
Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution.
Mastodon: @nextstrain@mstdn.science
Bluesky: @nextstrain.org
5 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

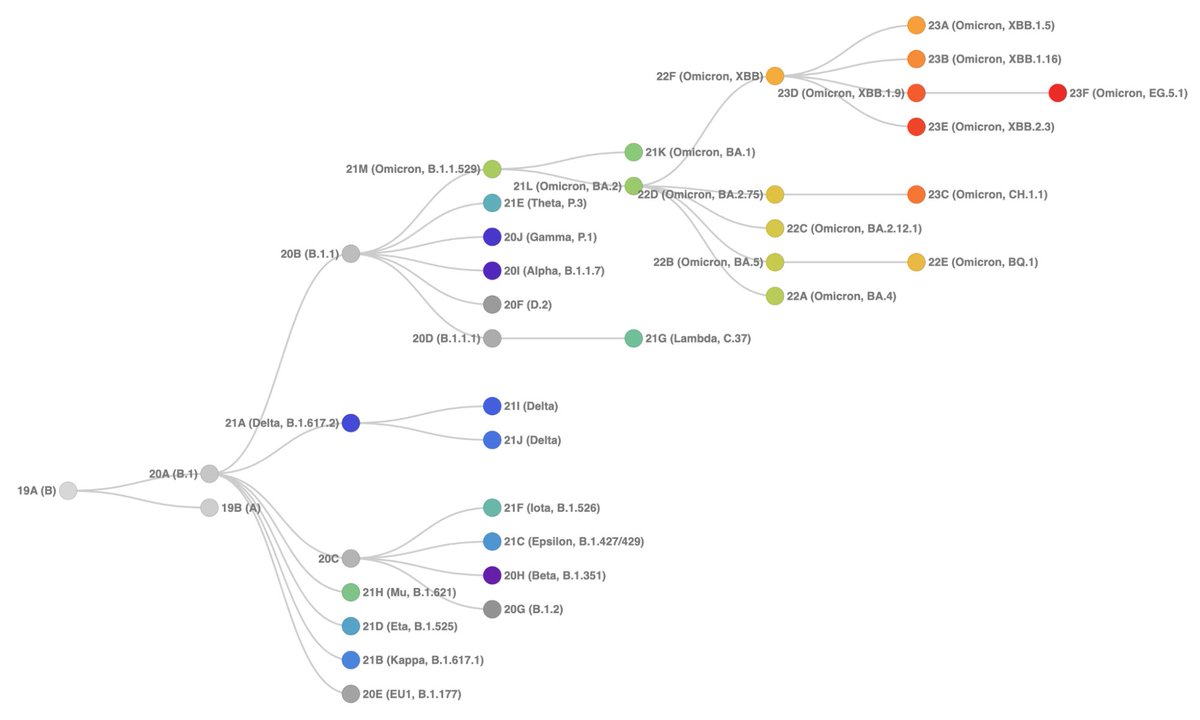
 23C (CH.1.1) is a sublineage of 22D (BA.2.75) with additional spike RBD mutations at 346T, 444T, 452R & 486S. This non-XBB lineage has persisted despite the dominance of XBB descendants.
23C (CH.1.1) is a sublineage of 22D (BA.2.75) with additional spike RBD mutations at 346T, 444T, 452R & 486S. This non-XBB lineage has persisted despite the dominance of XBB descendants.
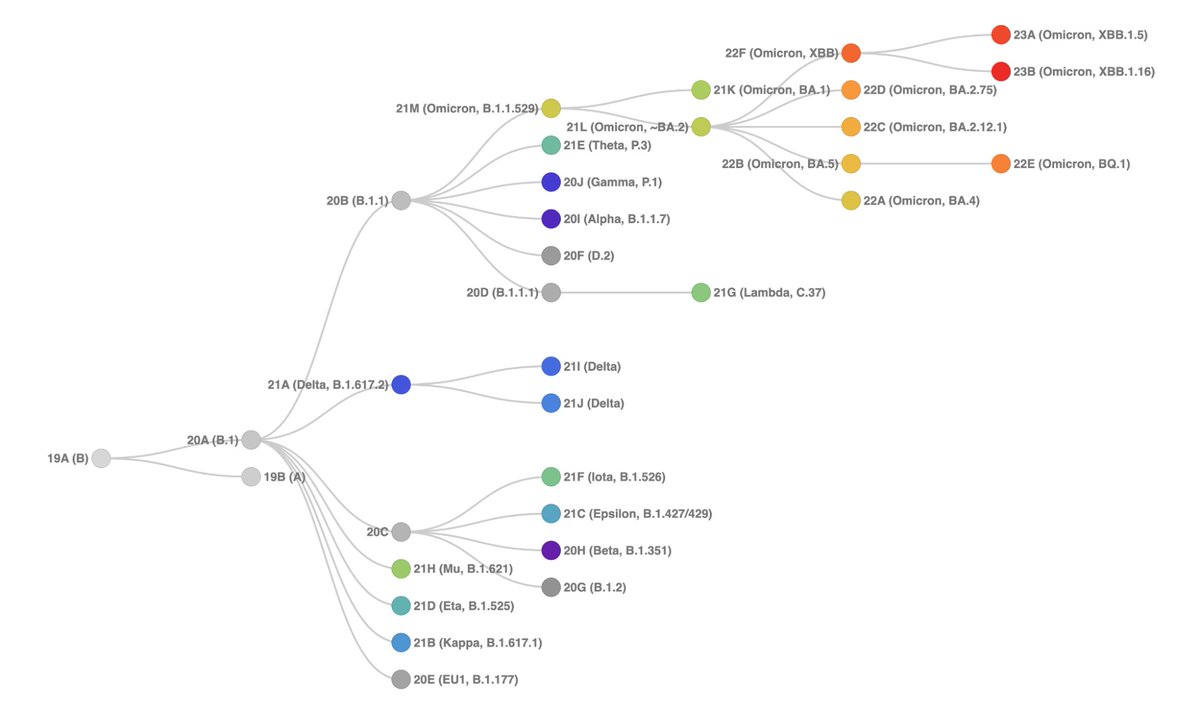
 23B (XBB.1.16) is different from 22F (XBB) primarily through 3 new Spike mutations - S:E180V; S:K478R; & S:486P (acquired independently from other XBB sublineages).
23B (XBB.1.16) is different from 22F (XBB) primarily through 3 new Spike mutations - S:E180V; S:K478R; & S:486P (acquired independently from other XBB sublineages). https://twitter.com/firefoxx66/status/1648588097381101570

 23A (XBB.1.5) is different from 22F (XBB) primarily through 2 new Spike muts - 1 in ancestor XBB.1 (S:G252V), & 1 in 23A itself S:486S -> S:486P. This 'P' change is associated with an increased ACE2 binding, which is likely why 23A is spreading.
23A (XBB.1.5) is different from 22F (XBB) primarily through 2 new Spike muts - 1 in ancestor XBB.1 (S:G252V), & 1 in 23A itself S:486S -> S:486P. This 'P' change is associated with an increased ACE2 binding, which is likely why 23A is spreading.https://twitter.com/firefoxx66/status/1611387923072417792
 22F/XBB is the result of a recombination between BJ.1 (BA.2.10.1.1) & BM.1.1.1 (BA.2.75.3.1.1.1) with breakpoint in S1 (first part of spike).
22F/XBB is the result of a recombination between BJ.1 (BA.2.10.1.1) & BM.1.1.1 (BA.2.75.3.1.1.1) with breakpoint in S1 (first part of spike).

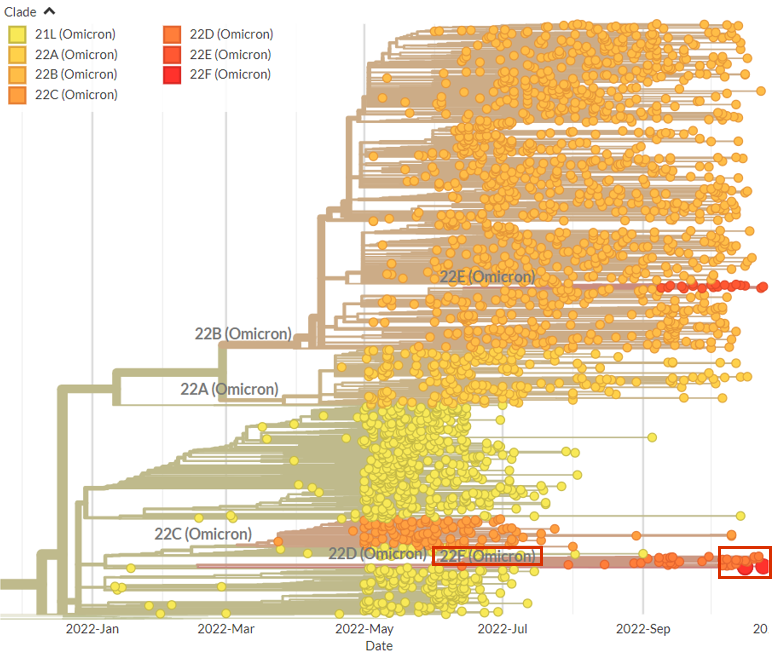
 Clade 22E (lineage BQ.1) has been growing in frequency at a rate of 0.11 per day in USA, which is equivalent to the initial growth of 22B (BA.5) in the US & UK.
Clade 22E (lineage BQ.1) has been growing in frequency at a rate of 0.11 per day in USA, which is equivalent to the initial growth of 22B (BA.5) in the US & UK.

 Lineage BA.2.75 / clade 22D has been growing in frequency at a rate of 0.12 per day in India, which is equivalent to initial growth of BA.5 in the US and the UK, and is now outcompeting BA.5 in India. 2/4
Lineage BA.2.75 / clade 22D has been growing in frequency at a rate of 0.12 per day in India, which is equivalent to initial growth of BA.5 in the US and the UK, and is now outcompeting BA.5 in India. 2/4 

https://twitter.com/HelenBranswell/status/1532742516755283975
 The Maryland sequence (2021-11) is ancestral to most of the recently detected #monkeypox sequences, suggesting this lineage has likely been circulating in humans for months, if not longer.
The Maryland sequence (2021-11) is ancestral to most of the recently detected #monkeypox sequences, suggesting this lineage has likely been circulating in humans for months, if not longer.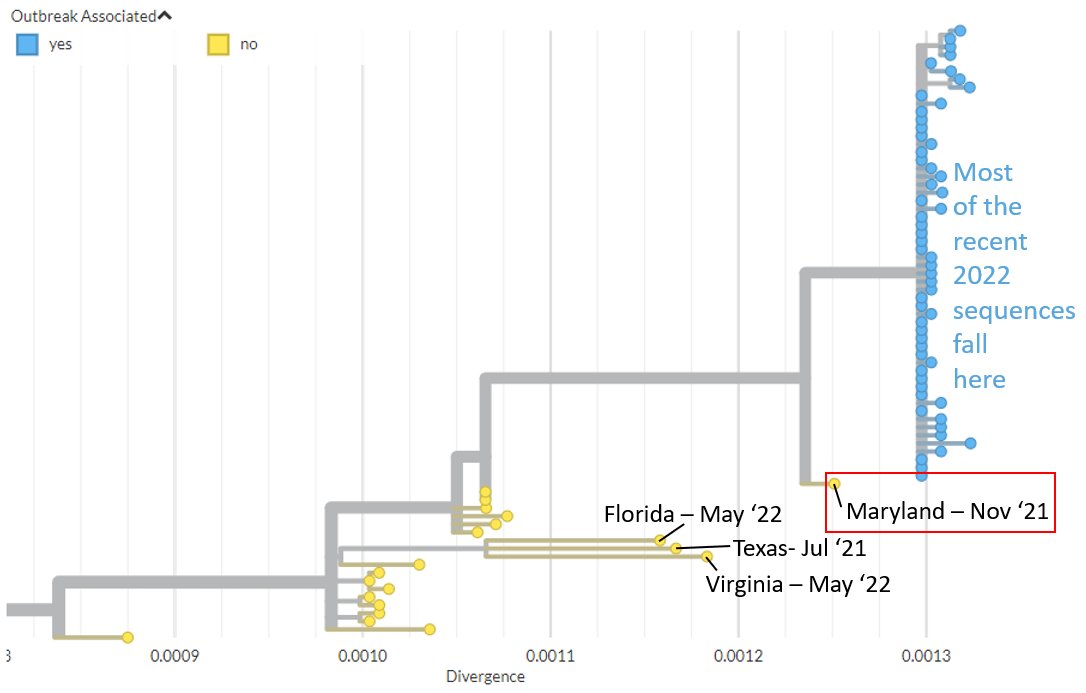
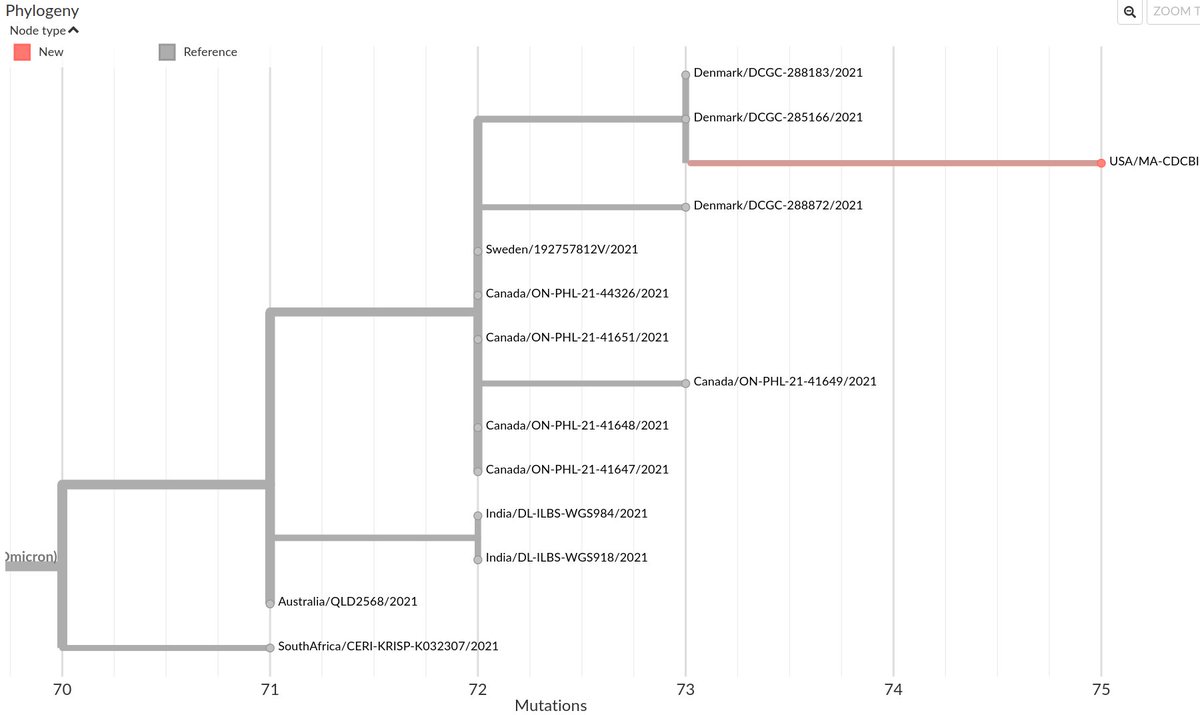
 These private mutations are split into three categories:
These private mutations are split into three categories:

 Clade 21I is still a Delta variant virus, but possesses additional spike mutation A222V and ORF1a mutations P1640L, A3209V, V3718A and T3750I. 2/4
Clade 21I is still a Delta variant virus, but possesses additional spike mutation A222V and ORF1a mutations P1640L, A3209V, V3718A and T3750I. 2/4 

 Thanks to all new submitters:
Thanks to all new submitters:
 Analysis now takes a few seconds to start, but overall it has become much faster and analyzing hundreds of sequences should be no problem. You can download the reference alignments, including translations of SARS-CoV-2 genes, for further analyses.
Analysis now takes a few seconds to start, but overall it has become much faster and analyzing hundreds of sequences should be no problem. You can download the reference alignments, including translations of SARS-CoV-2 genes, for further analyses.
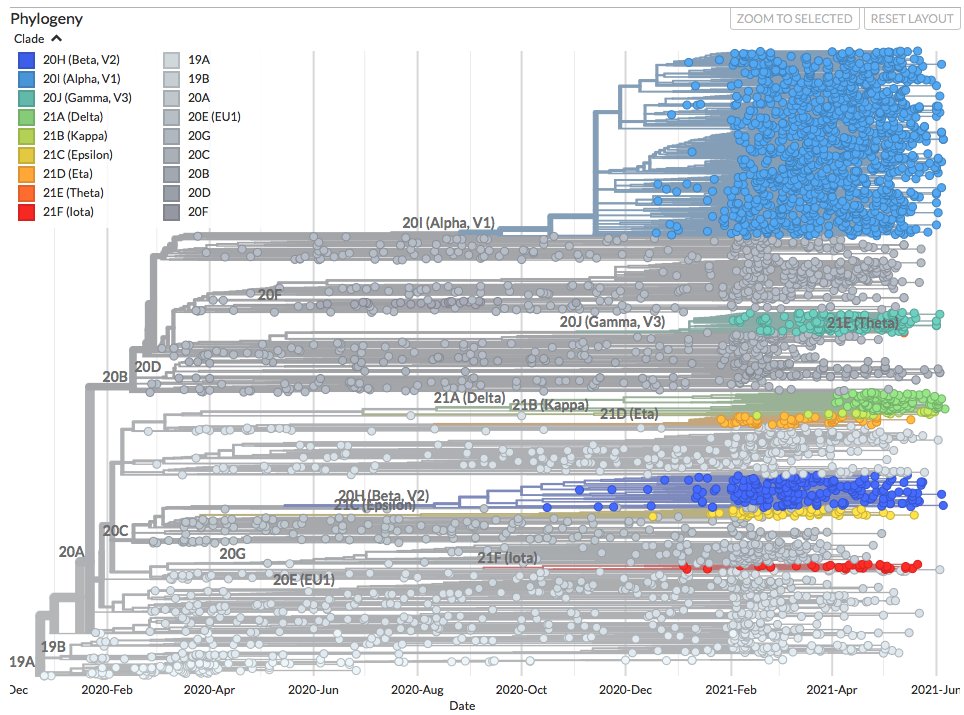
 You can see new sequences from Australia, Guadeloupe and Mexico on nextstrain.org/ncov/oceania and nextstrain.org/ncov/north-ame….
You can see new sequences from Australia, Guadeloupe and Mexico on nextstrain.org/ncov/oceania and nextstrain.org/ncov/north-ame….
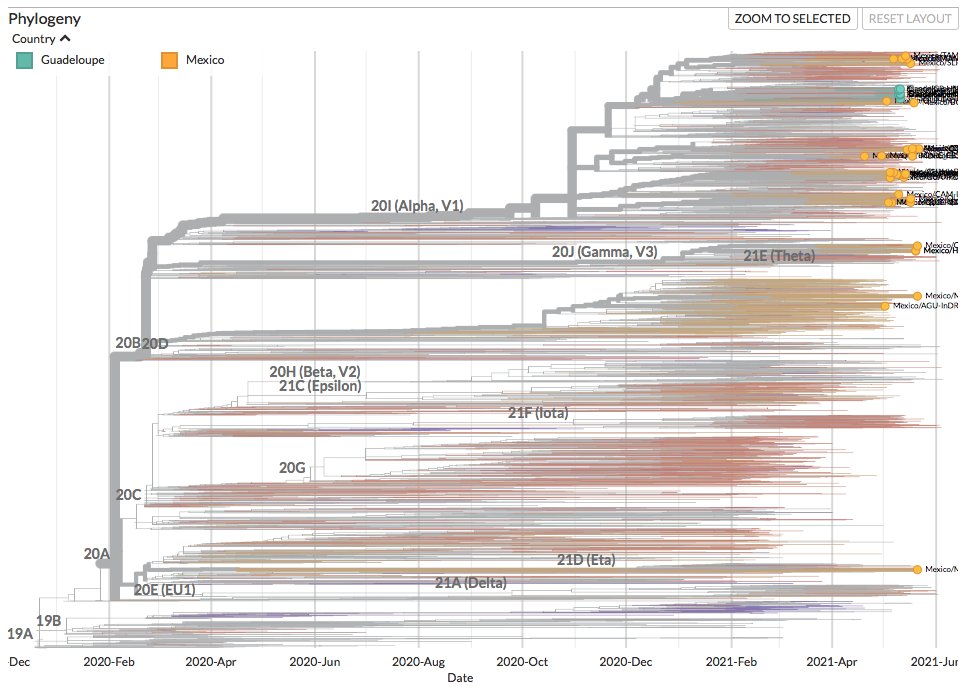

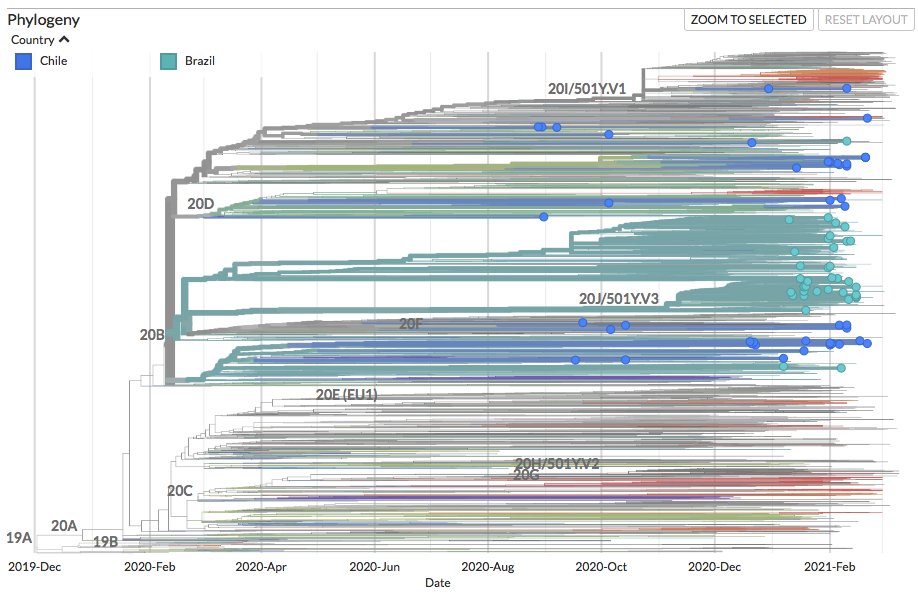
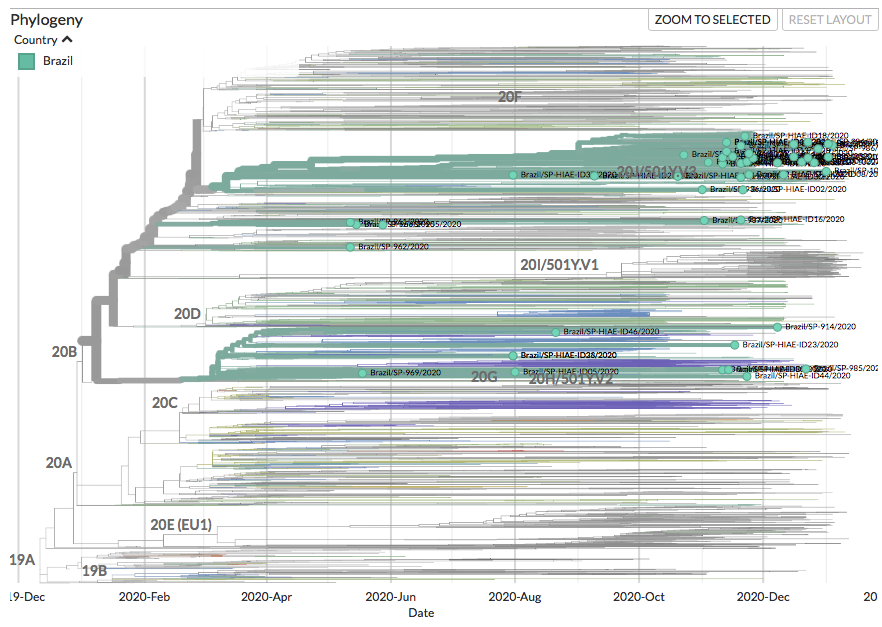
 New sequences from Aruba (36), Bonaire (26), Brazil (368) and Curacao (30) can be found on nextstrain.org/ncov/south-ame….
New sequences from Aruba (36), Bonaire (26), Brazil (368) and Curacao (30) can be found on nextstrain.org/ncov/south-ame….

 New sequences from Libya (76), Morocco (2) & Nigeria (1) can be seen on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa.
New sequences from Libya (76), Morocco (2) & Nigeria (1) can be seen on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa.

 Check out the new sequences from India (99), Indonesia (10) and Pakistan (12) on nextstrain.org/ncov/asia.
Check out the new sequences from India (99), Indonesia (10) and Pakistan (12) on nextstrain.org/ncov/asia.

 Check out the new seqs from Angola (71), Nigeria (11) and South Africa (276) on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa. Botswana (1) currently not visible due to random subsampling.
Check out the new seqs from Angola (71), Nigeria (11) and South Africa (276) on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa. Botswana (1) currently not visible due to random subsampling.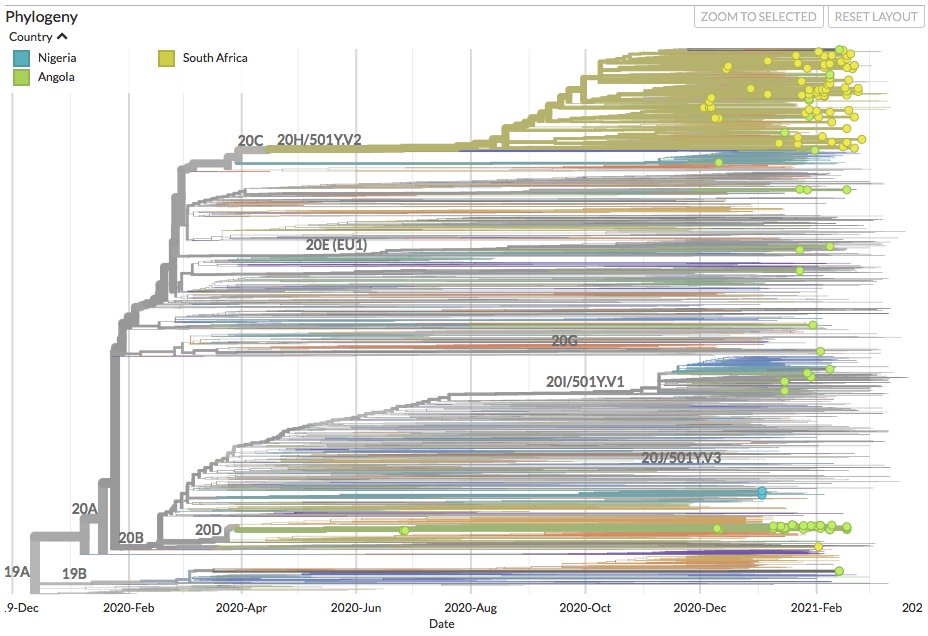

 New sequences from Botswana (2), Libya (1) and South Africa (4, currently not visible due to random subsampling) can be found on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa.
New sequences from Botswana (2), Libya (1) and South Africa (4, currently not visible due to random subsampling) can be found on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa.
 Check out the new sequences from Botswana (4), Burkina Faso (9), Rwanda (79) and Togo (1) on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa.
Check out the new sequences from Botswana (4), Burkina Faso (9), Rwanda (79) and Togo (1) on nextstrain.org/ncov/africa.


 @GISAID @UHASGhana @hosp_einstein @uandresbello Check out the new sequences from Belarus (25), Belgium (3), Finland (62), France (148) and Germany (93) on nextstrain.org/ncov/europe.
@GISAID @UHASGhana @hosp_einstein @uandresbello Check out the new sequences from Belarus (25), Belgium (3), Finland (62), France (148) and Germany (93) on nextstrain.org/ncov/europe.

 @GISAID @McMasterU USA (1091) seqs on nextstrain.org/ncov/north-ame….
@GISAID @McMasterU USA (1091) seqs on nextstrain.org/ncov/north-ame….


 @GISAID @ANLIS_Malbran @IEC_BR You can see the new sequences from Bangladesh (3), China (6), India (8), Myanmar (8) and South Korea (335) on nextstrain.org/ncov/asia.
@GISAID @ANLIS_Malbran @IEC_BR You can see the new sequences from Bangladesh (3), China (6), India (8), Myanmar (8) and South Korea (335) on nextstrain.org/ncov/asia.