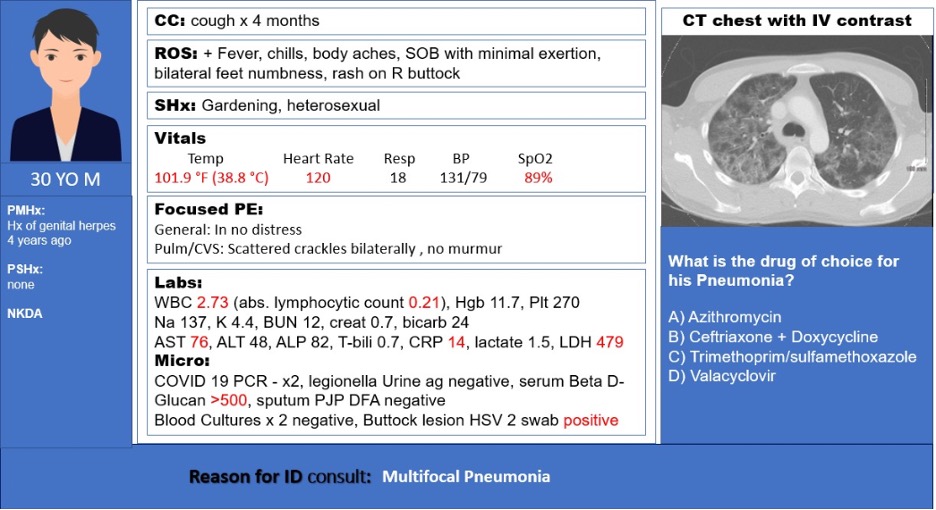
1/ Happy Opportunistic Monday #IDtwitter #IDfellows; another interesting case and learning opportunity, written by @johnhannamd and @KrutiYagnikDO 

2/ Following tissue diagnosis, what is the best next step in management?
3/ #IDpearls
Leading differential diagnosis of pulmonary infiltrates and skin lesions in HIV patients include:
Typical bacterial
TB, NTM
Cryptococcus, histoplasmosis, other dimorphic fungi
Lymphoma, KS
Leading differential diagnosis of pulmonary infiltrates and skin lesions in HIV patients include:
Typical bacterial
TB, NTM
Cryptococcus, histoplasmosis, other dimorphic fungi
Lymphoma, KS
4/ Check out this nice differential and work up for respiratory symptoms in HIV patients. From @bradcutrellmd 

5/ Our case was found to have:
-CT chest with innumerable flame-shaped peribronchovascular nodules throughout the lungs with enhancing adenopathy.
-Scattered non-scaly red violaceous lesions on face, trunk, extremities, and soft palate.
-Skin biopsy with Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS)
-CT chest with innumerable flame-shaped peribronchovascular nodules throughout the lungs with enhancing adenopathy.
-Scattered non-scaly red violaceous lesions on face, trunk, extremities, and soft palate.
-Skin biopsy with Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS)
6/ KS is an angioproliferative disorder associated with HHV-8.
-Major risk factor is immunosuppression.
-Incidence increased in the HIV era.
-Incidence decreased with introduction of ART
-There are 3 pathogenic stages of KS; patch, plaque, and nodular.
-Major risk factor is immunosuppression.
-Incidence increased in the HIV era.
-Incidence decreased with introduction of ART
-There are 3 pathogenic stages of KS; patch, plaque, and nodular.
7/ KS staging is based on:
-Extent of tumor (T0-1) [skin vs dissemination]
-Immune status (I0-1) [CD4>200 ->favorable diagnosis]
-Severity of systemic illness (S0-1) [Hx of opportunistic infection, thrush, B symptoms associated with poor prognosis]
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2671281/
-Extent of tumor (T0-1) [skin vs dissemination]
-Immune status (I0-1) [CD4>200 ->favorable diagnosis]
-Severity of systemic illness (S0-1) [Hx of opportunistic infection, thrush, B symptoms associated with poor prognosis]
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2671281/
8/ For HIV associated KS, mainstay of therapy is initiating ART to reconstitute immunity.
ART + chemotherapy is the regimen of choice for the following:
-Symptomatic visceral KS
-Extensive cutaneous KS
ART + chemotherapy is the regimen of choice for the following:
-Symptomatic visceral KS
-Extensive cutaneous KS
9/ In symptomatic cases with limited disease, intralesional chemotherapy vs radiation therapy may be considered.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
10/ IRIS can be induced by ART alone in patients with disseminated KS through increased inflammatory cytokines during immune reconstitution by ART, which may lead to death from further rapid dissemination.
11/ KS IRIS is more likely to develop in cases with:
-Advanced KS stage
-HIV VL >100k copies/ml
-Higher CD4 count
-KS associated edema
-Use of ART without chemotherapy
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16051964/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23462220/
-Advanced KS stage
-HIV VL >100k copies/ml
-Higher CD4 count
-KS associated edema
-Use of ART without chemotherapy
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16051964/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23462220/
12/ Predictive factors of KS IRIS poor prognosis:
-Lung involvement.
-Thrombocytopenia at week 12 follow up after ART initiation.
aidsrestherapy.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.11…
-Lung involvement.
-Thrombocytopenia at week 12 follow up after ART initiation.
aidsrestherapy.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.11…
13/ Kaposi’s sarcoma herpes virus (KSHV) related disorders represent a heterogeneous group of illnesses that includes:
-KS
-Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL)
-Multicentric Castleman’s disease (KSHV-MCD)
-KS-associated herpesvirus inflammatory cytokine syndrome (KICS)
-KS
-Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL)
-Multicentric Castleman’s disease (KSHV-MCD)
-KS-associated herpesvirus inflammatory cytokine syndrome (KICS)
14/ PEL is characterized by its predilection for body cavities such as the peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial spaces.
Castleman's disease is an uncommon lymphoproliferative disorder. Features include fever, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and massive lymphadenopathy.
Castleman's disease is an uncommon lymphoproliferative disorder. Features include fever, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and massive lymphadenopathy.
15/ KICS is characterized by clinical manifestations of systemic inflammation, elevated HHV-8 plasma viral loads, and high circulating levels of human and viral interleukin-6 as well as human interleukin-10.
16/ See this chart which compares KICS vs KSHV-MCD vs KS-IRIS.
Taken from: academic.oup.com/ofid/article/4…
Taken from: academic.oup.com/ofid/article/4…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh