
STOP VARIANTS—The AstraZeneca vaccine is ineffective for mild and moderate #B1351 variant from South Africa 🇿🇦. Prior to Oct 31st (before B1351), 75% effective for non-B1351.
Luckily B1351 isn’t fast. We need to stop pandemic & new variants soon. #COVID19 nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
Luckily B1351 isn’t fast. We need to stop pandemic & new variants soon. #COVID19 nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
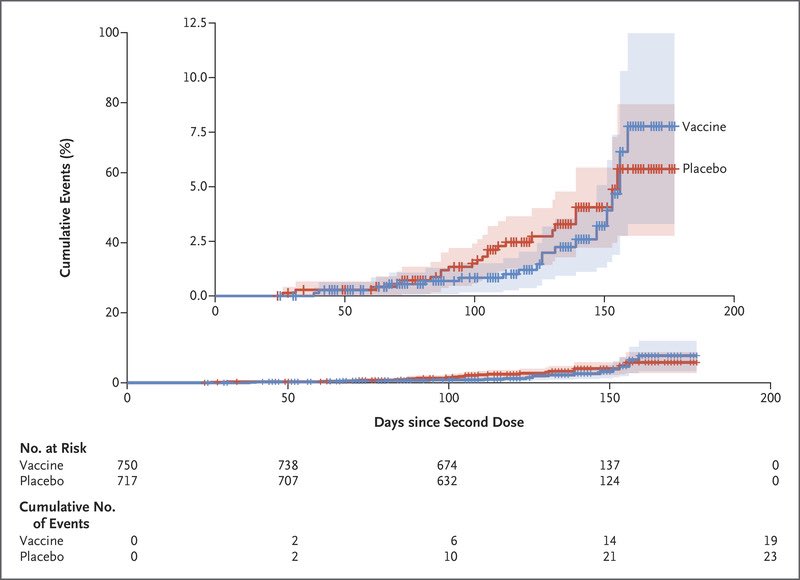
2) Look at the efficacy yourself — it is incredibly low overall 10-20% and not significant (not distinguishable from 0%).
It was only 75% in early part of the trial before #B1351 emerged.
It was only 75% in early part of the trial before #B1351 emerged.

3) Lots of questions about vaccines versus Indian variant #B16172– we just don’t know yet.
But what I worry is if some of the bad variants mix together and do recombination inside of a co infected person with both variants/strains… that could be very bad.
But what I worry is if some of the bad variants mix together and do recombination inside of a co infected person with both variants/strains… that could be very bad.
4) Thus, based on the AstraZeneca vaccine and #B1351 results (peer reviewed randomized trial in NEJM no less) the chief of WHO Europe is wrong wrong wrong….
https://twitter.com/afp/status/1395312488627855364
5) Reminder- there are many variants, and 4 key variants of concern… well 4 variant families because they India variant has the #B16172 that is most worrisome for its spread. I hope they don’t admix together and recombine together. That would be bad.
https://twitter.com/VincentRK/status/1394998689299578884
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh








