🧵In our paper Intraventricular Vector Flow Imaging with Blood Speckle Tracking in Adults: Feasibility, Normal Physiology and Mech… we use a new method, not only BST, and can be applied on adult probes. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34620522/
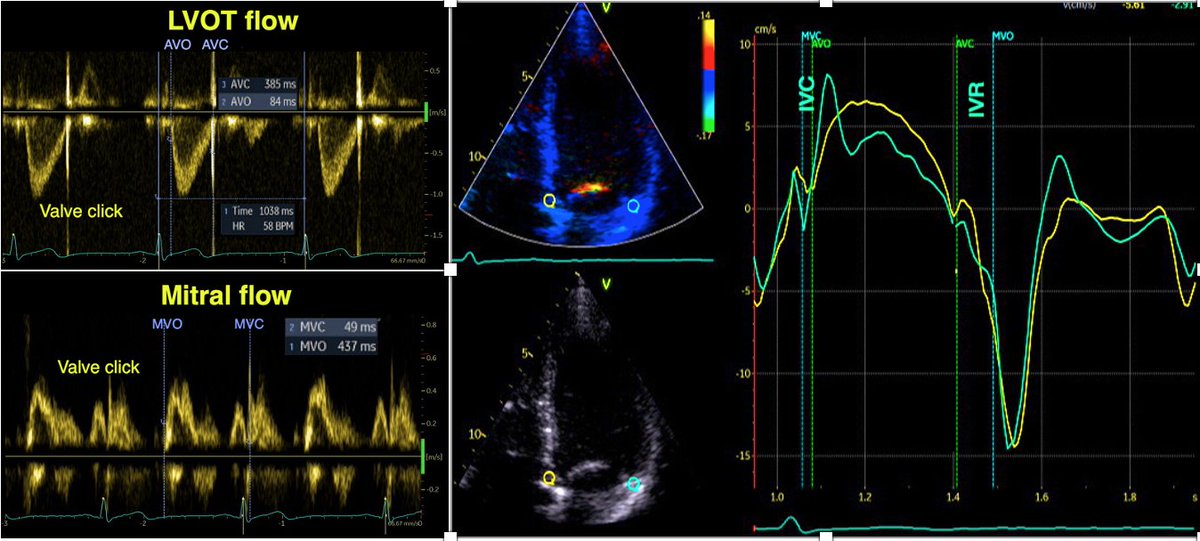
The main aim was to investigate the normal adult, intraventricular blood flow throughout the whole cardiac cycle, to compare with pw and colour Doppler M-mode and wall mechanics. (2D images courtesy of AS Daae).
As tweeted before, during IVR, there is simultaneous shortening of the base and elongation of the apex, inducing a volume shift with intraventricular apical flow, imparting a momentum and kinetic energy towards apex before start of early filling. This is thus *not* "wasted work" 

1/ At the time of MVO and start of inflow, the AV plane also starts to move basally. This expands the space in the LVOT and behind the mitral ring, thus diverting inflowing blood laterally. 

2/ This motion diverts blood flow downwards, creating vortices, counterclockwise in the LVOT, clockwise in the lateral part when viewed in a conventional 4-chamber view. The LVOT vortex is the largest as there is more room here. 

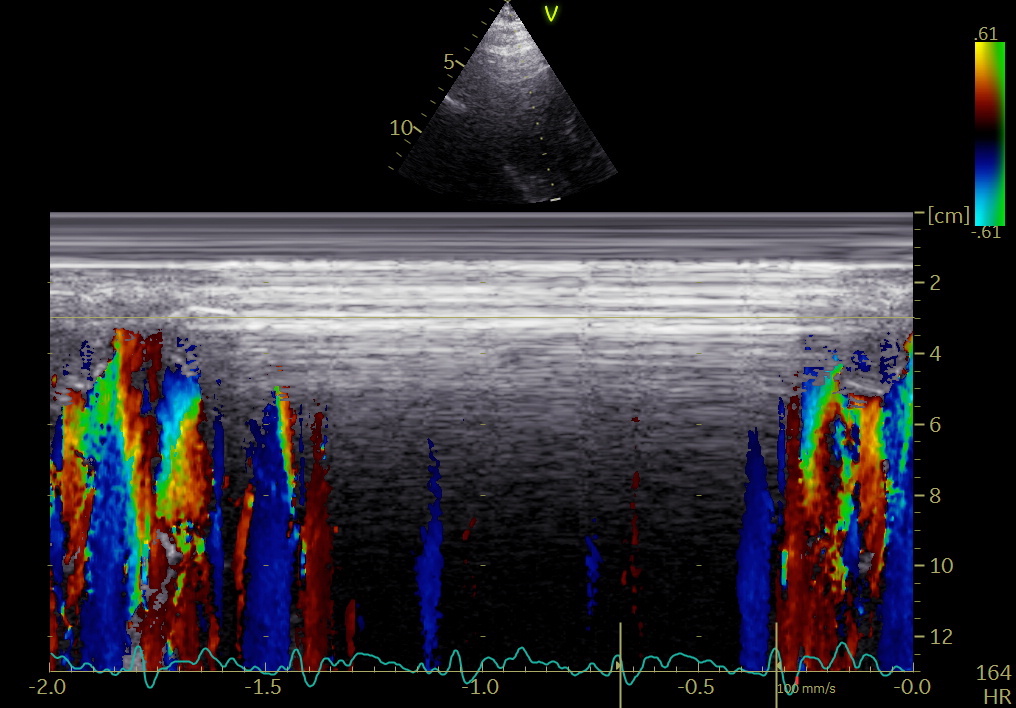
3/ This diversion of blood flow, and start of diastolic vortex, is due to the ventricle being wider than the orifice, plus the expansion of the basal space, and thus starts near the LV base, as can be easily seen by CMM. 

4/ The diverted flow into the LVOT is easily seen by pw Doppler, if you look for it, and is thus a normal phenomenon, although the E/A ratio in the LVOT will reflect the mitral E/A ratio, so a low E/A gives rise to the J-wave, which in reality is a high ALVOT. 

5/ contrary to what has been published previously, this is not return flow from the apex. In our study, there was no delay between mitral E and e', while ELVOT had a delay of 116 ms. With an E of 82 cm/s, return flow from the apex would arrive after about 2 s. 

6/ during early filling, the lateral vortex being smaller and clockwise, seem to be extinguished, while the counterclockwise LVOT vortex expands (LVOT continuing to expand basally and more blood being diverted basally, as well as inflowing blood being diverted closer to the apex) 

7/ This has previously been described as vortex propagation pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7867035/
but is actually an expansion, and apical propagation can be seen by colour M-mode; both negative vectors along the septum and positive vectors along the mid-lateral ventricle.
but is actually an expansion, and apical propagation can be seen by colour M-mode; both negative vectors along the septum and positive vectors along the mid-lateral ventricle.

unroll @threadreaderapp
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh