1/ Zomato S-1 just dropped.
FY20
--
Orders - 403M 🤯
GOV - $1.5B USD
Rev - $368M USD
Adj EBITDA - ($226M) USD
As you can see from the chart, COVID created a lot of volatility. Unlike in Europe and North America, a lot of restaurants were forced to close, esp in Q1 2020.
FY20
--
Orders - 403M 🤯
GOV - $1.5B USD
Rev - $368M USD
Adj EBITDA - ($226M) USD
As you can see from the chart, COVID created a lot of volatility. Unlike in Europe and North America, a lot of restaurants were forced to close, esp in Q1 2020.

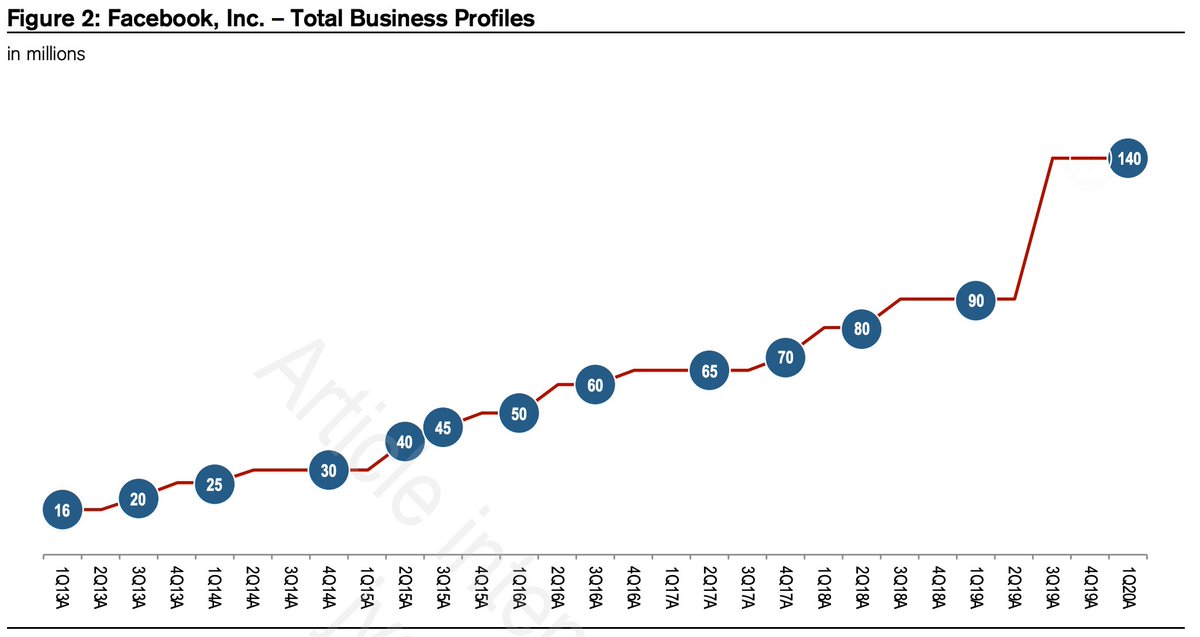
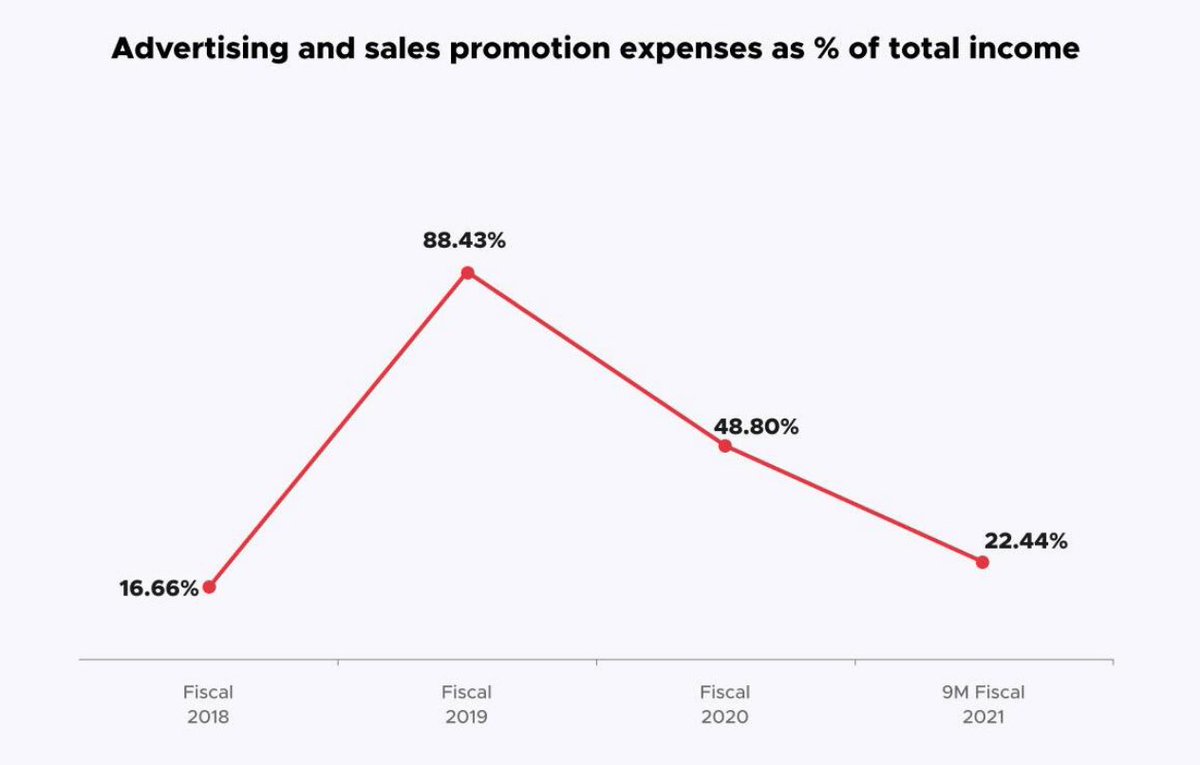
2/ You can also see they've been aggressively cutting costs. Adj EBITDA % losses as a % of revenue rapidly going down. 


3/ Exciting growth ahead for India over the next few decades (anxiously waiting for more Indian IPOs). 



5/ Supposedly they've dethroned Swiggy and have become the leader?
"According to RedSeer, we have consistently gained market share over the last four years to become the category leader in the food delivery space in India in terms of GOV from October 1, 2020 to March 31, 2021."
"According to RedSeer, we have consistently gained market share over the last four years to become the category leader in the food delivery space in India in terms of GOV from October 1, 2020 to March 31, 2021."
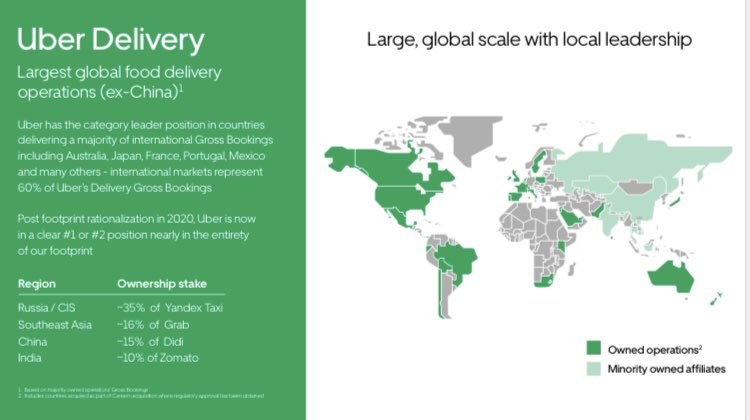
6/ $UBER owns about 9% of the business. Assuming they IPO at $6-$7B, this wouldn't be as good of a return as Grab or DiDi given the cumulative cash burn in India over the years 😞 

7/ Personally, given all of the volatility in India, I'm going to wait and see how they perform in the medium term. The current private valuation ($5.4B) feels a little rich. I'm also interested to see Swiggy's numbers once they file later this year.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh