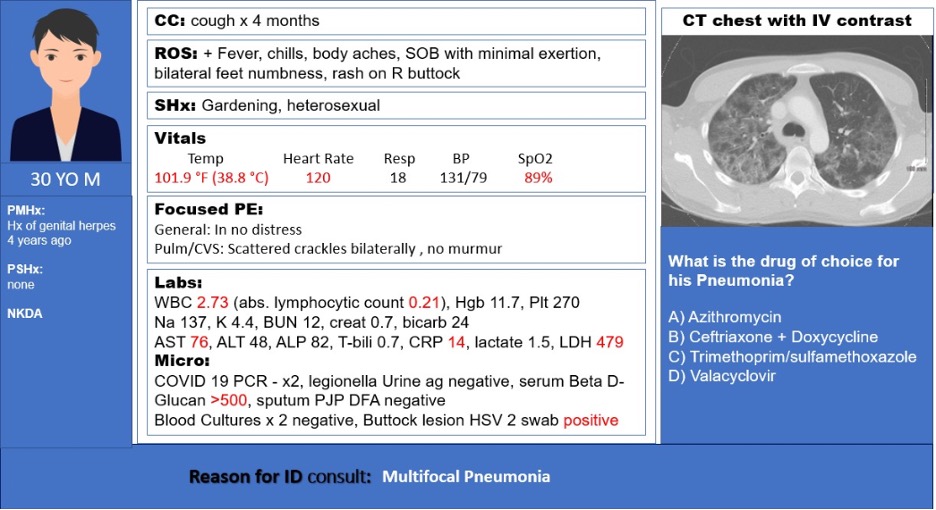
1/ Happy Opportunistic Monday #IDtwitter #IDfellows! Sharing another interesting learning case. Written by @johnhannamd and @KrutiYagnikDO 

2/ What is the best next therapeutic step?
3/ Differential diagnosis for suspected meningoencephalitis without CNS mass lesion in an HIV patient with low CD4 count include:
-Bacterial meningitis
-Neurosyphilis
-TB
-Cryptococcus
-Other endemic fungi
-HSV
-VZV
-CMV
-PML (JC virus)
-HIV encephalopathy
-Bacterial meningitis
-Neurosyphilis
-TB
-Cryptococcus
-Other endemic fungi
-HSV
-VZV
-CMV
-PML (JC virus)
-HIV encephalopathy

4/ Our patient with low CD4 count presents with headache, neck pain, nausea and vomiting that likely reflects increased intracranial pressure. Serum cryptococcal Ag is positive. The leading differential in his case is cryptococcal meningitis.
5/ #IDpearls
Cryptococcal meningitis(CM) is a severe fungal infection primarily seen in people with compromised cell‐mediated immunity. Most cases occur in advanced HIV disease with CD4 <1200.
Diagnostic confirmation of cryptococcal meningitis relies on lumbar puncture(LP).
Cryptococcal meningitis(CM) is a severe fungal infection primarily seen in people with compromised cell‐mediated immunity. Most cases occur in advanced HIV disease with CD4 <1200.
Diagnostic confirmation of cryptococcal meningitis relies on lumbar puncture(LP).
6/ LP is also essential to lower raised intracranial pressure (ICP). Often, may need repeated LPs to control and normalize ICP.
Adjunctive steroids did not show mortality reduction and was associated with more adverse events in HIV-associated CM.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Adjunctive steroids did not show mortality reduction and was associated with more adverse events in HIV-associated CM.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
7/ CSF CrAg is usually positive in patients with cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. However, early meningitis can present with negative CSF studies. Therefore, serum CrAg should always be performed in an immunocompromised cases.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26711635/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26711635/
8/ Obtaining CSF cultures is important as CM antifungal resistance is evolving.
In general, routine surveillance testing for serum CrAg in people with newly diagnosed HIV is recommended for patients with CD4 counts ≤100
In general, routine surveillance testing for serum CrAg in people with newly diagnosed HIV is recommended for patients with CD4 counts ≤100
9/ Induction treatment of CM & extrapulmonary cryptococcosis:
IV amphotericin B formulation + oral flucytosine x2 weeks with therapeutic drug monitoring (specially in patients with renal impairment).
IV amphotericin B formulation + oral flucytosine x2 weeks with therapeutic drug monitoring (specially in patients with renal impairment).
10/ Following 2-week induction; LP and repeat CSF culture should be performed. Clinically stable patients may be switched to consolidation therapy while awaiting CSF culture results.
11/ Successful induction therapy is defined as: clinical improvement and a negative CSF culture from the end-of-induction LP.
Induction is recommended to continue until clinical improvement & CSF cultures are negative in clinically unstable cases (or when no improvement).
Induction is recommended to continue until clinical improvement & CSF cultures are negative in clinically unstable cases (or when no improvement).
12/ Consolidation therapy:
Fluconazole 800 mg daily; early clinical trials that used 400 mg fluconazole for consolidation noted breakthrough cases.
Itraconazole can be used as an alternative therapy for consolidation, but it is inferior to fluconazole
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10064246/
Fluconazole 800 mg daily; early clinical trials that used 400 mg fluconazole for consolidation noted breakthrough cases.
Itraconazole can be used as an alternative therapy for consolidation, but it is inferior to fluconazole
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10064246/
13/ Duration of consolidation therapy is usually around 8 weeks from negative CSF culture.
Fluconazole 200 mg daily is used for maintenance treatment; usually continued for at least one year from initiation of antifungal therapy.
Fluconazole 200 mg daily is used for maintenance treatment; usually continued for at least one year from initiation of antifungal therapy.
14/ ART initiation should be deferred for 4-6 weeks after antifungal agents are started to prevent IRIS.
An estimated 10-30% of people with HIV who have cryptococcal meningitis experience IRIS after initiation or re-initiation of effective ART
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
An estimated 10-30% of people with HIV who have cryptococcal meningitis experience IRIS after initiation or re-initiation of effective ART
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
15/ Treatment failure is defined as:
A) Lack of clinical improvement + continued positive culture after 2 weeks of treatment and management of increased ICP.
OR
B) Relapse after an initial clinical response; symptoms recurrence + positive culture after ≥4 weeks of treatment.
A) Lack of clinical improvement + continued positive culture after 2 weeks of treatment and management of increased ICP.
OR
B) Relapse after an initial clinical response; symptoms recurrence + positive culture after ≥4 weeks of treatment.
16/ For CM treatment failure or relapse, verifying CSF culture sterility at the completion of re-induction therapy is important.
Followed by outpatient consolidation therapy (fluconazole at a higher dose of 1,200 mg/day and optimization of ART).
clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/guidelines/…
Followed by outpatient consolidation therapy (fluconazole at a higher dose of 1,200 mg/day and optimization of ART).
clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/guidelines/…
Typo clarification:
Most cases occur in advanced HIV disease with CD4 <100.
Most cases occur in advanced HIV disease with CD4 <100.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh