Some SQL Aggregate Functions that would come in handy! ➕ ➖ ➗ ✖️
Let's dive right into them. 🤩
Thread 🧵
Let's dive right into them. 🤩
Thread 🧵
☑️ Aggregate Functions
The motive of these functions is to perform a calculation on a set of values and return a single value as a result.
Different functions:-
1. COUNT
2. AVERAGE (AVG)
3. MAXIMUM (MAX)
4. MINIMUM (MIN)
5. SUM
The motive of these functions is to perform a calculation on a set of values and return a single value as a result.
Different functions:-
1. COUNT
2. AVERAGE (AVG)
3. MAXIMUM (MAX)
4. MINIMUM (MIN)
5. SUM
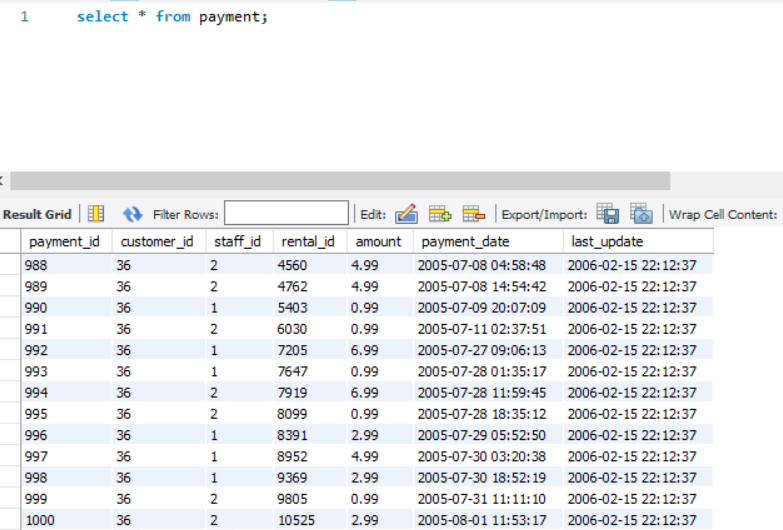
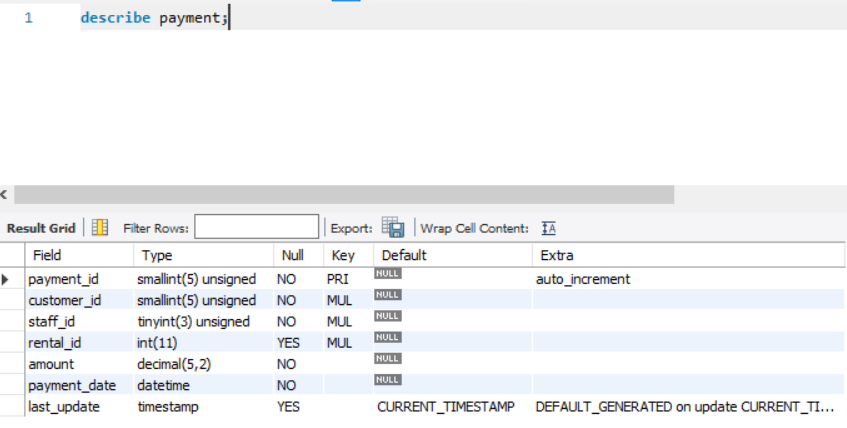
To understand most of the Advance SQL clauses, we will use the table named "payment". It consists of columns like payment_id, amount, staff_id, customer_id, etc. (See the image).
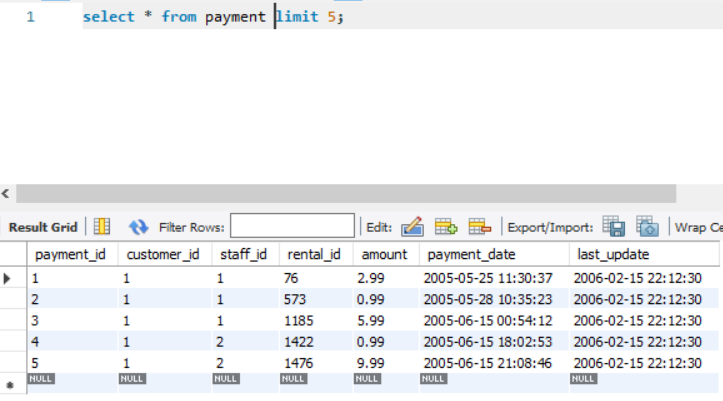
The first 5 rows of the table are also described for reference.

The first 5 rows of the table are also described for reference.
☑️ Count
1. To count all the rows in the table
👉 Query: select count(*) from table_name;
Note: count(*) includes the count of null values as well.
2. To count the rows in a specific column
👉 Query: select count(column_name) from table_name;
1. To count all the rows in the table
👉 Query: select count(*) from table_name;
Note: count(*) includes the count of null values as well.
2. To count the rows in a specific column
👉 Query: select count(column_name) from table_name;
Note: count(column_name) does NOT include the count of null values.
3. To count the no. of distinct values in a specific column
👉 Query: select count(DISTINCT column_name) from table_name;
3. To count the no. of distinct values in a specific column
👉 Query: select count(DISTINCT column_name) from table_name;
Let us see the examples of all three queries above:-
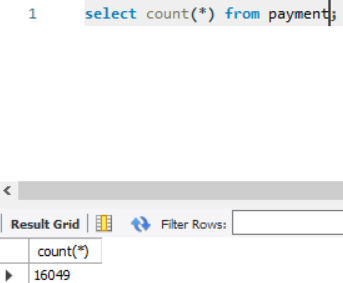
1. select count(*) from payment;
Op: 16049 [This ans includes NULL values]
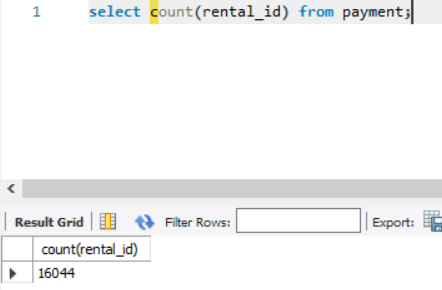
2. select count(rental_id) from payment;
Op: 16044

1. select count(*) from payment;
Op: 16049 [This ans includes NULL values]
2. select count(rental_id) from payment;
Op: 16044
3.
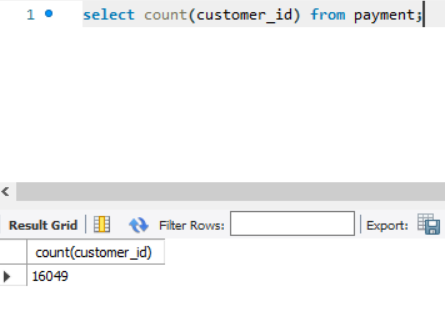
a) select count(customer_id) from customer_list;
Op: 16049
b) select count(distinct customer_id) from customer_list;
To find the number of unique customer_id
Op: 599
The total number of customer_id is 16049, out of which only 599 are DISTINCT.

a) select count(customer_id) from customer_list;
Op: 16049
b) select count(distinct customer_id) from customer_list;
To find the number of unique customer_id
Op: 599
The total number of customer_id is 16049, out of which only 599 are DISTINCT.

☑️ Average
Gives the average value for numeric data.
Note: For "avg" of any non-numeric column will not give an error; the result will be a ZERO.
Query: select AVG(column_name) from table_name;
Gives the average value for numeric data.
Note: For "avg" of any non-numeric column will not give an error; the result will be a ZERO.
Query: select AVG(column_name) from table_name;
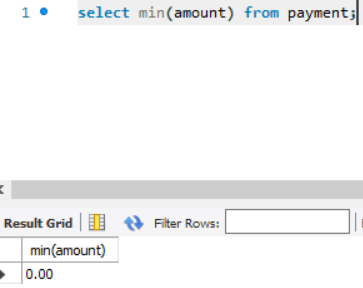
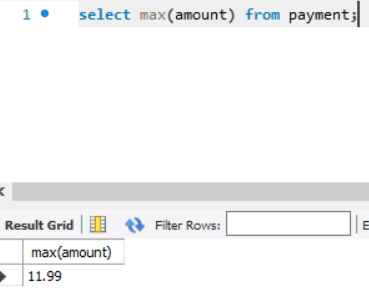
☑️ Maximum, Minimum
To find the max value and min value from a column.
Query (max): select max(col_name) from table_name;
Query (min): select max(col_name) from table_name;
To find the max value and min value from a column.
Query (max): select max(col_name) from table_name;
Query (min): select max(col_name) from table_name;
☑️ Sum
To calculate the sum of all the values.
Query: select sum(column_name) from table_name;
To calculate the sum of all the values.
Query: select sum(column_name) from table_name;
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh