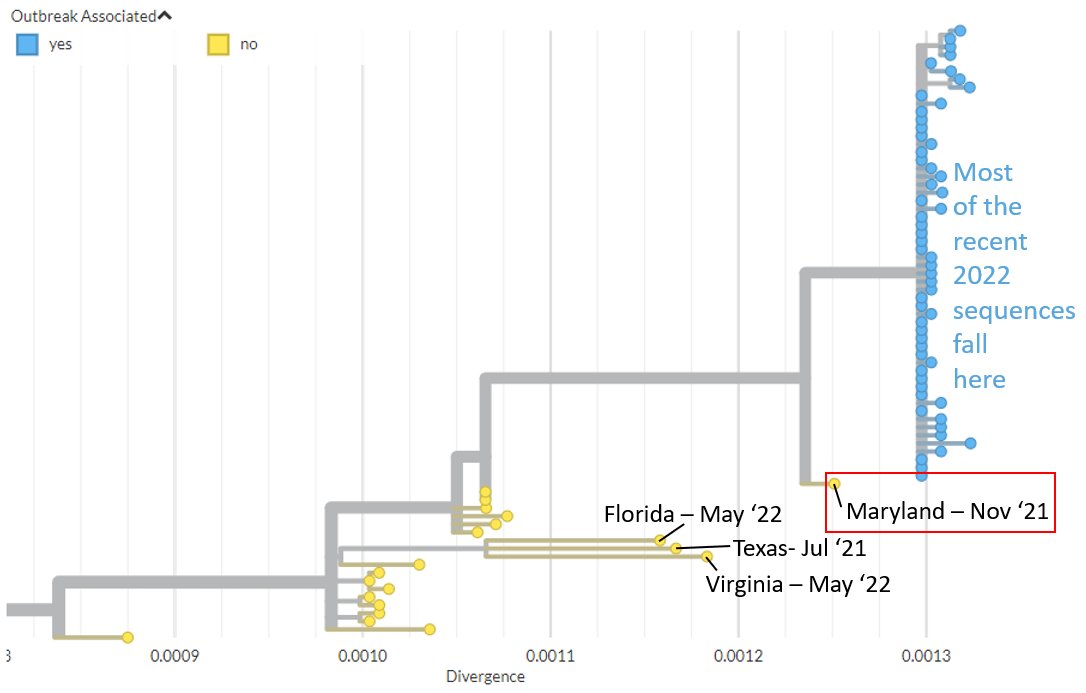
We have updated our #monkeypox build to include the latest #opendata sequences from @CDCgov from Maryland, Texas, Virginia, & Florida.
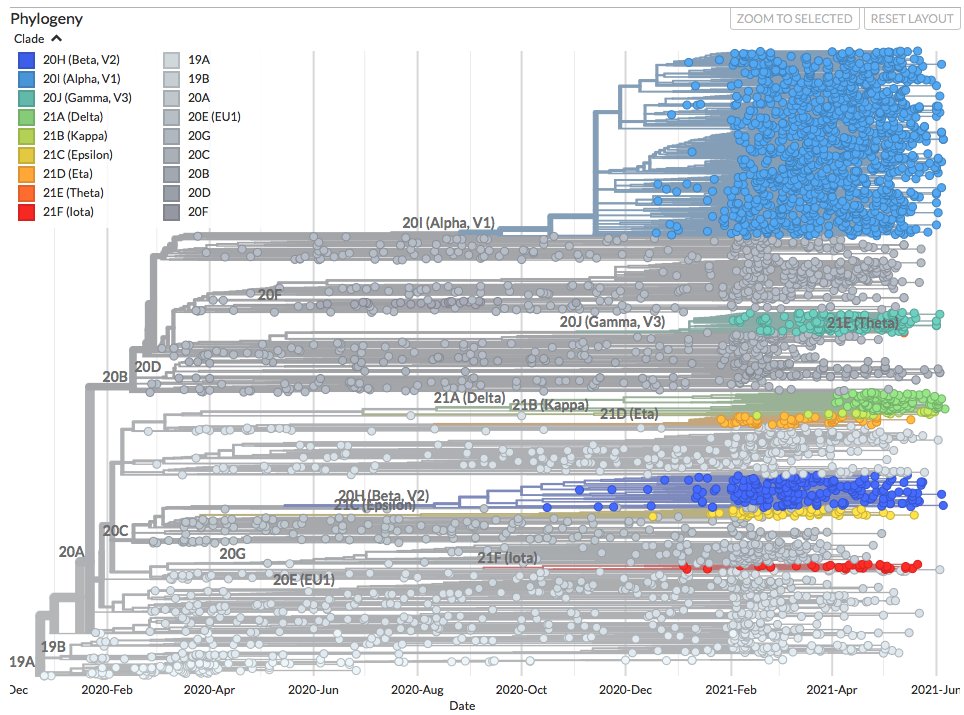
These sequences fall outside where most of the recent sequences cluster (blue).
nextstrain.org/monkeypox
1/6

These sequences fall outside where most of the recent sequences cluster (blue).
nextstrain.org/monkeypox
1/6
https://twitter.com/HelenBranswell/status/1532742516755283975

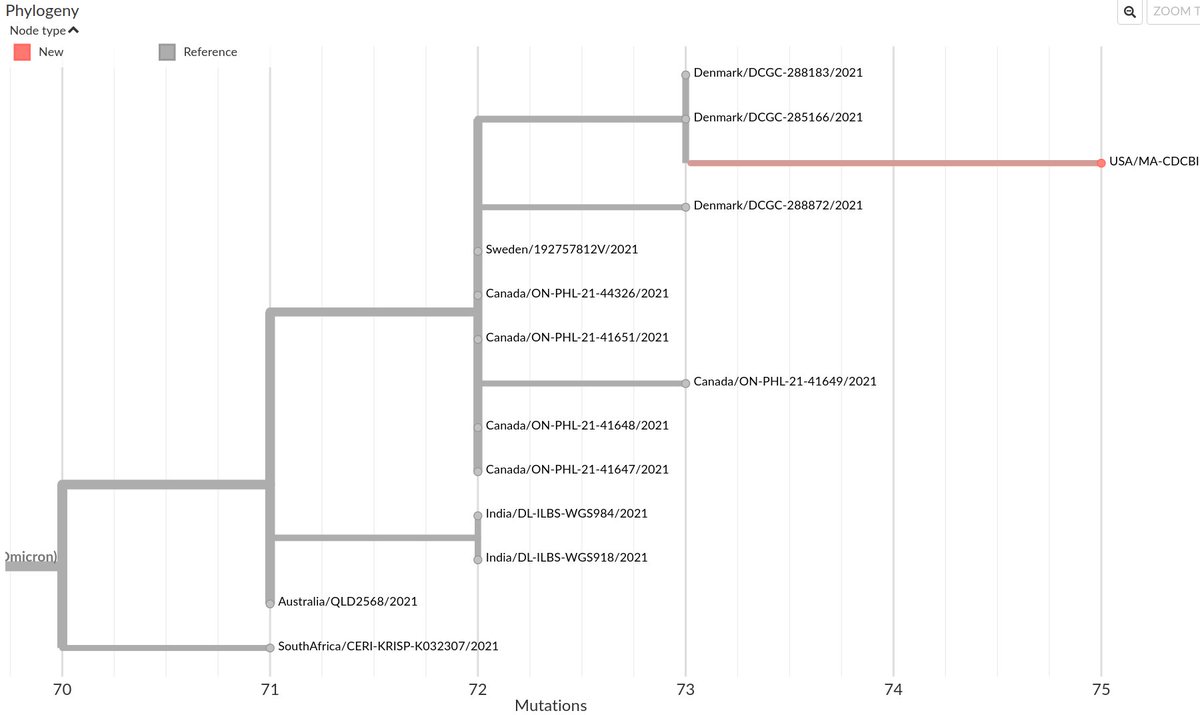
The Maryland sequence (2021-11) is ancestral to most of the recently detected #monkeypox sequences, suggesting this lineage has likely been circulating in humans for months, if not longer.
It may offer hints about how mutations in this lineage have accumulated.
2/6
It may offer hints about how mutations in this lineage have accumulated.
2/6
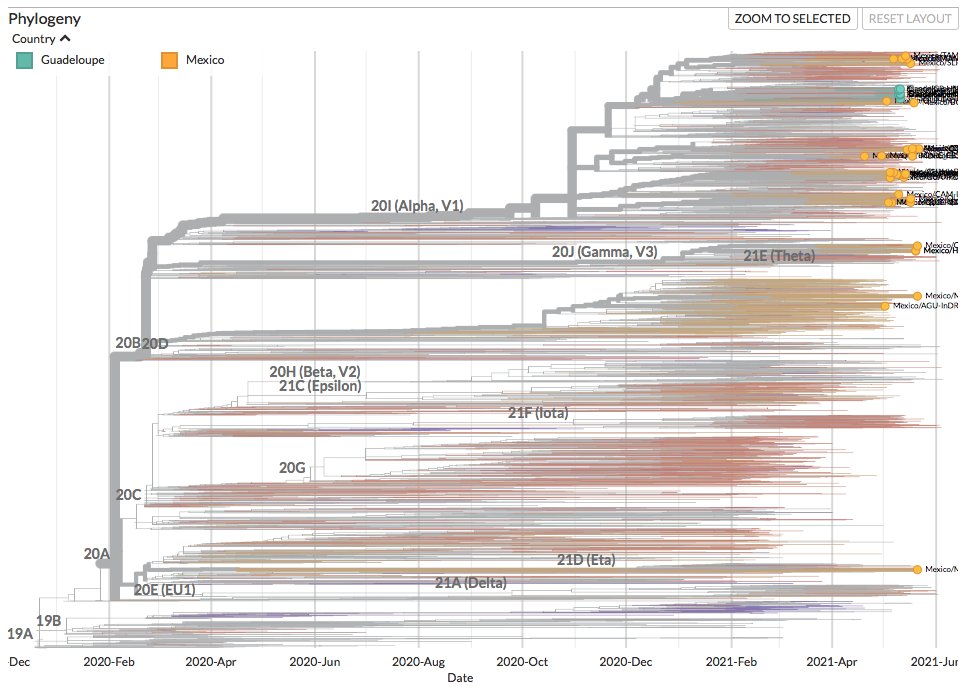
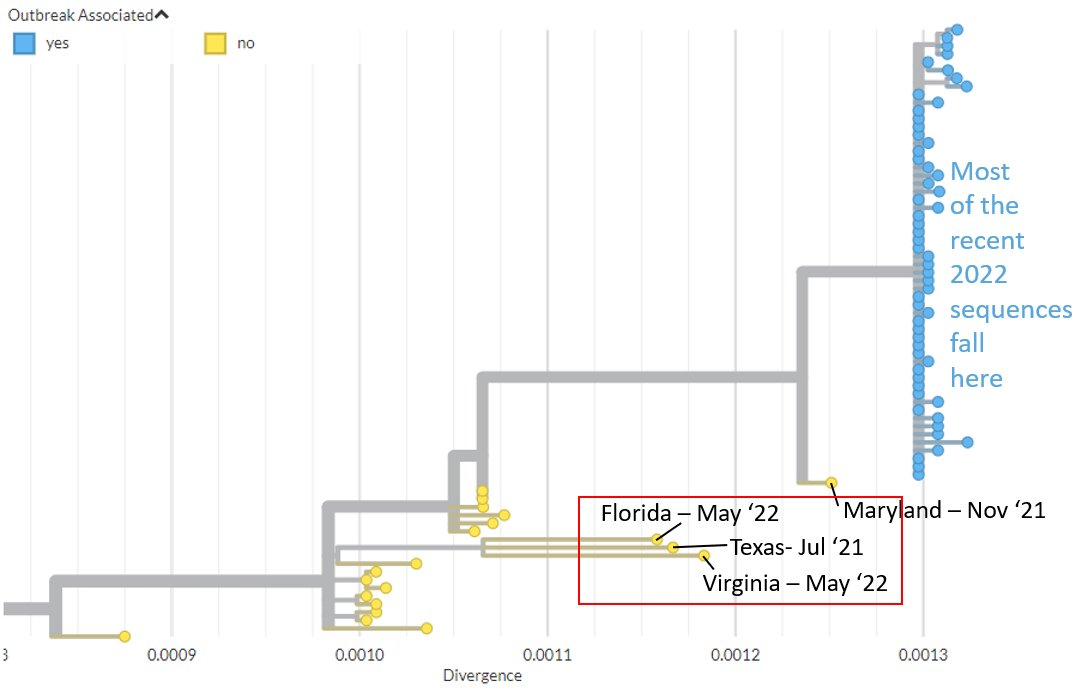
The Florida, Texas, & Virginia sequences stem from diversity most recently sampled in Nigeria in 2017, but were sampled after travel to a wide area, ranging from West Africa to East Africa or the Middle East.
3/6
statnews.com/2022/06/03/gen…
3/6
statnews.com/2022/06/03/gen…
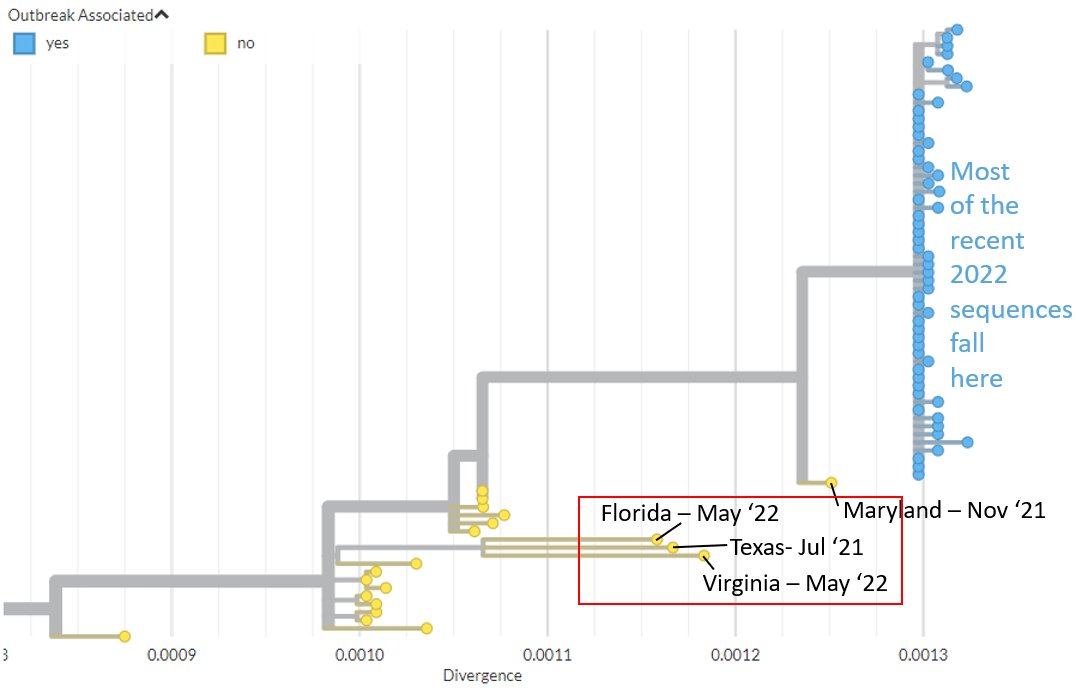
Their position & divergence may suggest that #monkeypox has been circulating in humans more globally than realised, over the last few years.
All 4 of these sequences have similar types of mutations to those previously observed - possibly the product of antiviral systems.
4/6
All 4 of these sequences have similar types of mutations to those previously observed - possibly the product of antiviral systems.
4/6
We are grateful for the fast #opendata sharing by @CDCgov & @CrystalGigante et al to @NCBI - & also the many other labs worldwide who have shared sequences openly, in the past & recently.
Without such sharing, none of these analyses would be possible, nor so accessible.🙏🏻
5/6
Without such sharing, none of these analyses would be possible, nor so accessible.🙏🏻
5/6
In particular, 1/2 of the current sequences come from @borges__vitor & @isidro_joana! 🎉
You can find these 4 recent sequences - alongside all of the other #opendata #monkeypox seqs - on @GenSpectrum & LAPIS API, for fast, easy, automated access.
mpox.genspectrum.org/explore
6/6
You can find these 4 recent sequences - alongside all of the other #opendata #monkeypox seqs - on @GenSpectrum & LAPIS API, for fast, easy, automated access.
mpox.genspectrum.org/explore
6/6
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh