
❓What is the state of knowledge on abrupt climate change, irreversibility, tipping points, low-likelihood, high impact outcomes, as assessed in the @IPCC_CH #AR6 2021 #ClimateReport ❓
🧵⬇️
(1/...)
🧵⬇️
(1/...)
➡️ Low-likelihood outcomes, such as ice sheet collapse, abrupt ocean circulation changes, some compound extreme events and warming substantially larger than the assessed very likely range of future warming cannot be ruled out and are part of risk assessment.
(4/...)
(4/...)
🇦🇶 There is limited evidence for low-likelihood, high-impact outcomes (resulting from ice sheet instability processes characterized by deep uncertainty and in some cases involving tipping points)...
(Figure FAQ9.1)
(5/...)
(Figure FAQ9.1)
(5/...)

... that would strongly increase ice loss from the Antarctic Ice Sheet for centuries under high greenhouse gas emissions scenarios.
Figure SPM8
(6/...)

Figure SPM8
(6/...)


🌡️ If global warming exceeds the assessed very likely range for a given greenhouse gas emissions scenario, including low greenhouse gas emissions scenarios ...
(7/...)
(7/...)

... global and regional changes in many aspects of the climate system, such as regional precipitation and other climatic impact-drivers, would also exceed their assessed very likely ranges.
(Box TS3 : ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1…)
(8/...)

(Box TS3 : ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1…)
(8/...)


Low-likelihood, high-impact outcomes could occur at global and regional scales even for global warming within the very likely range for a given greenhouse emissions scenario. The probability of low-likelihood, high impact outcomes increases with higher global warming levels.
9/



9/

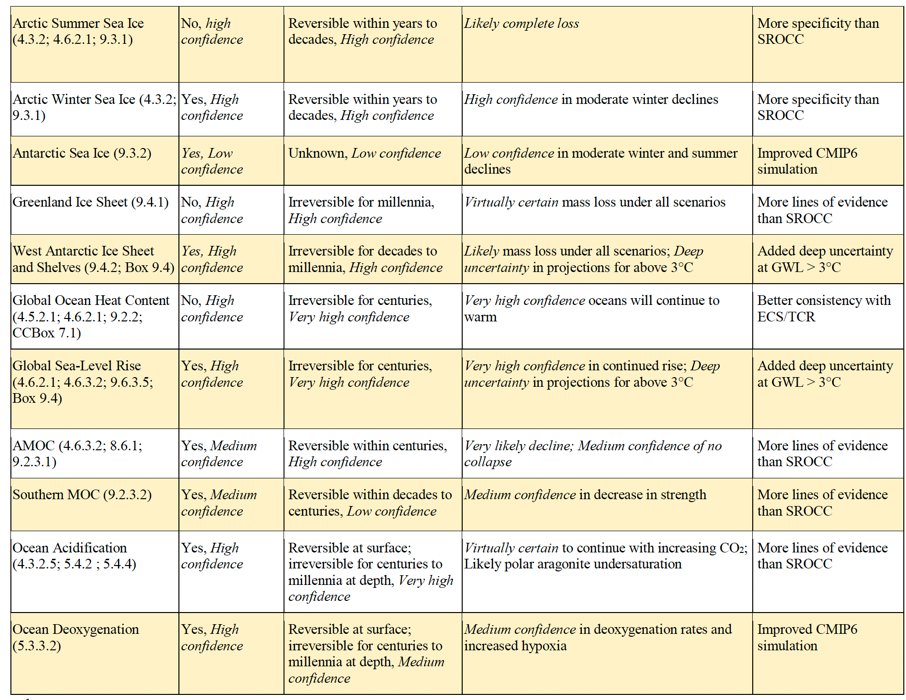


Abrupt responses and tipping points of the climate system, such as strongly increased Antarctic ice sheet melt and forest dieback, cannot be ruled out
(Tables from chapters 4, 5 and 12)
(10/...)
(Tables from chapters 4, 5 and 12)
(10/...)

Abrupt changes and tipping points in the biogeochemical cycles lead to additional uncertainty in 21st century greenhouse gas concentrations changes, but these are very likely to be small compared to the uncertainty associated with future anthropogenic emissions.
(11/...)
(11/...)
If global warming increases, some compound extreme events with low likelihood in past and current climate will become more frequent, ...
(12/...)
(12/...)
... and there will be a higher likelihood that events with increased intensities, durations and/or spatial extents unprecedented in the observational record will occur.
(13/...)
(13/...)

The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation is very likely to weaken over the 21st century for all emission scenarios.
(14/...)
(14/...)

While there is high confidence in the 21st century decline, there is only low confidence in the magnitude of the trend. There is medium confidence that there will not be an abrupt collapse before 2100.
Figure FAQ9.3 ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1…
(15/...)
Figure FAQ9.3 ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1…
(15/...)

If such a collapse were to occur, it would very likely cause abrupt shifts in regional weather patterns and water cycle, such as a southward shift in the tropical rain belt, weakening of the African and Asian monsoons and strengthening of SH monsoons, and drying in Europe.
16/
16/

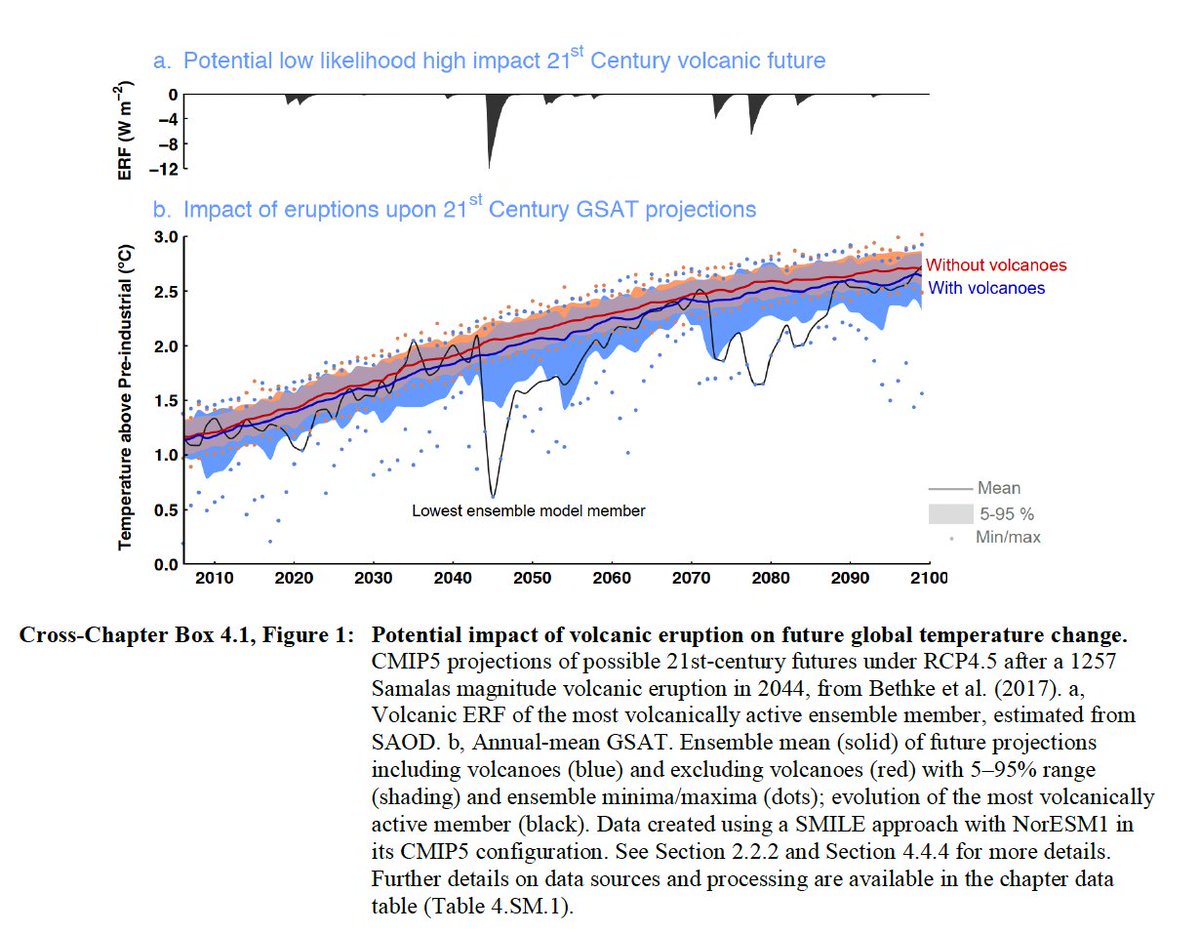
🌋Unpredictable and rare natural events not related to human influence on climate may lead to lowlikelihood, high impact outcomes...
(17/...)
(17/...)
A sequence of large explosive volcanic eruptions within decades has occurred in the past, causing substantial global and regional climate perturbations over several decades. Such events cannot be ruled out in the future.
(18/...)
(18/...)
See the summary of changes as a function of the level of global warming in Chapter 12 : extremes, trends...
(19/...)


(19/...)



🔎 Of course, you find will more detailed information in the relevant report chapters (1, 4, 5, 8, 9, 12).
🔦 This brief overview illustrates the use of physical climate storylines to communicate the plausible unfolding of eventualities associated with deep uncertainty.
END
🔦 This brief overview illustrates the use of physical climate storylines to communicate the plausible unfolding of eventualities associated with deep uncertainty.
END
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

















