🧨NO! There is no new variant that isn't detectable by PCR😤
The a new set of sequences, closely related to #Omicron has been detected & we *absolutely can* detect cases with PCR. What we can't tell as easily is /that they are Omicron or Omicron-like/.
theguardian.com/world/2021/dec…
The a new set of sequences, closely related to #Omicron has been detected & we *absolutely can* detect cases with PCR. What we can't tell as easily is /that they are Omicron or Omicron-like/.
theguardian.com/world/2021/dec…
First things first - I'm a huge @guardian fan & immensely disappointed by this irresponsible headline. This kind of alarmist headline causes panic & makes *the work of scientists like myself 10 times harder*.
Please do better.
2/N
Please do better.
2/N
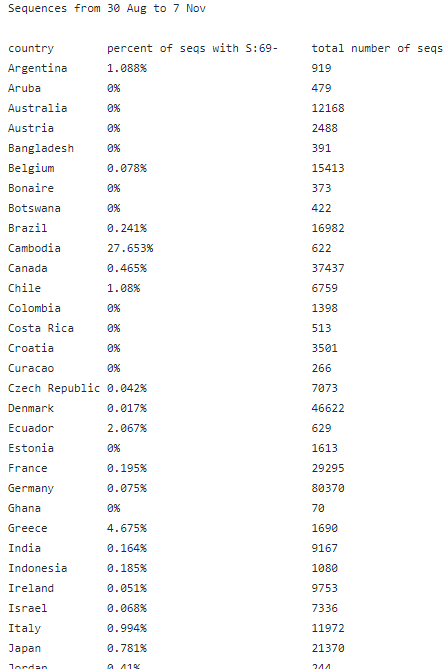
So what is this all about then? Well, one 'nice' thing about Omicron is that it has what we call S:69/70del - a deletion that means it has S-gene-drop-out (SGTF), meaning that some PCR tests can see straight away that it might be Omicron. This makes helps surveillance!
3/N
3/N
You can read more about SGTF, what it is, and how we can use it to help with detecting Omicron in this great thread. Not all SGTF is Omicron, but it's a handy tool to help us find Omicron. (And as Omicron cases ⬆️, it's more likely to be Omicron)
4/N
https://twitter.com/firefoxx66/status/1466325638026080257
4/N
Scientists have now identified another cluster of seqs which share many of the same mutations as 'original' Omicron (BA.1) - but is missing some, & has some other new ones. You can read a bit more about this here. The new seqs are called BA.2.
5/N
https://twitter.com/theosanderson/status/1468175286948835328
5/N
One key mutation that BA.2 is missing is the S:69/70del -- the one that causes the SGTF/S-drop-out. This means we can't use this 'shortcut' to find possible Omicron cases *for BA.2 only*. However, *the PCR test itself still works!* You'd test + for SARS-CoV-2.
6/N
6/N
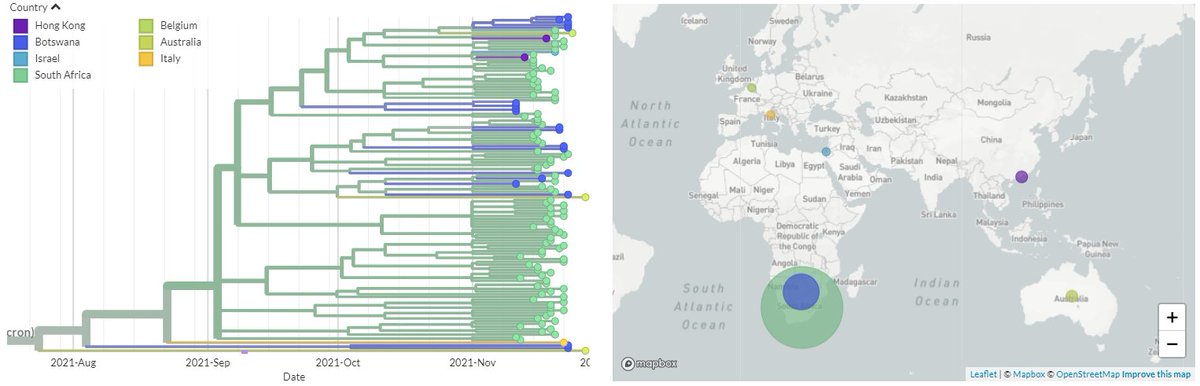
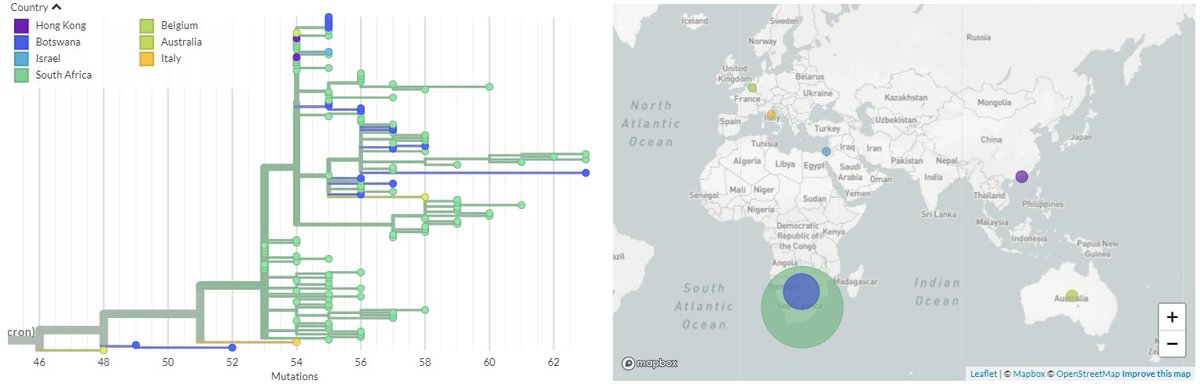
You can see where the BA.2 sequences are relative to BA.1 on this older 21K #Omicron build - I'm working on getting them incorporated into newer builds. The BA.2 is in blue.
You can mouseover the branches to see different mutations leading to each.
7/N
nextstrain.org/groups/neherla…
You can mouseover the branches to see different mutations leading to each.
7/N
nextstrain.org/groups/neherla…

Looks like the preview for this has updated - which is great! But my tweet now makes less sense. Here's a screenshot of the original, just so the original has some context! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh