Breaking. #ESETResearch discovered a new data wiper malware used in Ukraine today. ESET telemetry shows that it was installed on hundreds of machines in the country. This follows the DDoS attacks against several Ukrainian websites earlier today 1/n
We observed the first sample today around 14h52 UTC / 16h52 local time. The PE compilation timestamp of one of the sample is 2021-12-28, suggesting that the attack might have been in preparation for almost two months. 2/n
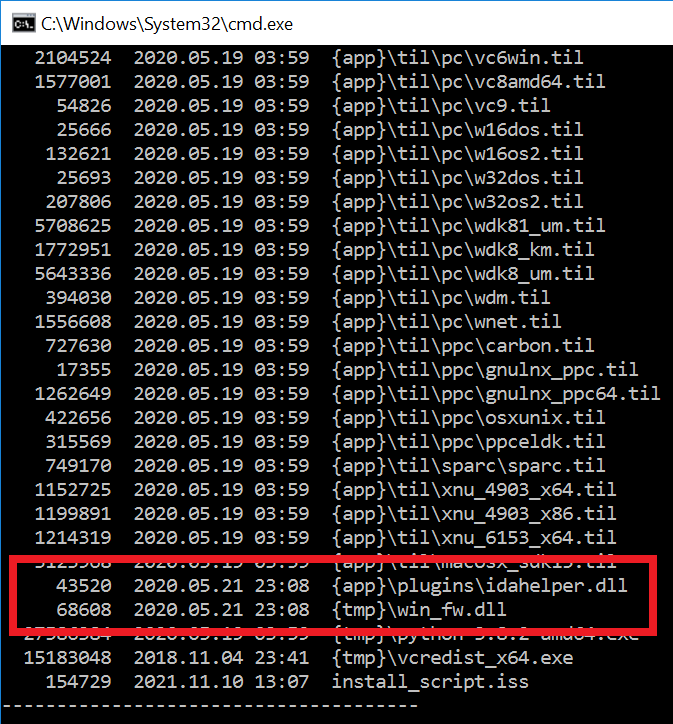
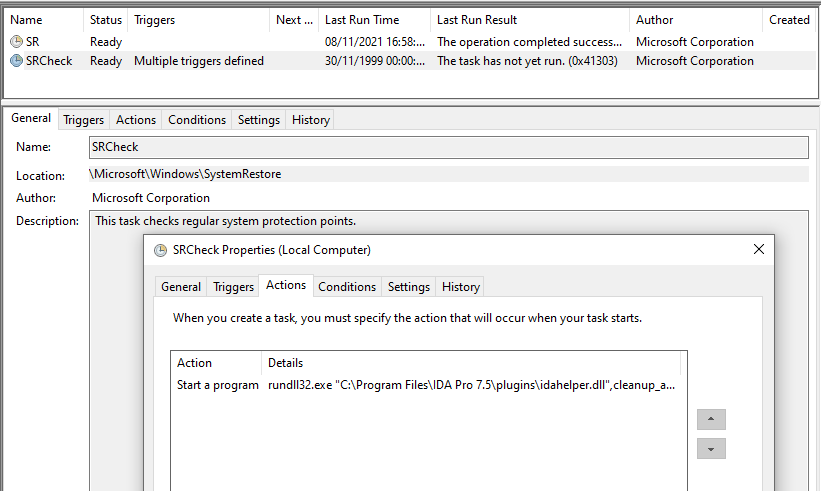
The wiper abuses legitimate drivers from the EaseUS Partition Master software in order to corrupt data. As a final step the wiper reboot computer 4/n 

In one of the targeted organizations, the wiper was dropped via the default (domain policy) GPO meaning that attackers had likely taken control of the Active Directory server. 5/n
This is a developing story and we will be making updates as we discover new data points.
IoC:
912342F1C840A42F6B74132F8A7C4FFE7D40FB77
61B25D11392172E587D8DA3045812A66C3385451
Win32/KillDisk.NCV trojan 6/n
IoC:
912342F1C840A42F6B74132F8A7C4FFE7D40FB77
61B25D11392172E587D8DA3045812A66C3385451
Win32/KillDisk.NCV trojan 6/n
Based on the discussion on Twitter by fellow researchers and discussing this naming at #ESETresearch, we will continue to call this malware #HermeticWiper 7/n
https://twitter.com/juanandres_gs/status/1496607141888724997
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh