[Thread] Missing / unpublished sequences
WANTED: Live isolates WIV15 & WIV6; Ra7896 (complete genome); EPI_ISL_402122; MT394201
WANTED: Live isolates WIV15 & WIV6; Ra7896 (complete genome); EPI_ISL_402122; MT394201

Two live isolates missing. Serious issue!
WIV6 and WIV15
WIV6 and WIV15
https://twitter.com/franciscodeasis/status/1333549440834088964
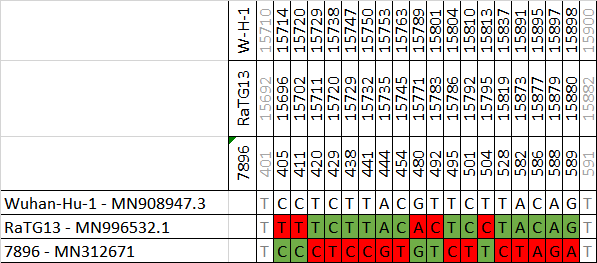
We need full disclosure of Ra7896 & clade. NOW!
https://twitter.com/franciscodeasis/status/1366750802057064449
Why a gap in this series?
What happened with EPI_ISL_402122?
Why IVDC-HB-02 & IVDC-HB-03 missing?
What happened with EPI_ISL_402122?
Why IVDC-HB-02 & IVDC-HB-03 missing?
https://twitter.com/franciscodeasis/status/1380111457531088896
NCBI cannot release this Accession which probably contains an ACE2 seq. It should by done by the authors. Waiting since summer 2020. Release it now!
https://twitter.com/franciscodeasis/status/1374887154921390084
Some other unpublished viruses
https://twitter.com/franciscodeasis/status/1336275756561952769
Oops, errata:
I mean MT394202, not MT394201
The link inside the tweet was correct:
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MT3942…
I mean MT394202, not MT394201
The link inside the tweet was correct:
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MT3942…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh