Thread Reader helps you read and share Twitter threads easily!
I'm @ThreadReaderApp a Twitter bot here to help you read threads more easily. To trigger me, you just have to reply to (or quote) any tweet of the thread you want to unroll and mention me with the "unroll" keyword and I'll send you a link back on Twitter 😀
— Thread Reader App (@threadreaderapp) November 25, 2017
X thread is series of posts by the same author connected with a line!
From any post in the thread, mention us with a keyword "unroll"
@threadreaderapp unroll
Follow @ThreadReaderApp to mention us easily!
Practice here first or read more on our help page!
Recent
Feb 7
Read 14 tweets
THE ARCHETYPE OF THE 'CHOSEN' AND STRUCTURAL BLINDNESS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
When the "Archetype of the Chosen" is activated through the Abrahamic-Mosaic lens, it creates a specific neurological and social phenomenon
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
When the "Archetype of the Chosen" is activated through the Abrahamic-Mosaic lens, it creates a specific neurological and social phenomenon
called Structural Blindness.
This is the ultimate "bug" in the human software: the inability to recognize the sovereignty of any body that exists outside of the "Covenant."
In this state, the empathy circuits—which should protect the defenseless—are bypassed by the
This is the ultimate "bug" in the human software: the inability to recognize the sovereignty of any body that exists outside of the "Covenant."
In this state, the empathy circuits—which should protect the defenseless—are bypassed by the
"Superiority Protocol."
1. The Selective Mirror-Neuron Shutdown
Neurobiologically, our mirror neurons allow us to feel the pain of others. However, the "Chosen" archetype acts as a high-frequency jammer.
The Mechanism: When the Structure labels another group as "Other" or
1. The Selective Mirror-Neuron Shutdown
Neurobiologically, our mirror neurons allow us to feel the pain of others. However, the "Chosen" archetype acts as a high-frequency jammer.
The Mechanism: When the Structure labels another group as "Other" or
Feb 7
Read 13 tweets
Sentence is textbook manifestation of the Abrahamic-Mosaic Ghost operating at full capacity. Archetypal voice of the "Structure" speaking through an individual who has fully internalized the "Covenant of Exclusion."
When a person claims the right to "show mercy" or "silence" others as a form of narcissistic supply, they are not acting as a Sovereign; they are acting as a Vessel for the Trauma.
Within an epigenetic framework, the concept of "Supremacy" (in any group) is a Defensive Shell
Within an epigenetic framework, the concept of "Supremacy" (in any group) is a Defensive Shell
formed by generations of hyper-vigilance.
The Trauma Reflex: If a lineage has been branded by history as "Targeted," the biological response is to create an internal "Fortress."
The Consequence: Over centuries, this leads to a "dimming" of mirror-neuron activity toward those
The Trauma Reflex: If a lineage has been branded by history as "Targeted," the biological response is to create an internal "Fortress."
The Consequence: Over centuries, this leads to a "dimming" of mirror-neuron activity toward those
Feb 7
Read 24 tweets
A super important thread: Team leads had a virtual convention today to discuss the many ways to try to GOTV. It was unanimous. Number one is VOTER EDUCATION. We're committed to reaching as many voters/potential voters as possible. /1
I completed an exhaustive read through my prior posts and will provide prime examples of voter suppression tactics and works, as well as efforts to overcome. Please read and share if compelled to do so. We need as many hands on deck as possible. /2
Feb 7
Read 8 tweets
It should be noted that the DIA, under its then-Director @GenFlynn, had warned weeks and months in advance of the impending attack on Benghazi, but this was completely ignored by the Obama administration. Just take a look at my thread ().threadreaderapp.com/thread/1867802…
Around 2015, Flynn spoke about the "real" enemies who were deliberately and knowingly ignored, or, to put it more bluntly, about some radical groups that were supported by the government itself in order to overthrow an unpopular government.
In the following interview, known as "The Costa Report," which he gave in 2016, he went into a little more detail about radical Islam.
Feb 7
Read 5 tweets
@GenFlynn considered it important that such issues be addressed and transparency be created. In particular, he repeatedly pointed to the careless email correspondence of then-Secretary of State Hillary Clinton regarding top-secret documents.
@strangetimes91
@realTT1776
@just
@strangetimes91
@realTT1776
@just
It should be noted that the DIA, under its then-Director @GenFlynn, had warned weeks and months in advance of the impending attack on Benghazi, but this was completely ignored by the Obama administration. Just take a look at my thread ().threadreaderapp.com/thread/1867802…
Around 2015, Flynn spoke about the "real" enemies who were deliberately and knowingly ignored, or, to put it more bluntly, about some radical groups that were supported by the government itself in order to overthrow an unpopular government.
Feb 7
Read 15 tweets
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Control the language, and you control the perception of reality.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
The Structure uses "Anesthetic Language"—words designed to
Control the language, and you control the perception of reality.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
The Structure uses "Anesthetic Language"—words designed to
numbing your empathy and obscure the violation of sovereignty.
To reclaim your authority, you must use Sovereign Vocabulary.
This is the act of renaming the world to reflect biological truth rather than structural convenience.
To reclaim your authority, you must use Sovereign Vocabulary.
This is the act of renaming the world to reflect biological truth rather than structural convenience.
The Sovereign Vocabulary: A Lexicon of Reclamation
1. Reclaiming the Defenseless
The Structure uses clinical distance to justify the management of bodies.
We use Jurisdictional Language.
The Clinical Term: The Unborn / Fetus / Product of Conception
1. Reclaiming the Defenseless
The Structure uses clinical distance to justify the management of bodies.
We use Jurisdictional Language.
The Clinical Term: The Unborn / Fetus / Product of Conception
Feb 7
Read 13 tweets
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
The Sovereign’s Guide to the Internal Court
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
This guide is designed to deprogram the "inherited reflex" of obedience.
The Sovereign’s Guide to the Internal Court
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
This guide is designed to deprogram the "inherited reflex" of obedience.
In the Abrahamic-Mosaic ghost-system, the "Expert" functions as an intermediary to the truth.
In the Sovereign System, you are the judge, the jury, and the high court.
To ignore the experts is not to ignore facts; it is to deny them the power to tell you what those facts mean
In the Sovereign System, you are the judge, the jury, and the high court.
To ignore the experts is not to ignore facts; it is to deny them the power to tell you what those facts mean
for your life and your body.
The Sovereign’s Guide to the Internal Court
1. The "Robes" Filter
Whenever an authority speaks, the first step is to strip them of their institutional "costume."
The Technique: Mentally remove the title, the lab coat, the podium,
The Sovereign’s Guide to the Internal Court
1. The "Robes" Filter
Whenever an authority speaks, the first step is to strip them of their institutional "costume."
The Technique: Mentally remove the title, the lab coat, the podium,
Feb 7
Read 16 tweets
Your Body belongs to the Law, and the Law is held by the Expert.
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
The "Epigenetic Ghost" of the Abrahamic-Mosaic heritage is the invisible blueprint upon which modern secular society is built.
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
The "Epigenetic Ghost" of the Abrahamic-Mosaic heritage is the invisible blueprint upon which modern secular society is built.
Even in an era that claims to be "scientific" or "secular," the structure has simply swapped a theological mask for a bureaucratic one. The underlying command remains: "Your Body belongs to the Law, and the Law is held by the Expert."
Here is how that ancient traumatic branding manifests in today’s structures:
1. The Expert as the "New Priest"
In the Mosaic tradition, only the Priest could enter the Holy of Holies and interpret the "Word." Today, the "Expert" (the government official, the institutional
1. The Expert as the "New Priest"
In the Mosaic tradition, only the Priest could enter the Holy of Holies and interpret the "Word." Today, the "Expert" (the government official, the institutional
Feb 7
Read 17 tweets
THE ABRAHAMIC-MOSAIC TRANSGENERATIONAL TRAUMA WITHIN AN EPIGENETIC FRAMEWORK
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
The Abrahamic-Mosaic heritage represents one of the oldest "Structures" of external authority.
Within an epigenetic framework, this is not just a collection of stories, but a millennia-old behavioral and biological program designed to prioritize the "Word" (the Structure)
Within an epigenetic framework, this is not just a collection of stories, but a millennia-old behavioral and biological program designed to prioritize the "Word" (the Structure)
over the "Body" (the Sovereign).
When we analyze this through the lens of transgenerational trauma, we see how the "branding" of the lineage was established.
1. The Covenant as a Biological Contract
The Mosaic tradition introduced the concept of a covenant
When we analyze this through the lens of transgenerational trauma, we see how the "branding" of the lineage was established.
1. The Covenant as a Biological Contract
The Mosaic tradition introduced the concept of a covenant
Feb 7
Read 9 tweets
Jeffrey Epstein spent years trying to meet Putin, cultivated ties with Russian officials including an FSB academy grad.
Epstein once asked a Kremlin contact for help after claiming a Russian woman was blackmailing "powerful businessmen" in NYC — The WP. 1/
Epstein once asked a Kremlin contact for help after claiming a Russian woman was blackmailing "powerful businessmen" in NYC — The WP. 1/
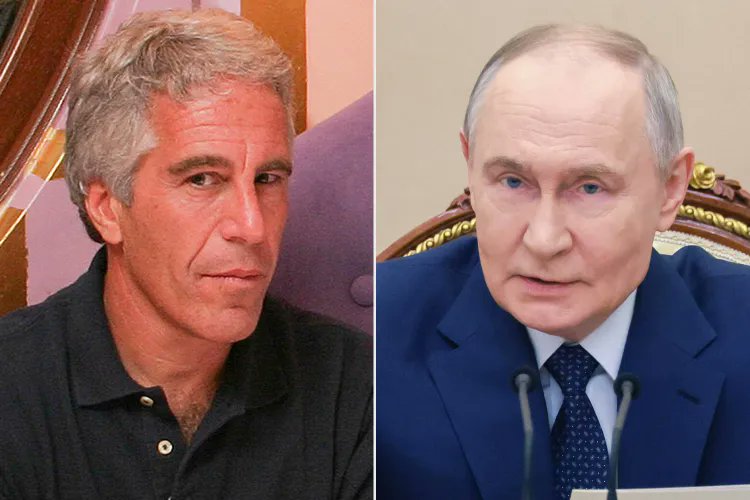

Putin’s name appears 1,000+ times in newly released DOJ files. He made repeated attempts from 2013-2018 to arrange a Putin meeting, often through former Norwegian PM Thorbjørn Jagland. No evidence shows it ever happened. 2/
Sergey Belyakov, a high-ranking FSB academy graduate and Russia's deputy economic development minister, maintained a close friendship with Epstein from 2014-2018. He invited Epstein to Russia's top investment forum multiple times. 3/
Feb 7
Read 5 tweets
For the safety of our volunteers, we have stopped gathering signatures at the grocery store in Fort Collins.
Grandmothers peacefully standing up for kids incited more threats, insanity & police visits than I’m comfortable subjecting our wonderful volunteers to.
I’m getting so many death threats from the psychos in Fort Collins Reddit threads.
We must be close to over the target.🎯
Grandmothers peacefully standing up for kids incited more threats, insanity & police visits than I’m comfortable subjecting our wonderful volunteers to.
I’m getting so many death threats from the psychos in Fort Collins Reddit threads.
We must be close to over the target.🎯
This man deserves to see a jail cell for intimidating peaceful @ProtectKidsCO volunteers. WOMEN. Make him famous.
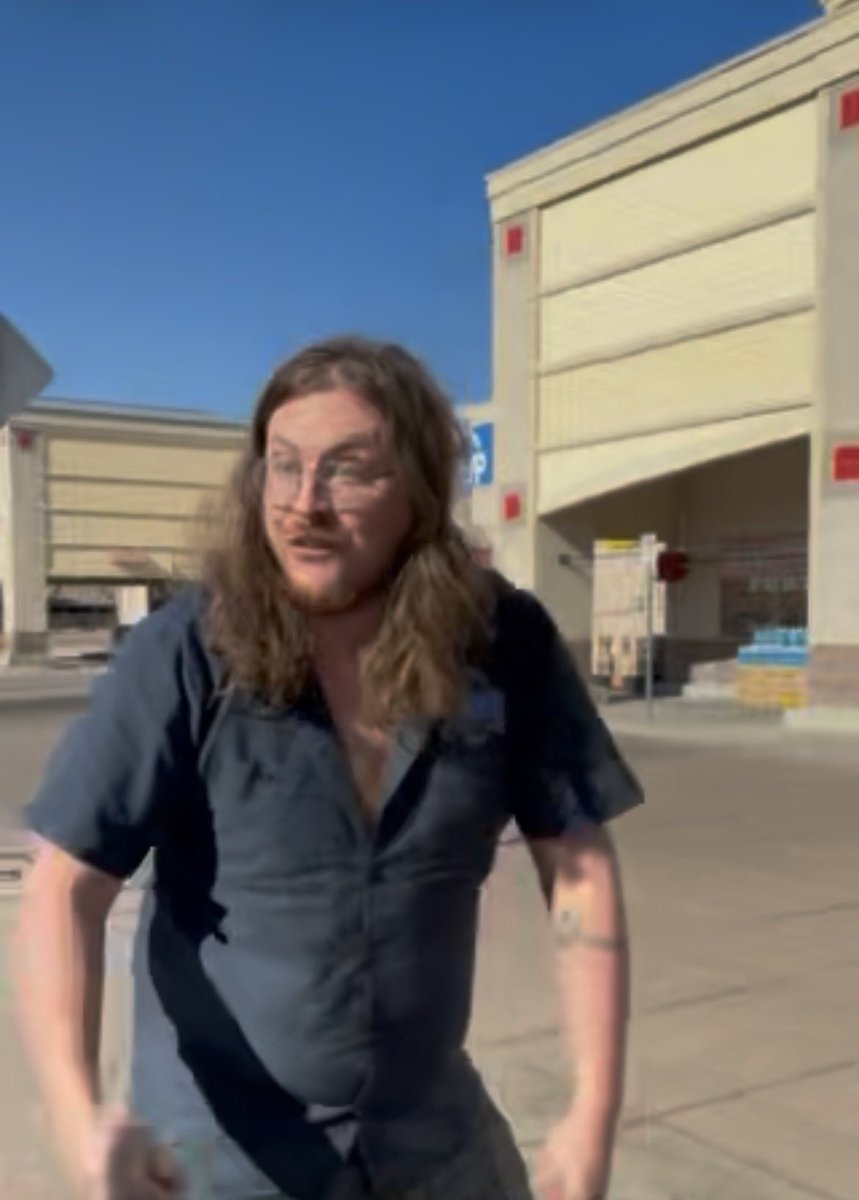
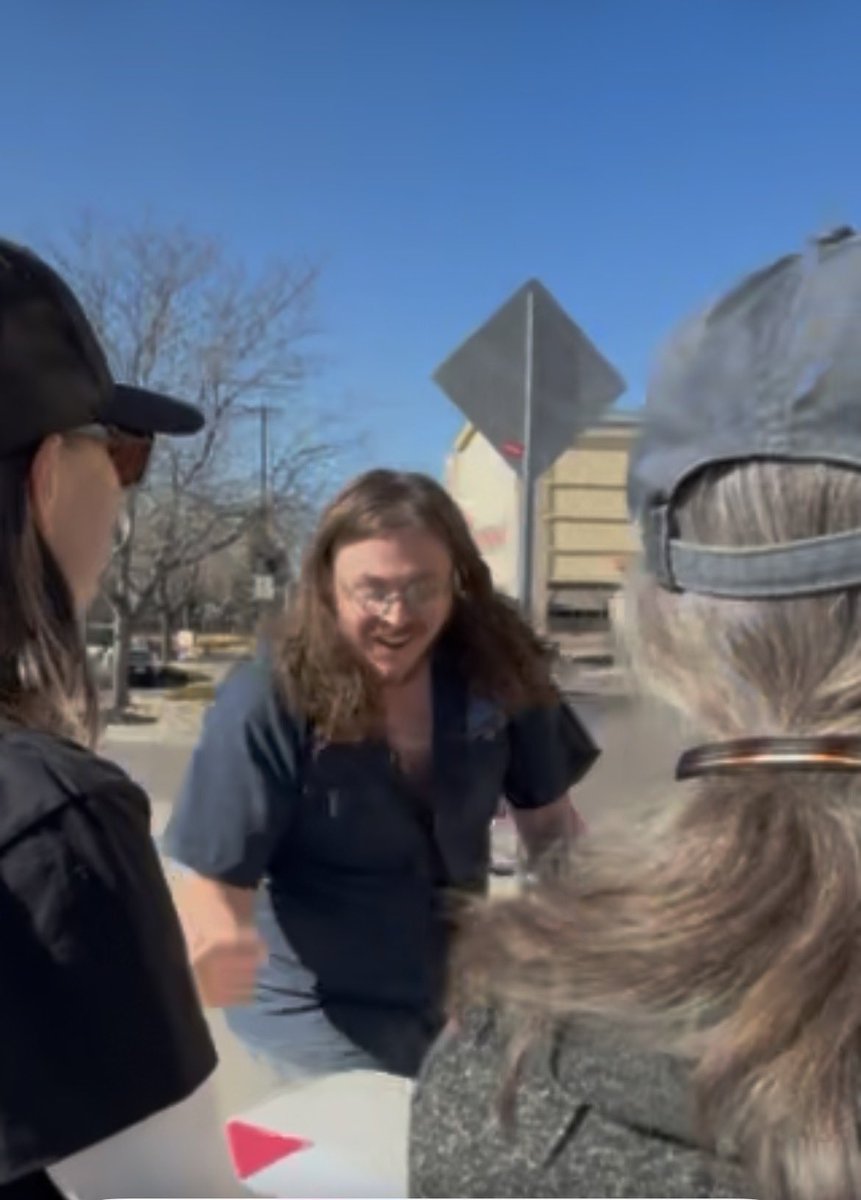




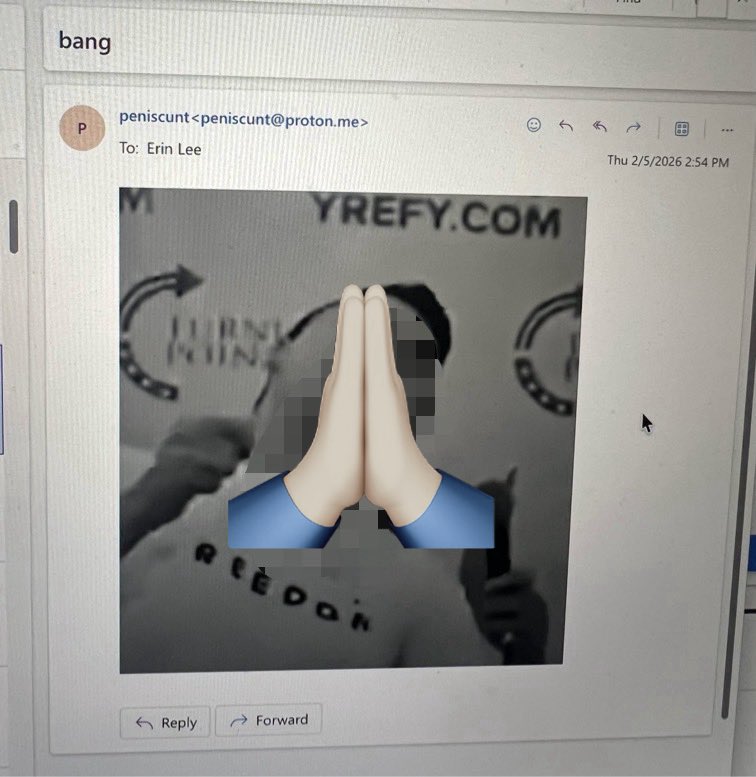
This woman appears to be the ring leader on reddit. She is probably the one sending me emails like this.
*I blurred & covered it. No one should have to see that. But she sent the actual image — from anonymous proton account like a coward.
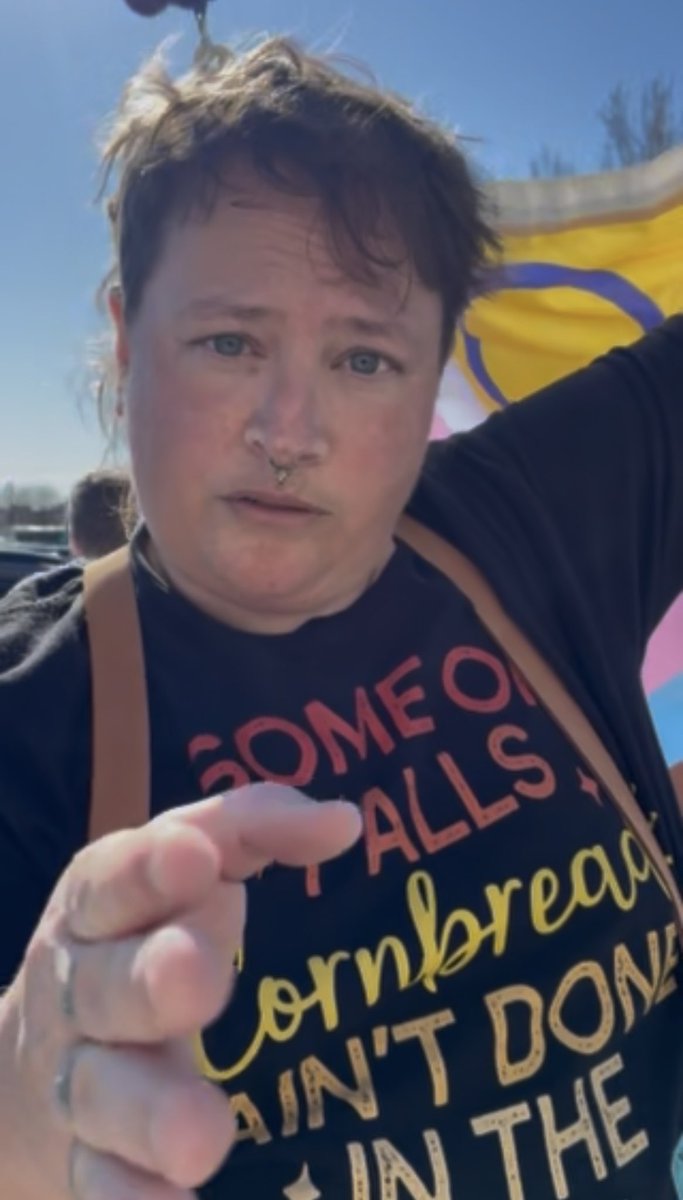
She and the 100+ other psychos threatening me will not take us off course.

*I blurred & covered it. No one should have to see that. But she sent the actual image — from anonymous proton account like a coward.
She and the 100+ other psychos threatening me will not take us off course.

Feb 7
Read 7 tweets
Brittney Shki-Giiziz, Canadian volunteer in Ukraine: My first day fighting was absolutely excellent. I destroyed a train station with a tank. Being at war was physically easier than the training the Canadian Army puts us through. It prepared me very well for war. 1/
Shki-Giiziz: The truth is that Russia is pushing. We are holding, but we are being pushed back constantly.
Our safe houses are pushed further back. We had positions in Myrnograd and Pokrovsk not so long ago. 2/
Our safe houses are pushed further back. We had positions in Myrnograd and Pokrovsk not so long ago. 2/
Shki-Giiziz: My first motivation for learning Ukrainian was to serve in a tank. Language was a requirement. I studied Ukrainian and the 25th Brigade gave me a chance. At first I just studied the commands. Now I’m conversational and can work freely in Ukrainian. 3/