As if small scorpions weren’t scary enough, scientists have discovered an ancient fossil of a sea scorpion that was 16 times larger than the present-day scorpion—almost as big as a dog!
Read: weather.com/en-IN/india/bi…
📸: Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology/Y Dinghua
Read: weather.com/en-IN/india/bi…
📸: Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology/Y Dinghua
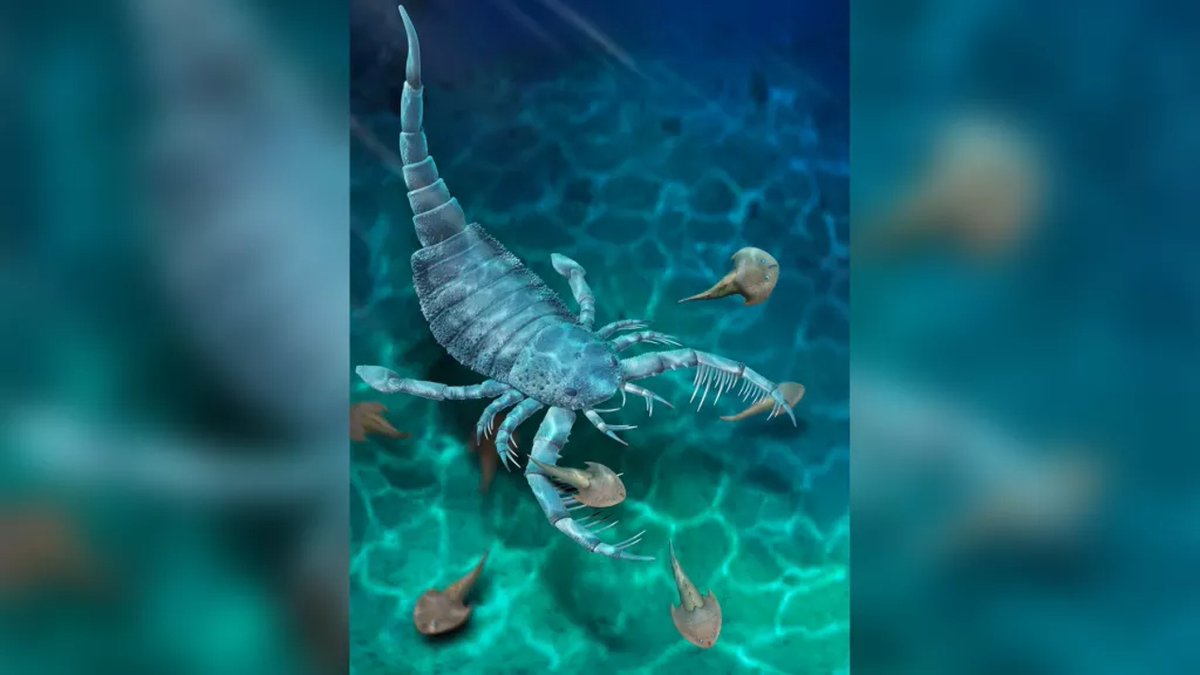

Named Terropterus xiushanensis, this arachnid was a relative of the present-day horseshoe crab and whip spider.
It had similar spiny attacking forelimbs & belonged to mixopterids—a group of eurypterids (sea scorpions)—also recognised for their specialised arms for catching prey.
It had similar spiny attacking forelimbs & belonged to mixopterids—a group of eurypterids (sea scorpions)—also recognised for their specialised arms for catching prey.
The fearsome beast is suspected of having lived during the Silurian period—somewhere between 443.8 million and 419.2 million years ago—where it would have been an apex underwater predator.
Previous research has indicated that sea scorpions were top predators long before the existence of barracudas or sharks, & this fossil confirms it.
This apex underwater predator used its giant spiny arms & its tail, weaponized by serrated spiny tips, to prowl on fish & molluscs.
This apex underwater predator used its giant spiny arms & its tail, weaponized by serrated spiny tips, to prowl on fish & molluscs.
Previously, mixopterids knowledge was limited to four species in two genera, all based on fossil records from 80 years ago.
However, this well-preserved fossil gives better clarity on the morphological diversity of mixopterids.
📸: Nanjing Institute of Geology & Paleontology
However, this well-preserved fossil gives better clarity on the morphological diversity of mixopterids.
📸: Nanjing Institute of Geology & Paleontology
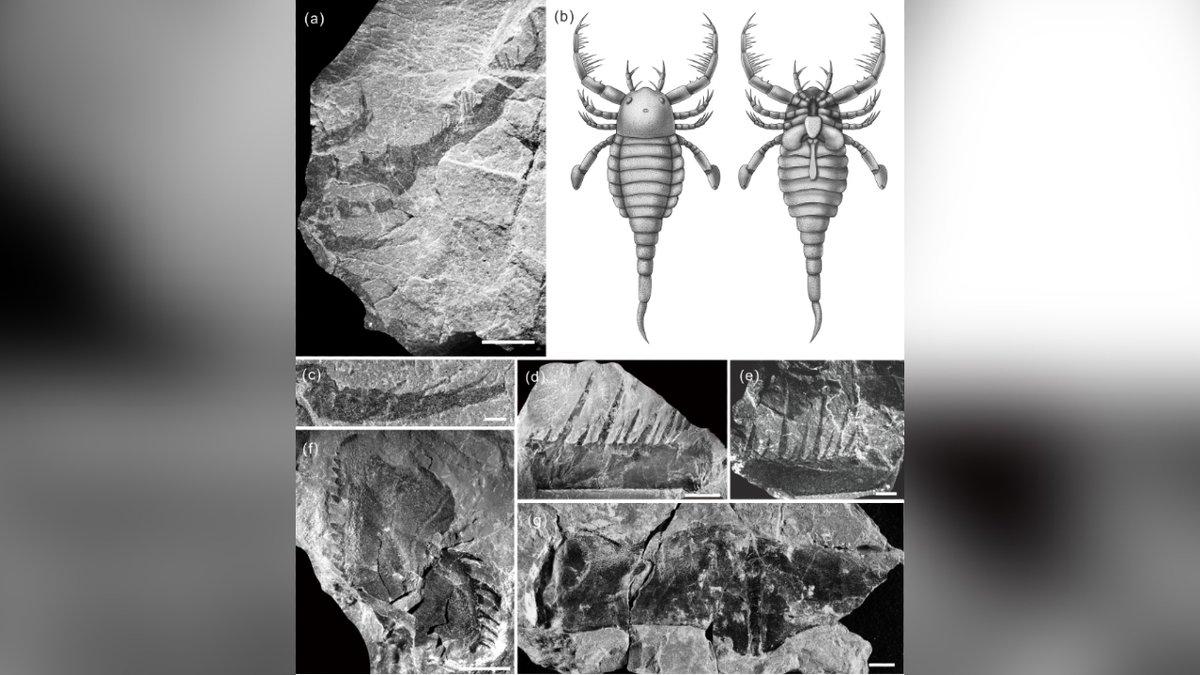

T xiushanensis is the first mixopterid reported from the Gondwana supercontinent, which formed when the large landmass of Pangaea split into two.
This suggests an under-collecting bias in the group.
This suggests an under-collecting bias in the group.
"Future work, especially in #Asia, may reveal a more cosmopolitan distribution of mixopterids and perhaps other groups of eurypterids," say the researchers.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh