1/
Should you use Sotrovimab (SOT) to treat high-risk outpatients with #COVID19?
Spoiler alert: Yes, if you can find it.
Here's #HowIReadThisPaper on the COMET-ICE trial by Gupta et al in @NEJM
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
(Thread)
Should you use Sotrovimab (SOT) to treat high-risk outpatients with #COVID19?
Spoiler alert: Yes, if you can find it.
Here's #HowIReadThisPaper on the COMET-ICE trial by Gupta et al in @NEJM
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
(Thread)
2/
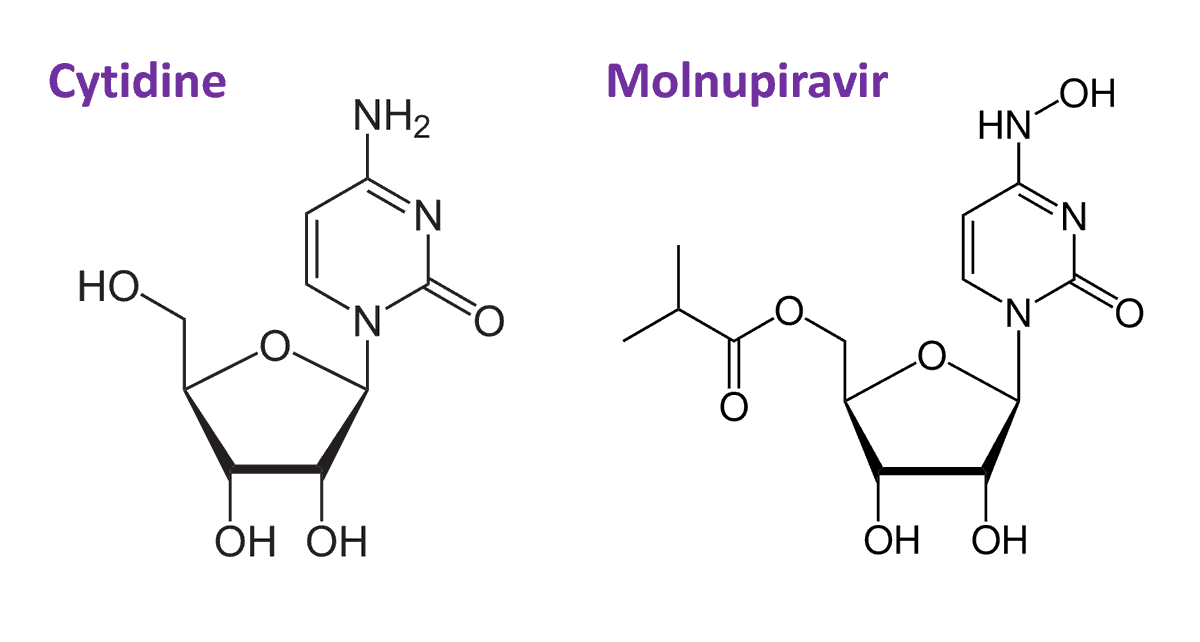
The origin story of SOT is amazing:
It was developed from an antibody in a frozen blood sample from a patient who survived the SARS epidemic of 2003.
It binds to a highly conserved part of the coronavirus spike protein and blocks cell entry.
nature.com/articles/d4158…
The origin story of SOT is amazing:
It was developed from an antibody in a frozen blood sample from a patient who survived the SARS epidemic of 2003.
It binds to a highly conserved part of the coronavirus spike protein and blocks cell entry.
nature.com/articles/d4158…
3/
Returning to COMET-ICE: what was studied?
Patients were randomized (double-blind) to receive a one-time IV infusion of SOT or placebo.
The primary outcome was the relative reduction in patients hospitalized for >24h or who died from any cause through day 29.
Returning to COMET-ICE: what was studied?
Patients were randomized (double-blind) to receive a one-time IV infusion of SOT or placebo.
The primary outcome was the relative reduction in patients hospitalized for >24h or who died from any cause through day 29.
4/
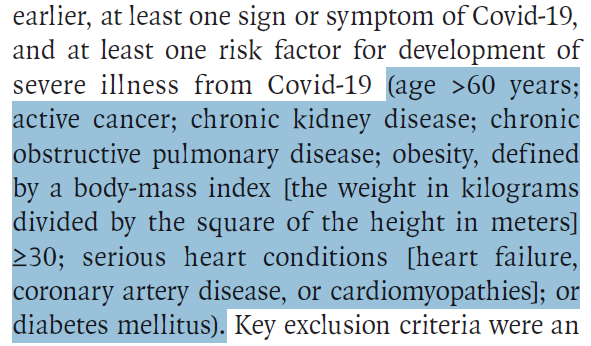
Who was studied?
583 unvaccinated outpatients
> 18 years old
With symptomatic COVID19 (but without hypoxemia)
For <5 days
At high risk for severe disease: >1 of the following risk factors: Age > 55, DM2 requiring treatment, obesity, CKD, CHF, COPD, mod/severe asthma
Who was studied?
583 unvaccinated outpatients
> 18 years old
With symptomatic COVID19 (but without hypoxemia)
For <5 days
At high risk for severe disease: >1 of the following risk factors: Age > 55, DM2 requiring treatment, obesity, CKD, CHF, COPD, mod/severe asthma
5/
~90% of patients enrolled in USA
Characteristics and risk factors well-balanced
Median age: 53 years
Most common comorbidities: Age >55, obesity, DM2
Most common variant not reported
% with prior infection not reported
60% of patients had symptom onset <3 days
~90% of patients enrolled in USA
Characteristics and risk factors well-balanced
Median age: 53 years
Most common comorbidities: Age >55, obesity, DM2
Most common variant not reported
% with prior infection not reported
60% of patients had symptom onset <3 days

6/
What were the main findings?
Primary outcome: 85% relative reduction (97.24% CI: 44 - 96)
Absolute risk reduction: 6% (7% vs 1%)
All patients admitted to ICU (5), requiring intubation (2), or who died (1) were in the placebo group.
No concerning safety signals
What were the main findings?
Primary outcome: 85% relative reduction (97.24% CI: 44 - 96)
Absolute risk reduction: 6% (7% vs 1%)
All patients admitted to ICU (5), requiring intubation (2), or who died (1) were in the placebo group.
No concerning safety signals
7/
Another very positive study.
How confident should we be in the conclusions?
Let’s look for sources of chance and bias that could threaten them.
First, the study was stopped for efficacy.
Did this make a positive result more likely by chance?
Another very positive study.
How confident should we be in the conclusions?
Let’s look for sources of chance and bias that could threaten them.
First, the study was stopped for efficacy.
Did this make a positive result more likely by chance?
8/
No - it makes a negative result more likely:
Usually, enrolling fewer people than planned = ↓ power
However, these data suggest a large effect of SOT.
As a result, fewer people than expected were needed to find it.
Here, this increases my confidence in the results.
No - it makes a negative result more likely:
Usually, enrolling fewer people than planned = ↓ power
However, these data suggest a large effect of SOT.
As a result, fewer people than expected were needed to find it.
Here, this increases my confidence in the results.
9/
Another source of confidence in these results:
The secondary outcomes suggest SOT = ↓ emergency department visits, disease progression, ICU admission, and death.
Though the numbers are small, the pattern is in-line with what we expect based on the mechanism.
Another source of confidence in these results:
The secondary outcomes suggest SOT = ↓ emergency department visits, disease progression, ICU admission, and death.
Though the numbers are small, the pattern is in-line with what we expect based on the mechanism.

10/
Other positives:
✅Because the binding site of SOT is highly conserved, it should work against future variants
✅No safety signals, no drug interactions
✅Long half-life (49 days!) = good option for immunosuppressed patients who have received B-cell depleting therapies
Other positives:
✅Because the binding site of SOT is highly conserved, it should work against future variants
✅No safety signals, no drug interactions
✅Long half-life (49 days!) = good option for immunosuppressed patients who have received B-cell depleting therapies
11/
Two important things were omitted:
Patients’ autologous antibody status
&
The dominant circulating variant.
Are either of these sources of chance or bias that could have influenced the results?
Let’s first examine antibody positivity.
Two important things were omitted:
Patients’ autologous antibody status
&
The dominant circulating variant.
Are either of these sources of chance or bias that could have influenced the results?
Let’s first examine antibody positivity.
12/
Seropositivity would indicate one of two things:
Prior infection
Or
Immune response to the current infection.
This would have been a useful subgroup analysis to infer how these data might apply to patients with some immunity from prior infection or vaccination.
Seropositivity would indicate one of two things:
Prior infection
Or
Immune response to the current infection.
This would have been a useful subgroup analysis to infer how these data might apply to patients with some immunity from prior infection or vaccination.
13/
It does not appear that patients with prior infection were excluded (only patients with prior hospitalization for COVID were excluded).
How many people could this be? Hard to say. 20% of patients had prior infection in the MOVe-OUT trial:
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
It does not appear that patients with prior infection were excluded (only patients with prior hospitalization for COVID were excluded).
How many people could this be? Hard to say. 20% of patients had prior infection in the MOVe-OUT trial:
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
14/
Since any degree of prior immunity would likely attenuate the benefit of SOT
And
Since patients with prior infection are likely to be distributed evenly,
This creates a bias towards a negative (null) finding and increases my confidence in these results.
Since any degree of prior immunity would likely attenuate the benefit of SOT
And
Since patients with prior infection are likely to be distributed evenly,
This creates a bias towards a negative (null) finding and increases my confidence in these results.
15/
Turning now to the dominant variant:
The study was completed in 3/2021, before the emergence of delta & omicron.
Based on the mechanism of action of SOT, this shouldn’t matter, and it should still be effective.
In vitro studies support this:
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
Turning now to the dominant variant:
The study was completed in 3/2021, before the emergence of delta & omicron.
Based on the mechanism of action of SOT, this shouldn’t matter, and it should still be effective.
In vitro studies support this:
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
16/
Finally, the major downside:
Producing a biologic in large amounts is time-consuming and resource-intensive.
We should expect limited availability.
As of today, the number of doses distributed is <1% of the total reported number of cases in the US:
phe.gov/emergency/even…
Finally, the major downside:
Producing a biologic in large amounts is time-consuming and resource-intensive.
We should expect limited availability.
As of today, the number of doses distributed is <1% of the total reported number of cases in the US:
phe.gov/emergency/even…
17/
Bottom line:
SOT led to a large reduction in hospitalizations, disease progression, and death from #COVID19 through day 29 in high-risk unvaccinated outpatients.
It appears safe and is expected to retain activity against future variants.
(End)
Bottom line:
SOT led to a large reduction in hospitalizations, disease progression, and death from #COVID19 through day 29 in high-risk unvaccinated outpatients.
It appears safe and is expected to retain activity against future variants.
(End)
18/
My deepest gratitude to @tony_breu for the thoughtful peer review.
If you haven't already, please read the paper and add your observations below!
My deepest gratitude to @tony_breu for the thoughtful peer review.
If you haven't already, please read the paper and add your observations below!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh