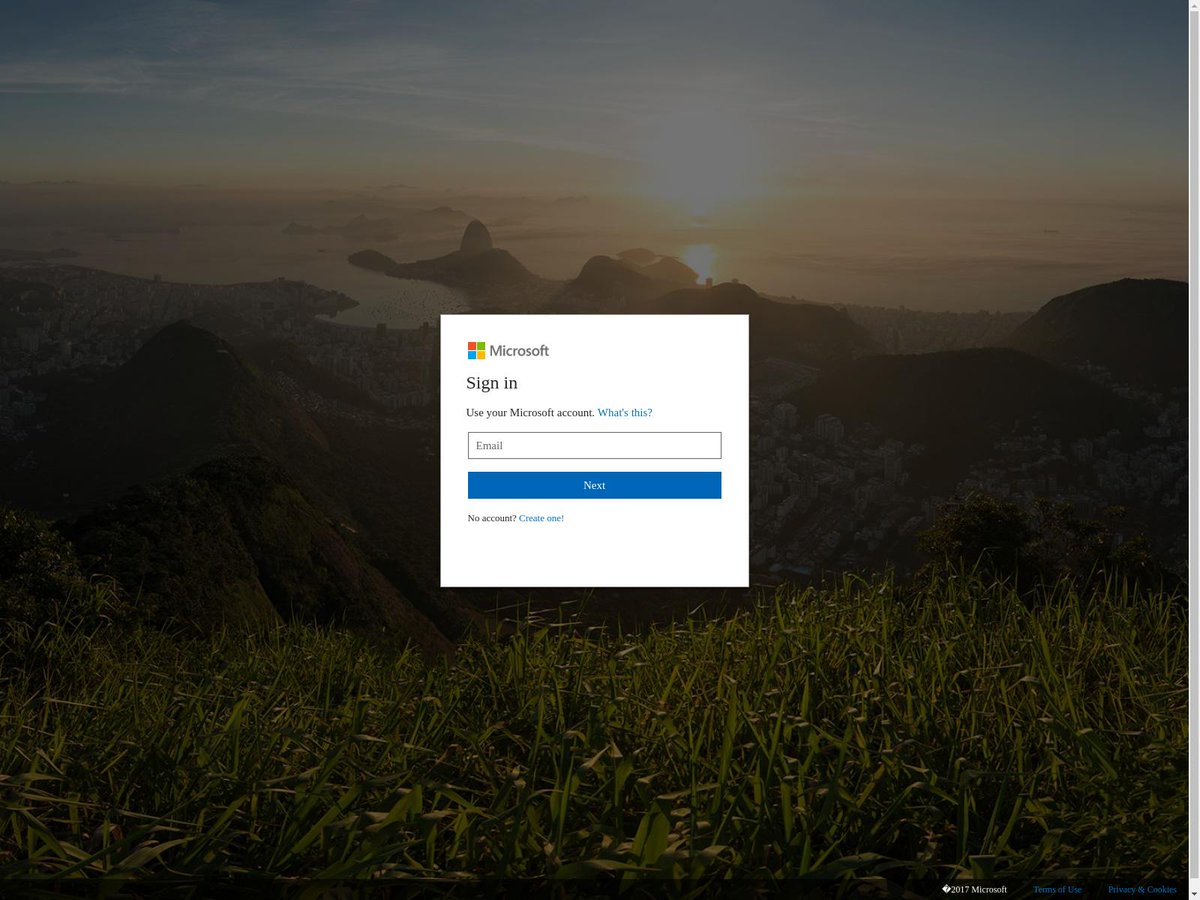
So you want to learn about phishing kits 🧑🎓
🧵 In this thread I will highlight threat hunting skills and IoCs within phishing kits to look for ⤵️
Retweets are appreciated ♻️
🔍Follow me for more #phishing intelligence @Jcybersec_
🧵 In this thread I will highlight threat hunting skills and IoCs within phishing kits to look for ⤵️
Retweets are appreciated ♻️
🔍Follow me for more #phishing intelligence @Jcybersec_

📁What is a phishing kit?
When a threat actor wants to create a phishing page they will create the page on their own machine.
Zipping it up 🤐
And then putting this zip on a website to then deploy 🌐
When a threat actor wants to create a phishing page they will create the page on their own machine.
Zipping it up 🤐
And then putting this zip on a website to then deploy 🌐

🥷Building threat actors create these kits and sell them to other threat actors 💰
Deploying / Controlling threat actors put the kits online and then extract the content to instantly upload a working phishing site 🦹
Deploying / Controlling threat actors put the kits online and then extract the content to instantly upload a working phishing site 🦹

🗄️Why do we collect kits?
Phishing kits contain very valuable information such as PHP code, configuration settings and all the phishing sites resources. 👀
We are then able to link, cluster, and attribute these phishing sites back to actors and individuals. 🔄
Phishing kits contain very valuable information such as PHP code, configuration settings and all the phishing sites resources. 👀
We are then able to link, cluster, and attribute these phishing sites back to actors and individuals. 🔄
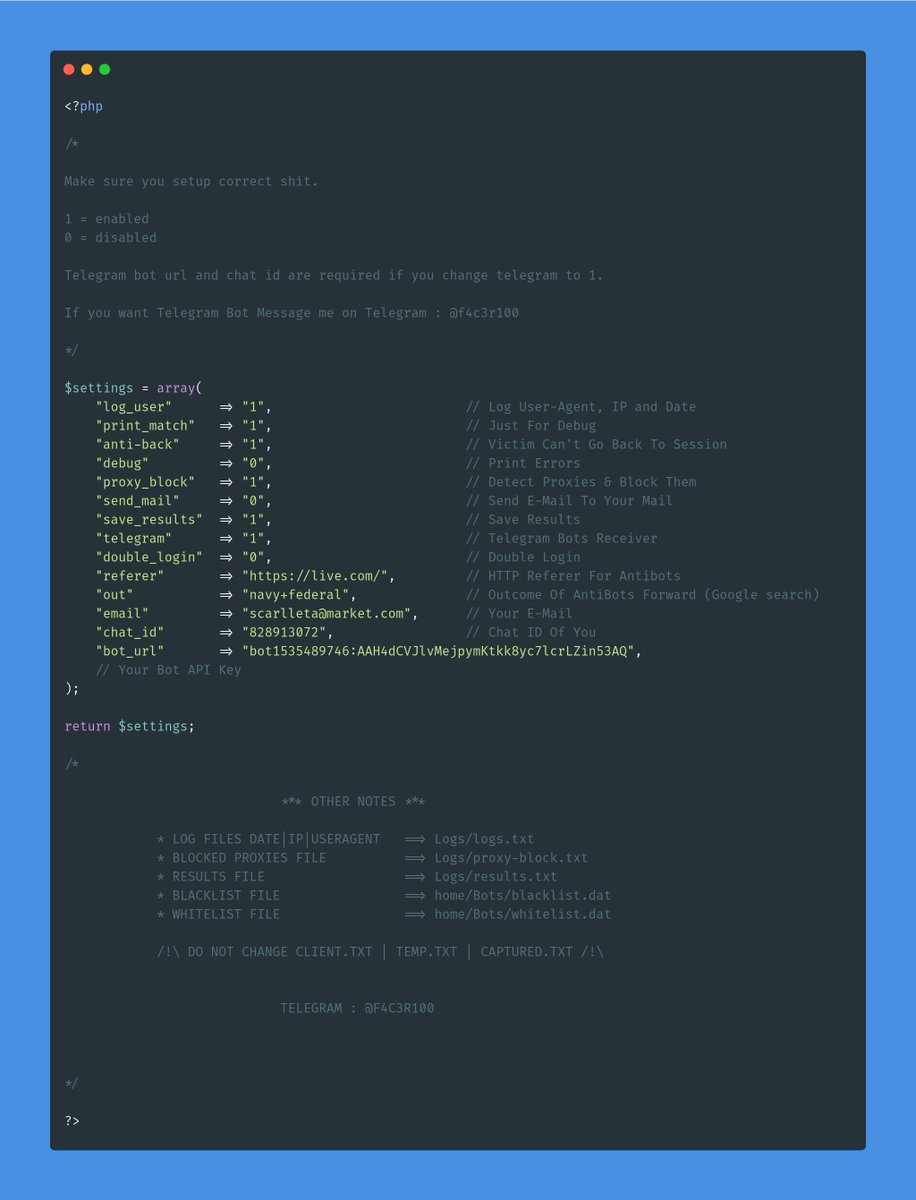
🔍What should you look for in a phishing kit?
This is a deep dive into phishing kits and items of interest which have been seen in phishing kits...
This is a deep dive into phishing kits and items of interest which have been seen in phishing kits...
✅ Configuration Files
These files are interesting as it shows us how the website is configured and what settings are available to the controlling actor.
These files are interesting as it shows us how the website is configured and what settings are available to the controlling actor.

Config pages are often written in PHP but can also be in JSON or another text format. 🔠
Common options available are exfil email, file write, geo blocks, user agent blocks etc. 📨
Common options available are exfil email, file write, geo blocks, user agent blocks etc. 📨

✉️Email Exfiltration Script
This is the piece of code used to send the stolen data back to the actor. ➡️
We can often find unique strings and actor fingerprints in these items as well as understanding at a quick glance what data is stolen from a victim 📤
This is the piece of code used to send the stolen data back to the actor. ➡️
We can often find unique strings and actor fingerprints in these items as well as understanding at a quick glance what data is stolen from a victim 📤

🤖Antibot files
These are crude attempts by builders to block unwanted visitor is such as researchers and bots.🚫
💻Methods used are often IP ranges, Useragents, and proxy checkers.
These are crude attempts by builders to block unwanted visitor is such as researchers and bots.🚫
💻Methods used are often IP ranges, Useragents, and proxy checkers.

It is frequent to see these antibot files being used across multiple kits as builders just steal and use other actors IP lists in a hope to remain undetected for as long as possible. 🕵️ 

✴️Admin Panels
I have already written an extensive (now outdated) thread on attributing admin panels.
I have already written an extensive (now outdated) thread on attributing admin panels.
https://twitter.com/JCyberSec_/status/1156545729952976896
Within phishing kits we find source code to the admin panel.
This allows us to understand how the panel works, authentication configurations, and any weaknesses in the code. 🦾
This allows us to understand how the panel works, authentication configurations, and any weaknesses in the code. 🦾

📳 2FA bypass
We are seeing more websites and users now using two factor authentication for their accounts and as a result phishing kits are now targeting these codes. 📱
Within phishing kits we get to see how these 2FA stealing methods work. #⃣
We are seeing more websites and users now using two factor authentication for their accounts and as a result phishing kits are now targeting these codes. 📱
Within phishing kits we get to see how these 2FA stealing methods work. #⃣

Often they are basic with no automation, whilst other kits will automate the login of an account triggering a 2FA code to be sent via SMS to the victim.
👁️How do you find kits?
Threat actors need to use kits to upload their sites. 🕸️
There are a number of ways in which you can grab them from them. 📍
Threat actors need to use kits to upload their sites. 🕸️
There are a number of ways in which you can grab them from them. 📍
If a threat actor leaves a kit in an open directory.😅
🏁 This can occur if they forget to remove it or you can capture it before they remove it then you can download the kit with ease.
🏁 This can occur if they forget to remove it or you can capture it before they remove it then you can download the kit with ease.

You can try guessing where the kit might be stored and this can be done by simply appending .zip to the end of the URL. 🍡 

Although you can't see the file structure behind the website the actor have extracted the kit and kept the directory names the same.
What next? 🤓
If you now have a kit look into it:
Read the code 🔍
Understand how it works ❓
Share this research online so we can all see what is happening 🌐
Tag me into any phishing finds and research- twitter.com/JCyberSec_
If you now have a kit look into it:
Read the code 🔍
Understand how it works ❓
Share this research online so we can all see what is happening 🌐
Tag me into any phishing finds and research- twitter.com/JCyberSec_
Thanks for reading 👍
💡Did I miss anything or do you use another skill which I didn't mention...
Post a comment below! ⤵️
💡Did I miss anything or do you use another skill which I didn't mention...
Post a comment below! ⤵️
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh